The characteristics of component devices may contain various parameters that are often incomprehensible to the user. So, when choosing a processor, video card or cooling system, you can notice such a value as TDP, related to thermal characteristics and expressed in watts. Let’s consider what this parameter reflects, why the owner of the computer may need it and how to determine it, and also whether its value can be influenced.

Contents
What does TDP stand for
Not all users who have noticed the line with the TDP abbreviation in the characteristics of the processor know exactly what this means. The decoding of the parameter sounds like Thermal Design Power, which means “design thermal power”.
The value indicates the maximum amount of heat that is generated by the chip during operation (meaning average load indicators), the same heat should be removed by the cooling system. So, the parameter speaks about the design requirements for heat dissipation and can serve to determine the required specifications, for example, when choosing a suitable cooler.
The value is expressed in watts, which introduces confusion and causes TDP to be equated with power consumption. Although the connection between these concepts can be traced, the manufacturer, when specifying TDP, implied a slightly different message, since the meaning does not relate to electrical, but thermal watts. Thus, in the case of TDP, we are not talking about electrical power, the parameter is abstract and is used by Intel and AMD to denote information about the heat dissipation of processors and video cards. Taking into account the characteristics, it is recommended to select and cooling for the correct operation of the device.
Parameter interpretation by manufacturers
At the same time, different manufacturers can calculate and interpret TDP in different ways (the value is calculated using formulas during the operation of the device under certain loads and conditions), which should also be taken into account. So, the declared TDP cannot reflect power consumption and performance, and the value is not used to compare these parameters, in particular, when it comes to devices of different architectures and manufacturers.
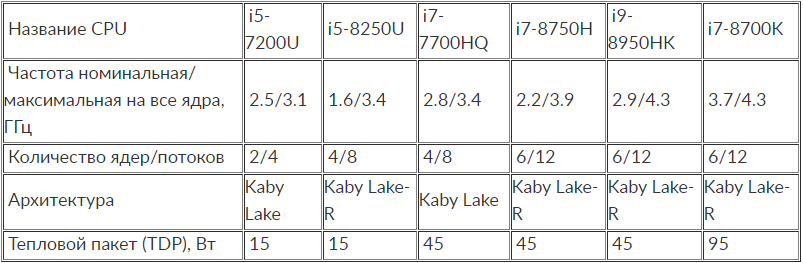
For modern Intel processors, this term refers to the heat in watts that the CPU generates during prolonged operation at the base frequency. But there is also a Turbo Boost mode, and when higher frequencies are reached, the TDP also rises, that is, even with a slight difference between the base and Turbo, the cooling system, which is designed for the nominal TDP, may not cope with its task. So, the actual heat generated and the power consumption can grow above the specified TDP parameter, which means that Intel products will have this value lower than the maximum power consumption and dissipation.
AMD has a completely different picture. Here, the declared characteristics of the TDP CPU and GPU are already closer to the real indicators of the maximum allocated and consumed power during normal operation.
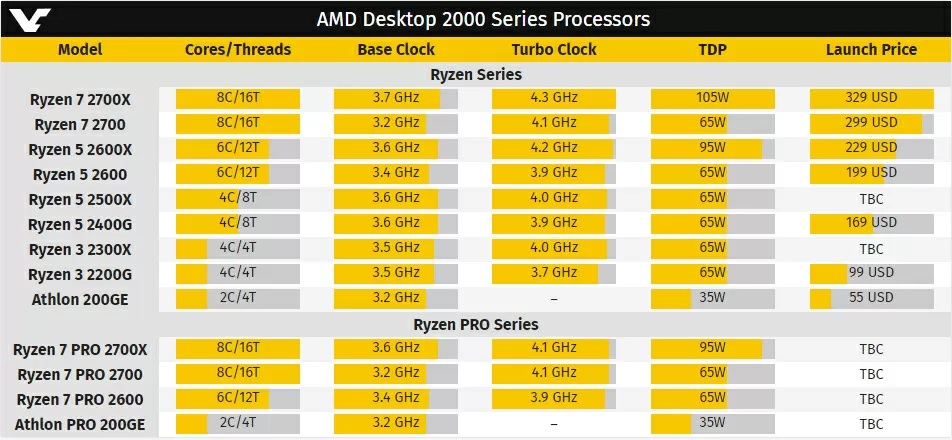
As for NVIDIA, the manufacturer equals power consumption and power dissipation, defining the TDP parameter as the highest power consumed by the system during operation, and the maximum amount of heat required to be removed by the cooling system.
Why you need to know the TDP of the processor
When self-assembling a computer or upgrading, as well as overclocking the system, the process should be approached with full responsibility and many factors should be taken into account, so that in the end all the components are compatible with each other and work harmoniously. Information about the calculated thermal power of the processor is useful to the owner of the computer and can be used:
- when choosing the most suitable option for the cooling system – a similar parameter is also stated in the characteristics. So, the value of the dissipated heat for the efficiency of heat dissipation, and, accordingly, maintaining a normal temperature and proper operation of the device, must correspond to the TDP (at least) or be higher than the heat dissipation of the processor. It is better if the cooling system is purchased with a margin of 50% of the declared TDP indicator, and when planning overclocking, even more stringent requirements should be imposed on cooling, since the cooler will have to remove much more heat. When choosing a cooling system, you need to pay attention to such a parameter as a socket on the motherboard;

- when choosing a power supply that is suitable in terms of power characteristics, selected taking into account the parameters of those components that have already been installed or are planned for installation. It should also be borne in mind that Intel’s peak power consumption may even be twice the TDP declared in the technical documentation.

Power consumption and performance of processors with the same TDP may differ. Most often, the requirements for heat dissipation are stated not for a specific model, but for a whole family of processors, despite the fact that less heat will need to be dissipated by the cooling system in the case of younger models. The specified frequencies do not affect the parameter declared in the characteristics, there are many options for devices with different frequencies, but the same TDP. At the same time, the dependence of power consumption on frequency is nonlinear, an increase in clock frequencies above a certain threshold will also require an increase in the supply voltage. With overclocking, the heat dissipation becomes higher than in the normal mode, and the TDP parameter loses its relevance, while the cooling system should be even more powerful.
Determining the TDP of the processor
Although TDP is an abstract value that does not determine the real heat dissipation of a processor, it serves as a guideline when choosing a cooling system or a power supply unit. In the main characteristics of the device, the parameter is not spelled out by the manufacturer, and therefore many are wondering how to find out the TDP.
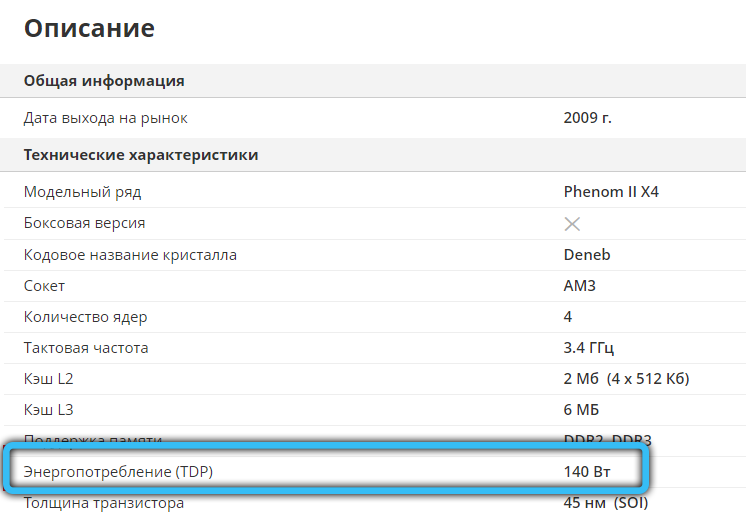
There are several ways to find out this information:
- information on processor heat dissipation is available in extended specifications, namely in the thermal characteristics section of a product card in any store;
- you can also determine the TDP by the device model by looking for the specification on the manufacturer’s website;
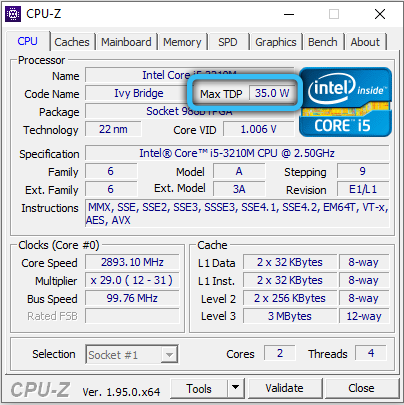
- another way is to use special utilities such as CPU-Z, AIDA64, Sandra.
Is it possible to change the TDP
Thanks to the flexible setting of the parameter, manufacturers can adapt the same chip for different devices for different tasks, ensuring the stable operation of the processor under certain conditions, hence the difference in performance, which is often noticeable. In practice, TDP limits make the same chips different. It can be either a thin ultrabook or a desktop PC, and, of course, their heat dissipation requirements are different – for example, 65 W for a laptop will be a lot, but for a computer it is considered acceptable.
In the case of a CPU or GPU of laptops, a decrease in the indicator improves the autonomy of operation and reduces heating, while the performance will be lower, since the frequencies are dropped under prolonged load, although in the case of resource-intensive, but fast tasks, there will be practically no difference in performance. This decision is usually associated with the rest of the device configuration, when the installed cooling system is not able to effectively cool the device with the specified characteristics. That is, for example, the processor has a TDP of 15 W, while the maximum value of the same chip can reach 25 W, and in the case of using this configuration with the same processor, it will be more efficient. In the first case, if you compare two devices, you can count on a greater autonomy of the device (with the same battery capacity) and low heating.
Adjustment of the TDP value is carried out in various ways, and not only the manufacturer, but also the user himself can increase or decrease this parameter. Most often, the value is adjusted by software by manipulating the processor clock frequency and voltage, which is done through BIOS settings or through special utilities. So, it is possible to reduce heating (and at the same time the consumed amount of power and performance) if you reduce the TDP, while controlling the stability of the device so that the procedure is safe.
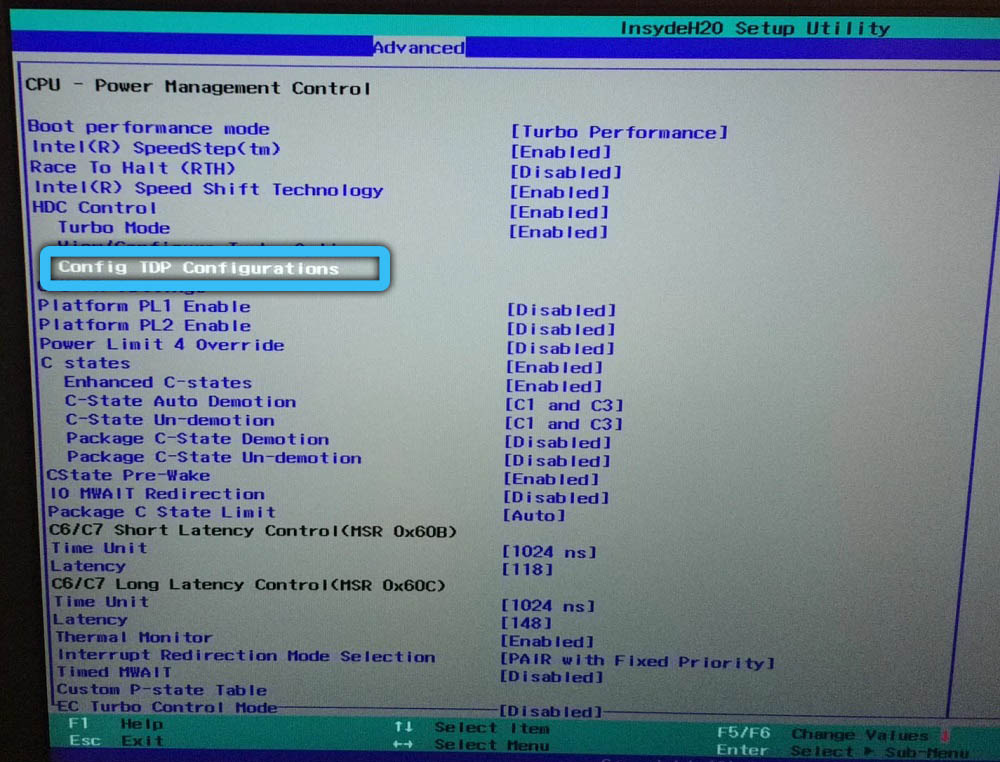
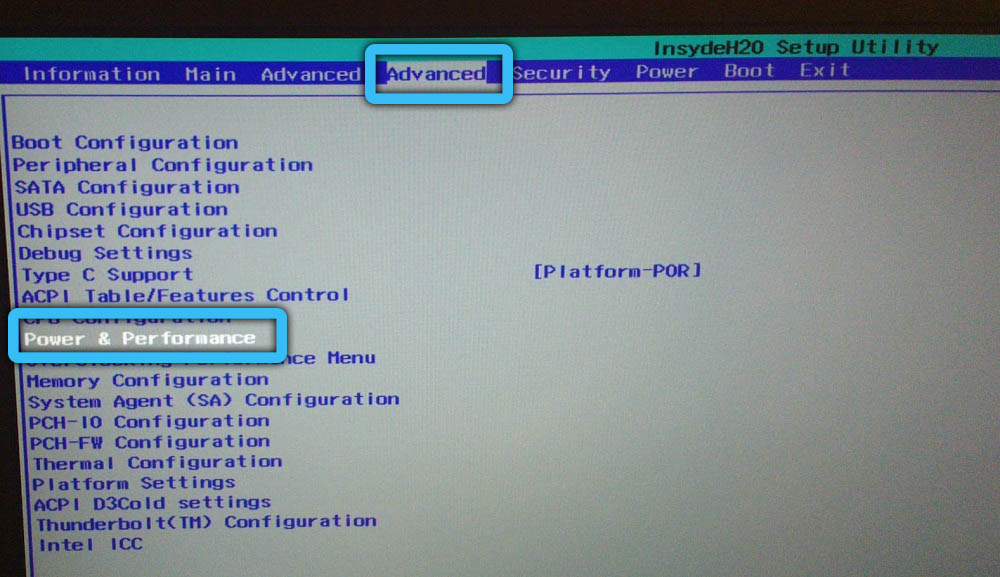
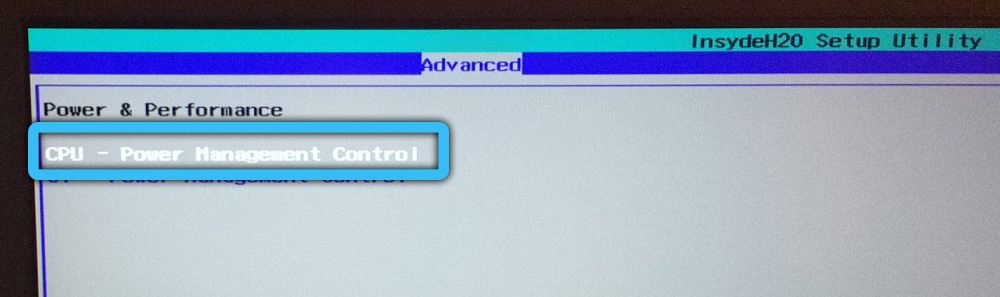
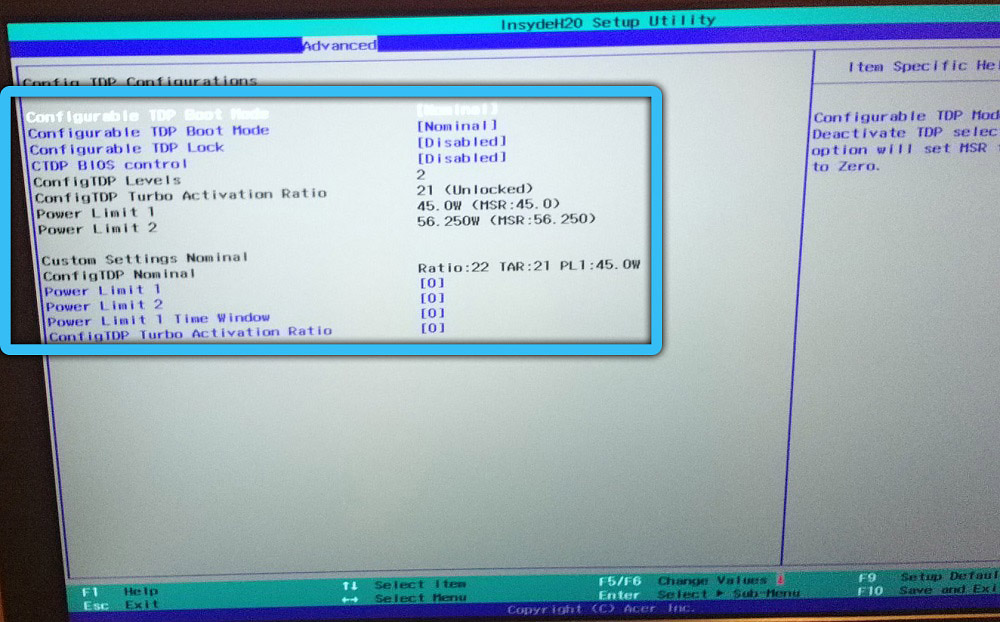
Some motherboards offer the ability to manually change the TDP limit, which does not prevent the processor from using automatic overclocking technology, but only reduces the limits in which it will run. In the BIOS settings, for this you need to find the cTDP parameter, most often it is located in the Advanced tab (the location of the option may differ depending on the motherboard). Opposite the parameter, the value changes, for example, at 95 W, you can set 65 W, and at a value of 65 W, 45 W or 35 W are assigned, after which you need to save the changes and exit the BIOS.
An alternative option is to decrease the system bus frequency, usually in the BIOS this parameter is called CPU Clock or CPU Frequency. The nominal value just needs to be reduced to the desired value.
The change in the temperature of the processor or power consumption is checked by testing using special software.