Contents
Google’s HWASan tool uses memory tagging to better find memory errors in native Android code.Reading time:2 min.Save in pocketreadPrint viewread comments
Google has released a new Android tool aimed at developers who create apps with the Native Development Kit (NDK). The target group is therefore explicitly not those who write their applications in Kotlin or Java for the JVM, but native code with languages such as C and C ++.
Since native apps are responsible for memory management themselves, they are susceptible to typical memory access errors such as buffer overflows. Programming errors lead, among other things, to use-after-free or double-free vulnerabilities, i.e. the use of memory areas that have already been released or the double release of memory. Apart from the fact that the memory errors can lead to unpredictable behavior such as crashes, they also provide entry points for targeted attacks. Among other things, attackers can use code to inject code into the area that has been released but reused by the application.
Analysis as a brake
Google has been offering a scanner to find memory errors for some time: Address Sanitizer (ASan) detects errors, but at the price of noticeably lower performance and a memory requirement that is two to three times higher.
The now introduced HWASan (Hardware-Assisted Address Sanitizer) should only need about 15 percent more memory and work much more efficiently than ASan. Google already uses HWASan internally to detect errors in Android and has now released the tool for NDK developers.
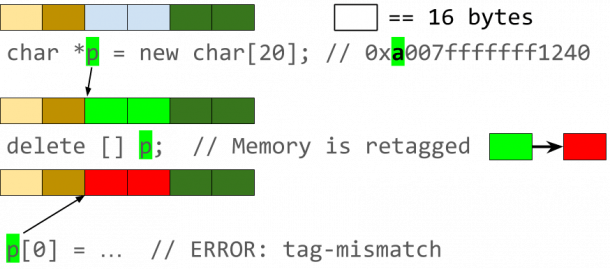
Marked memory
HWASan uses so-called memory tagging, which marks all memory blocks, to track down memory errors. To do this, it uses the additional field in 64-bit ARM CPUs, which is called Top Byte Ignore (TBI) . Specifically, the system stores a random 8-bit value in the MSB (Most Significant Byte).
For testing purposes, HWASan uses shadow memory to track memory usage. It compares the pointers and set tags in memory each time the memory is accessed and issues an error if the values do not match. In shadow memory, the tool sets the tag to a random value each time memory is allocated and released.
Chance as a residual risk
That way, the tool is most likely to recognize when a program is accessing shared memory or trying to access outside the reserved area. Google points out, however, that the approach is not deterministic, meaning that multiple executions without changing the code and values can produce different results. There is a 1 in 256 chance that the randomly generated byte corresponds to the comparison value. A second start of the analysis reduces the likelihood of errors being overlooked by the random number.
When an error is found, HWASan ends the process and creates a trash dump with the information about the memory area and the process that triggered the error.
Further details on HWASan can be found in the Android developer blog . Instructions for the use of HWASan can be found in the documentation for the NDK. Instructions for creating system images with HWASan are available on Android Source , which are also available pre-made .
