During the installation of the Windows operating system, the user sets the name of the computer, which will be subsequently accessed by programs, devices connected by a local network, a web server, FTP and other network services. The NetBIOS protocol is extremely important for the operation of the system, therefore it is recommended to know about its structure and its functions in order to better understand how data is exchanged between processes, applications or computers.
NetBIOS – device and principle of operation
Windows uses this interface as its primary network I / O system, as well as the ability to set up sharing of network devices and files. Data packets are transmitted over the local network through sessions of the reference model of interaction of open systems, and through network protocols applications can exchange information on them. In simple words, this system is a network protocol designed to work in local networks and exchange information, values and other data within them. Starting with Windows 2000, the NetBIOS over TCP / IP Helper is called NetBT.
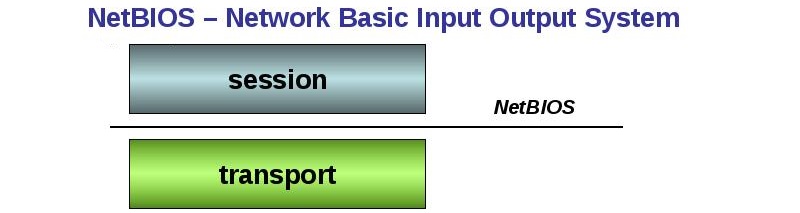
Using the protocol, programs find the resources they need, send requests for information, or give their own data. First, a session with a NetBIOS request is opened, an IP address is set, the system determines a suitable port for a specific type of operation (the name service uses port 137, datagrams – 138, and sessions – 139), data packets are exchanged, when the stream stops, the session is closed. One message can be up to 131,071 bytes or 131 KB. Several unique sessions can be established at one time. The NetBIOS address has the following form: IP. **. **. **. **, where under the asterisks is the IP address, and under the IP is the type of operation being performed. The protocol uses its own commands for data exchange (send, receive, call, remote program load, session status, reset, hang up, cancel and others),as well as special primitives for interacting with datagrams (receive datagram, send datagram, receive broadcast datagram, send broadcast datagram). Edge nodes NetBIOS are classified into the following types:
- Broadcast b-nodes.
- Point-to-point P-nodes.
- Mixed type M-nodes.
Depending on the IP-address, a specific type of request is used, for example, NBNS name server and NBDD datagram distribution server will be used to carry out data transmission by nodes P- and M-.
NetBIOS services
For operation, the protocol uses NetBIOS-NS (name service), NetBIOS-SSN (session service) and NetBIOS-DGM (datagram distribution service). NS performs the function of registering and resolving names, DGM is suitable for connectionless data transmission, and the last service, SSN, transmits connection-oriented packets.
The protocol provides commands and support for the following services, giving them access to sessions of the OSI Open Systems Interconnection Reference Model:
- Monitoring and control protocol and adapter;
- Session establishment and termination;
- Unreliable data transmission without establishing a connection;
- Registration and verification of the network name;
- Reliable connection-oriented transfer of session data.
First, the name service registers the application name with NetBIOS before starting a session or distributing datagrams. The primitives used are “add name” (name registration), “add group name” (record the NetBIOS group name), “delete name” (delete the registration of an application or group name), “find name” (search for a NetBIOS name on the network).
The datagram service runs on UDP port 138 and is responsible for the connectionless exchange mode. Using the primitives “send datagram” (sending a datagram to a remote name), “receive datagram” (switching to the waiting mode for receiving a packet), “send broadcast datagram” (sending a datagram to all registered names from the NetBIOS network), and also “receive broadcast datagram »(Waiting to receive a data packet from the broadcast datagram sending session) – information is exchanged without an established connection.
In session mode, the SSN service (TCP port 139) is used, which allows you to establish a connection between two computers and exchange messages (covering several packets at once), and is also responsible for providing diagnostics and error correction. The session takes place using these types of primitives:
- Call – start a session;
- Send – sending a packet to another computer;
- Receive – transition to the state of requesting a packet from the computer at the other end of the session;
- Hang up – end of the session;
- Listen – listening to attempts to start a session;
- Send No Ack – data transmission without a confirmation request from the second session participant.
The computer initiating the session must send an Open request, and then must request to start the session using Call. The receiver replies to each transmitted packet positively (ACK) or negatively (NAK). In order for the session to be closed, the non-initiating computer must send a Hang Up request to terminate and receive confirmation from the initiator.
Starting and disabling the NetworkBIOS service
Before stopping NetBIOS over TCP / IP, remember that the service is relatively important for the computer and after this operation the ability to access the network computer by the NetBIOS name will not be able to function properly. If the personal computer is connected to a network, it is not recommended to disable this service to avoid errors.
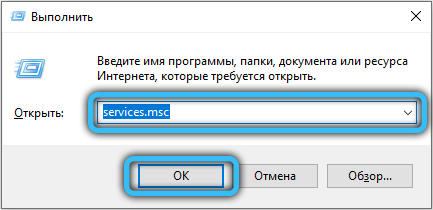
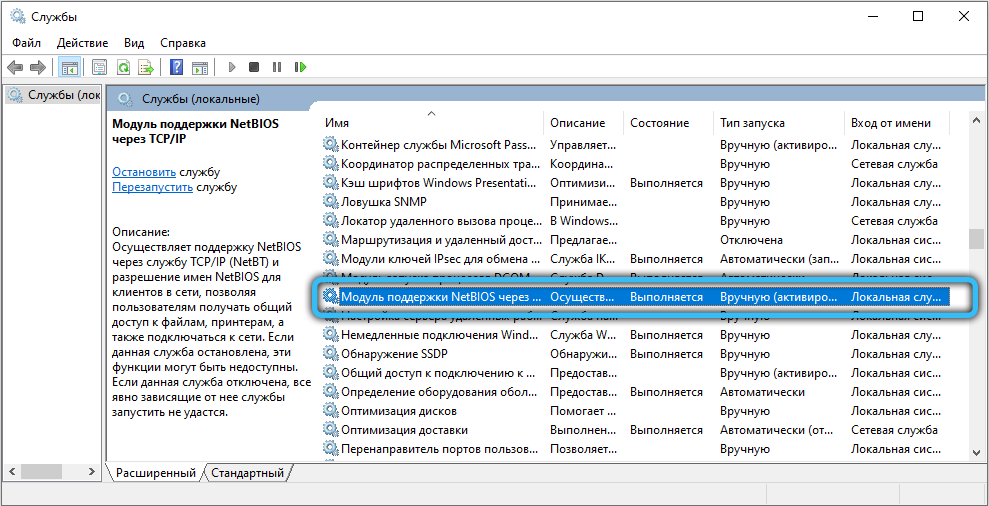
Users are wondering how to find out the status of a service in Windows 10 (and other editions). In order to do this, you need to call the system application “Run” using the combination Win + R, then enter the value “services.msc” in the “Run” field and click OK. For a convenient search, you can sort the list alphabetically by clicking on the “Name” column. Here you need to find the service you are interested in, in our case it is “NetBIOS Support Module” over TCP / IP “. The “Status” column displays whether the service is currently running or not. By default, this module is in the running state if the computer is connected to the network.
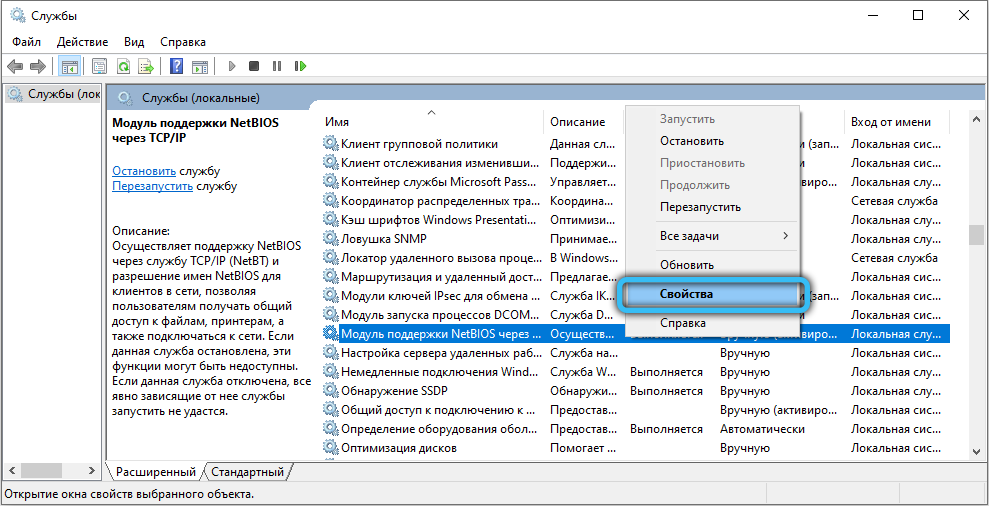
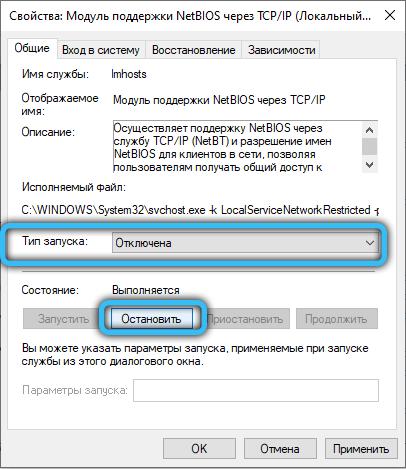
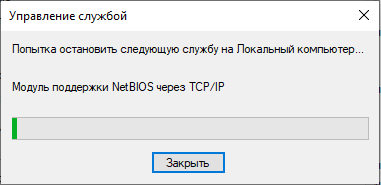
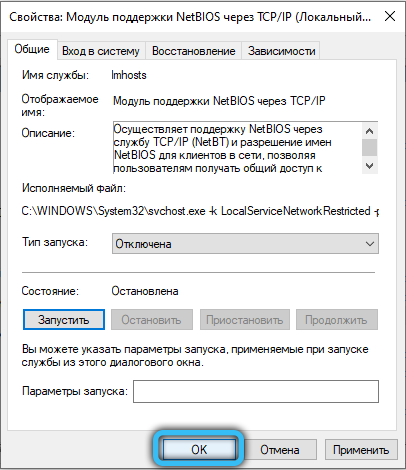
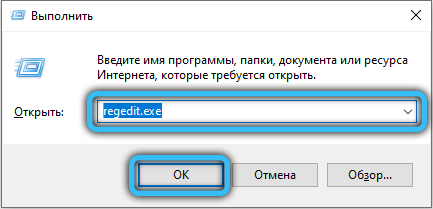
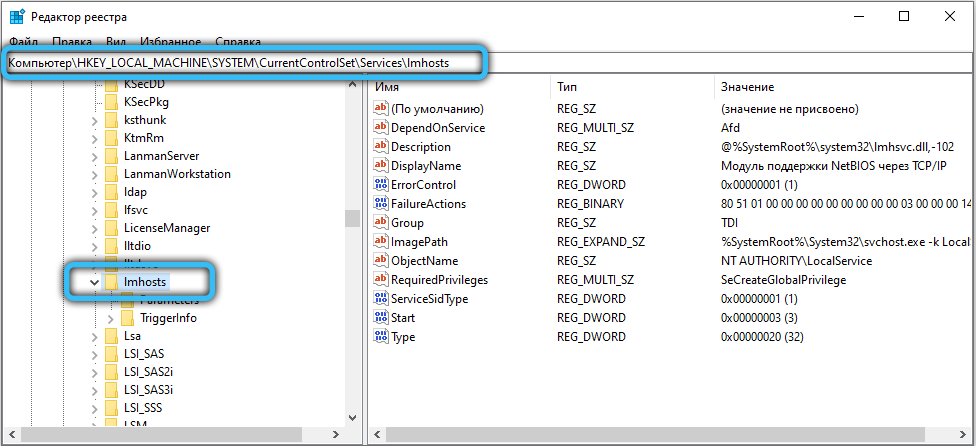
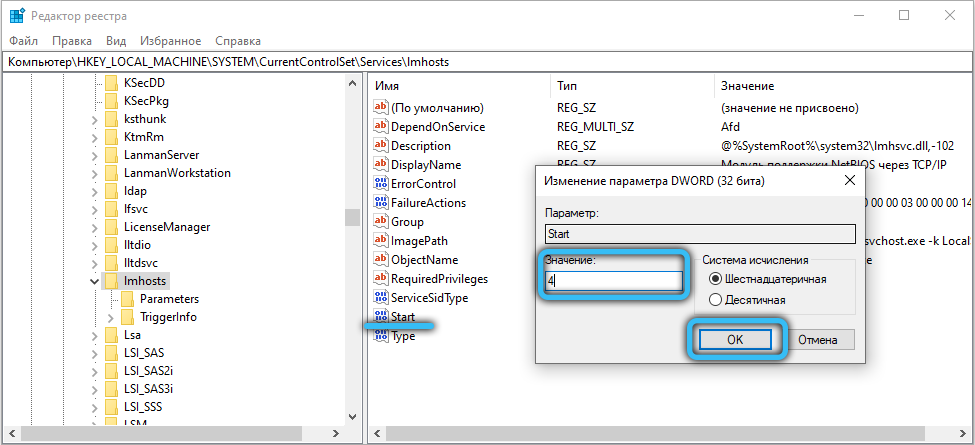
To disable NetBIOS, right-click on the corresponding item in the list and select Properties from the context menu. In the NetBIOS service settings, click on the “Stop” button, and then set the startup type to “Disabled” a little higher (if you need to start, then you should select “Manual” or “Automatic”). Apply the changes, then click OK and close the Services application. Now start the registry editor by using the Win + R combination and requesting the launch of “regedit.exe”. Go to the directory “HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE / SYSTEM / CurrentControlSet / Services / lmhosts” and change the value of the “Start” attribute to “4” (2 – automatic, 3 – manual and 4 – disable, select according to the desired action) and click OK, then press the F5 key on your keyboard. Restart your computer and make surethat NetBIOS no longer starts automatically.
We hope you figured out how this important network protocol works, which previously had the status of a necessity on every computer (now that time has passed, now only the Service Message Block or SMB connection is used). If you still have any questions related to this topic, or if you have problems while disabling the Windows network component, write your answers in the comments. Do not forget about the rating, rate the article using a special form.