Contents
Introduction
Today, almost every home has several devices with Internet access. In order to connect them into one network and connect to the global network, a router is used. From this article we will learn what a router is and why you need it.

Definition of a router and its purpose
A router (in everyday speech “a router”) is a special network device that allows you to distribute the Internet signal received from a provider among several end users – and the “user” in this context is a device, not a person.
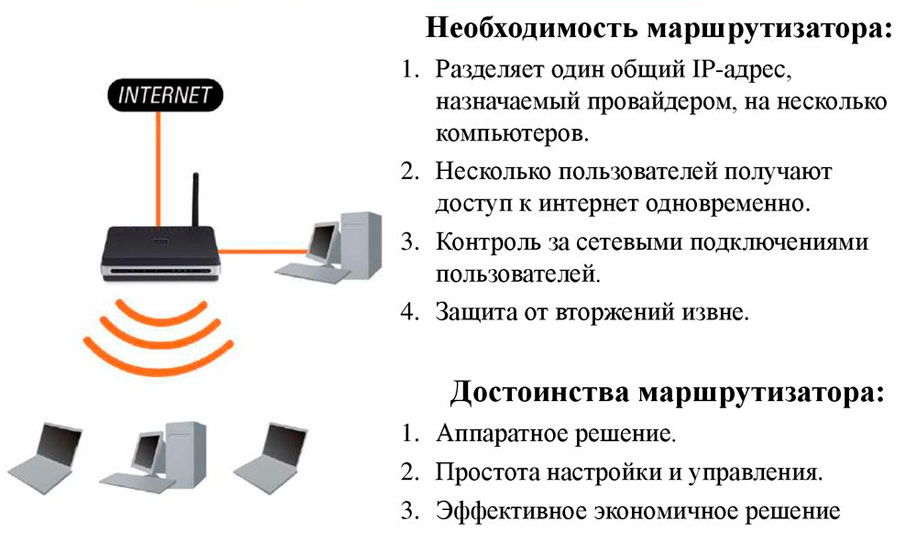
Despite the abundance of models with diverse functionality, the main functions of the router are:
- implementation of Internet access as an access point for multiple devices;
- with a sufficient range of action – the creation of a home network;
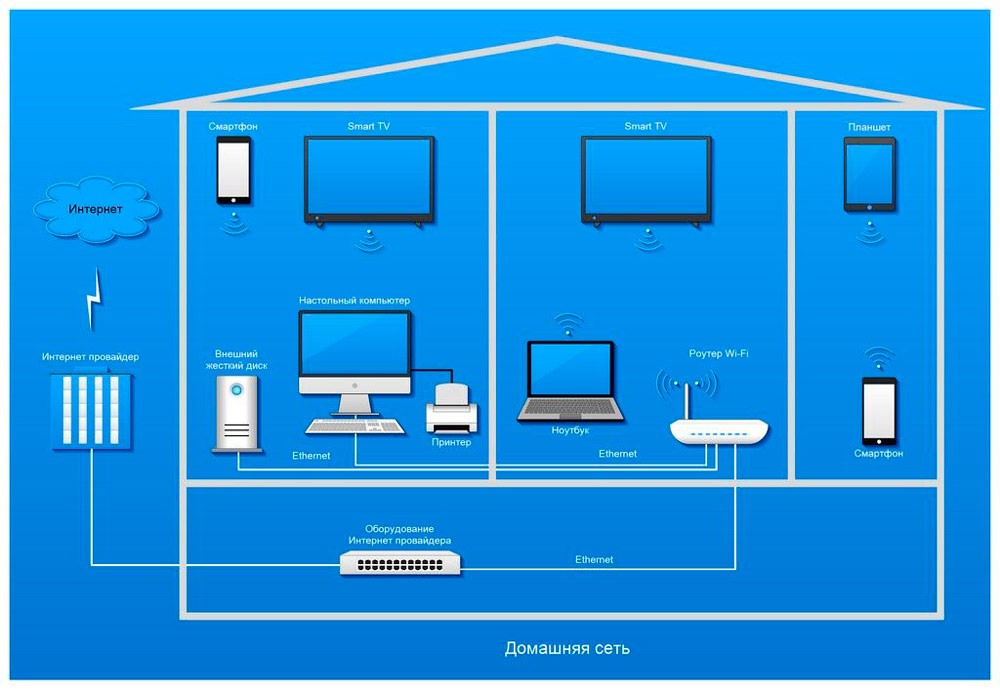
- increasing the coverage area of the network;
- Internet providers use special powerful routers (the so-called “main routers”) to integrate local computer networks with the Internet backbone – part of the global infrastructure that provides Internet access to all countries and continents.
Types of routers
By the method of connecting to a computer
- External – in the form of a separate unit connected to a PC via a network cable or Wi-Fi. More versatile in connection, mobile and relatively easy to get along with any computers.

- Internal – built into the body. Does not take up space on the table, but takes up a PCI or M.2 slot in the system unit.

By use:
- Home – Standard models for home use.
- Automotive – compact mobile routers powered by a car cigarette lighter or battery.
- Mini-routers are portable models with limited functionality, often no larger than a little finger.
- 3G / 4G Wi-Fi router – equipped with a SIM card slot, battery operated.

- Heavy-duty “edge” and “core” routers are used by ISPs to organize the Internet infrastructure.
Main functions
Internet access type
ADSL – the connection works through a telephone line, through which you can simultaneously call and use the Internet. The maximum speed is several tens of megabits per second. 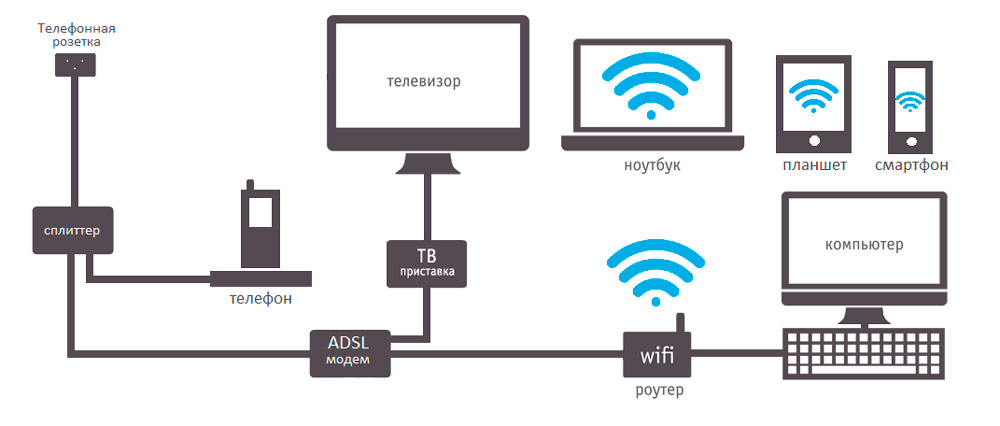
Ethernet (FTTB) is a fiber optic cable. The fastest kind of connection. The speed offered by providers is up to 100 megabits, and in rare cases – up to 1 gigabit. 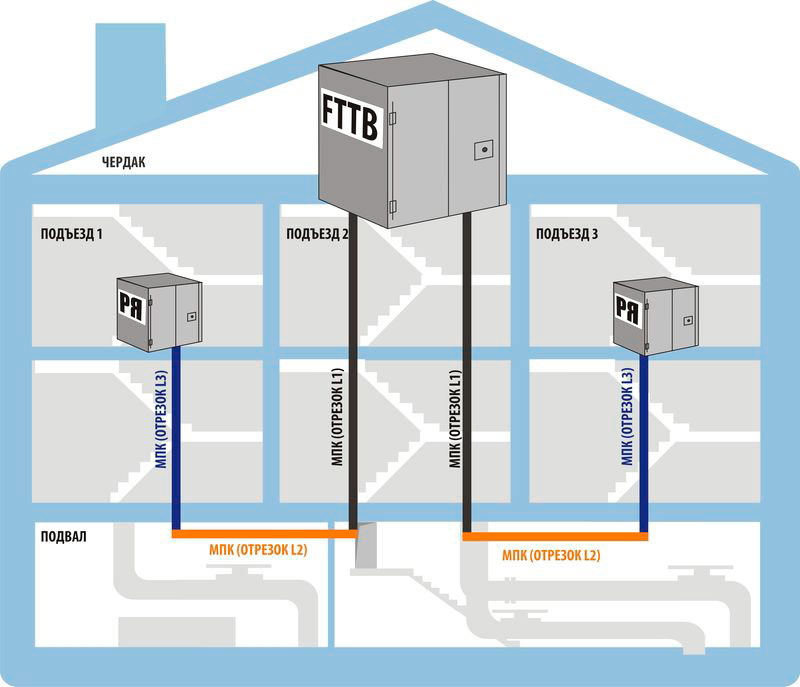
3G / 4G / LTE – allows you to distribute mobile Internet. The speed is limited by the capabilities of the telecom operator and the quality of the coverage.
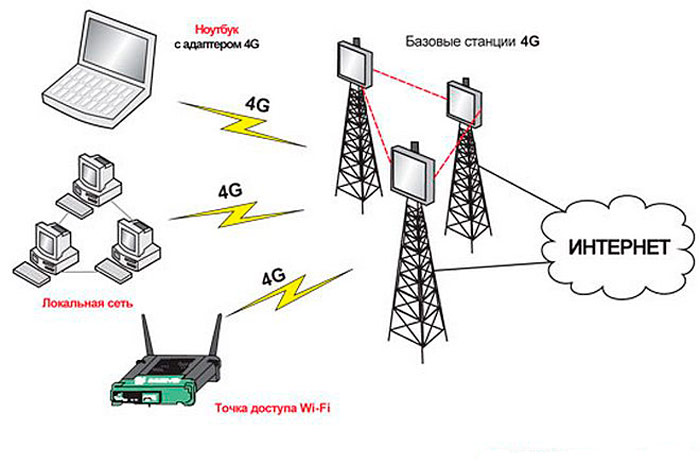
There are combined models capable of distributing a network obtained from different sources. You can usually find out what technology the Internet access uses for you personally in a contract concluded with your provider, or by contacting his office in person.
Communication standard and connection speed
There are more than 30 communication standards, each of which provides a different data transfer rate. In practice, for an ordinary user, the most noticeable standards will be:
- 11b – up to 11 Mbps, operates at 2.4 GHz;
- 11g – up to 54 Mbps, works at the same frequency;
- 11n – up to 600 Mbps, operates at 2.4 and 5 GHz, also known as Wi-Fi 4;
- 11ac – over 1 Gbps, operates at 5 GHz with wider bandwidths than previous standards. Also known as Wi-Fi 5.
- 11ax – up to 11 Gbps, operates at frequencies from 1 to 6 GHz. By the end of 2020, it becomes the global standard. Also known as Wi-Fi 6. There is also a 6E modification designed to work in bands higher than 6 GHz.
There is also a rather nimble, but rather exotic 802.11ad standard, which has a wide channel, but very poorly works with physical obstacles.
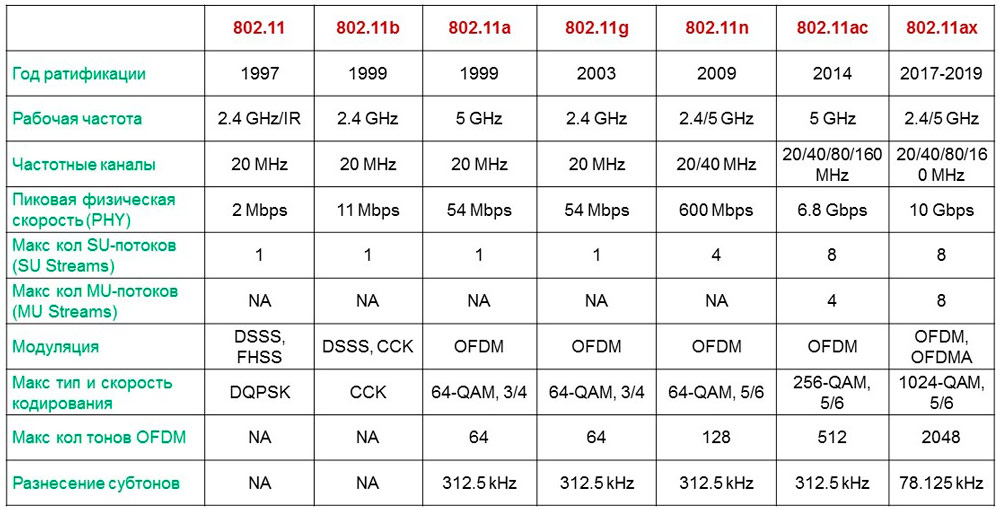
The 802.11ay standard, which has been in development since 2017, boasts speeds of up to 40 Gbps, and its final test is expected in March 2021 before it goes live.
Different models of routers support different communication standards – and, of course, older models will simply not know about the new communication standards. The communication standards available for your router can be viewed in its settings, which can usually be opened by typing the address 192.168.0.1 in the browser.
The frequencies at which the router operates indicate the channel width (in most cases, the standard 60 Hz) and its quality. At 2.4 GHz, the signal will not be lost due to walls or other obstacles, but its maximum size will be small. At frequencies of 5 GHz and higher, the opposite is true – the data transfer rate is higher, but the signal itself can easily get lost on the way to your device.
Number of antennas and range
The signal quality and range of the router depend on many factors: the number and thickness of walls and their material, the number of antennas, and the distance to the receiving device. The cheapest and low-power Wi-Fi routers are equipped with one antenna, more expensive and more powerful models are equipped with two, three or more. The simplest router is quite enough for an apartment, but in a private house you need to take a more powerful model (or better, several).
Data encryption
With an insufficiently secure communication channel, attackers can easily intercept your logins, passwords, and financial data. Be sure to encrypt the Wi-Fi communication channel!
Communication security standards ranging from the simplest to the latest are WEP, WPA, WPA2 and WPA3. The latter is considered the most reliable, we recommend choosing it if your router supports it.
Connection interfaces
Each router can distribute the Internet not only via Wi-Fi, but also via a wire. Most models are equipped with multiple ports. What are they useful for? For example, if you have a stationary computer or an interactive TV set-top box, you can connect them via cable. In cheaper models, the LAN port operates at 100 Mbps, while the more expensive devices are equipped with ports designed for 1 Gbps or more.
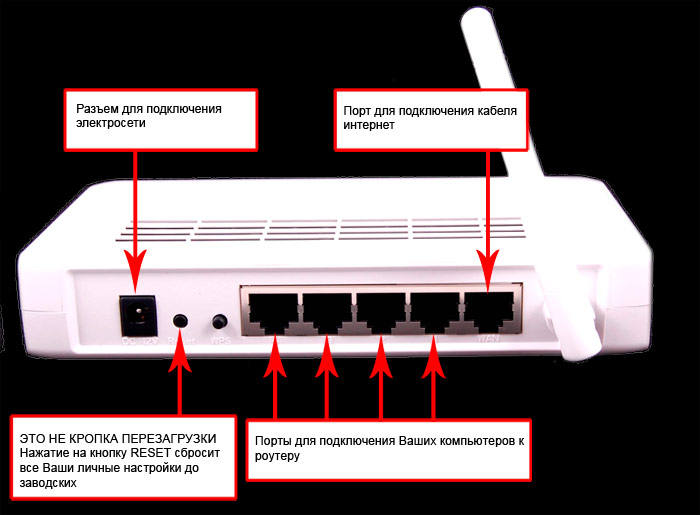
The presence of a USB slot will allow you to connect memory cards, external hard drives to the router, and then the data stored on them will become available to the rest of the network participants. And by connecting a printer, you can print from any device, anywhere in the home.
For a user who cannot connect to a traditional provider for technical reasons, the ability to connect a 3G modem will come in handy. Its presence will be a backup option, a safety net in case of problems with the usual connection.
Conclusion
A Wi-Fi router is a very necessary device in the arsenal of an active user of the World Wide Web. Now you know what it is for and how it works. We hope this information was useful to you and improved your computer literacy. We will be glad to receive your comments with feedback on the material.