When downloading various software (games, software), you may notice two versions of the same file of a specific program – 32-bit and 64. Many users are perplexed: what kind of bit is this? In this article, we will figure out how to find out the number of bits in your Windows system and what they mean.
The bitness of the software you download must be the same as in the installed Windows operating system. The bit depth is the number of bits that are processed simultaneously by a specific device or transmitted via the bus. Systems are 32-bit and 64. You can also find the value x86, which means the same as x32.
Now you need to figure out what is the difference between the x32 and x64 versions of Windows. The main difference is that a 32-bit system works well with 2GB of RAM. In the event that you have 4 GB installed, the system will be able to “see” only 3.5 of them. The computer will work fine, but it is simply impractical. No matter how huge the amount of RAM, the system will not accept more than 3.5 GB.
In turn, the 64-bit version can recognize up to 192 GB of RAM. Therefore, if your computer has 4 or more gigabytes of RAM, it is recommended to install the x64 version. And the 64-bit version allows you to work with 32-bit programs, but not vice versa, since some programs, games require 4 or more gigabytes of RAM. If your system only “sees” 3.5 GB, then nothing will work. Therefore, the 64-bit version is more versatile and preferable.
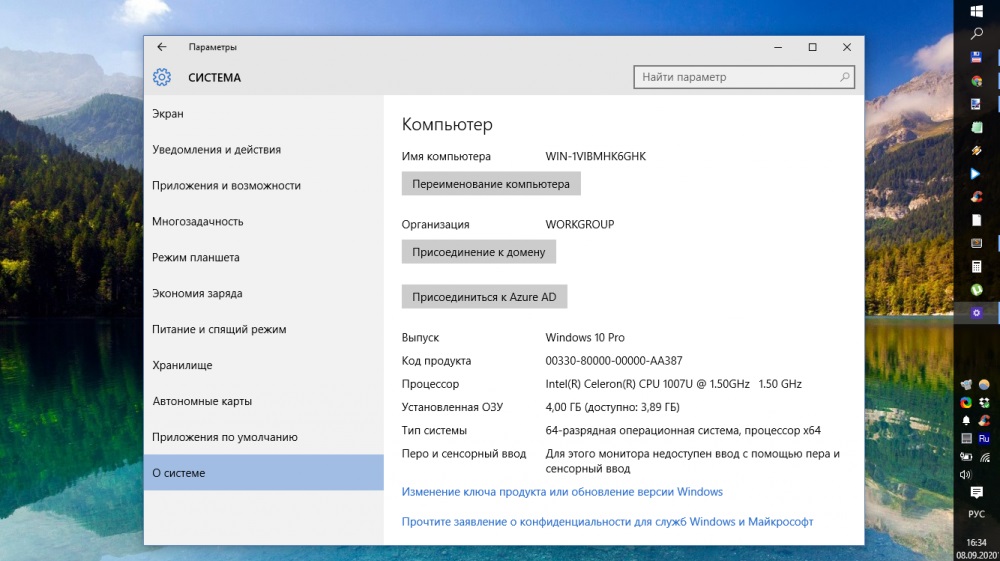
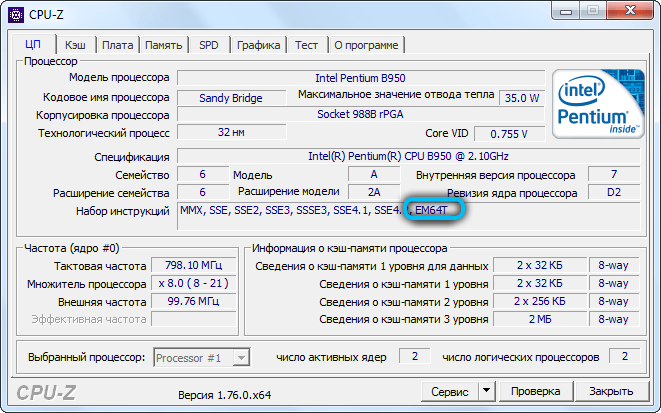
It should be understood that not everything depends only on the OS. What is important is what bit depth your processor supports, so you should definitely find out. To do this, you will have to download a special utility, since it is not possible to find out this using the built-in tools. A simple CPU-Z program can be recommended. After you download and install CPU-Z, open the utility and pay attention to the “Specification” section in the “CPU” tab. There you will find the information you need.
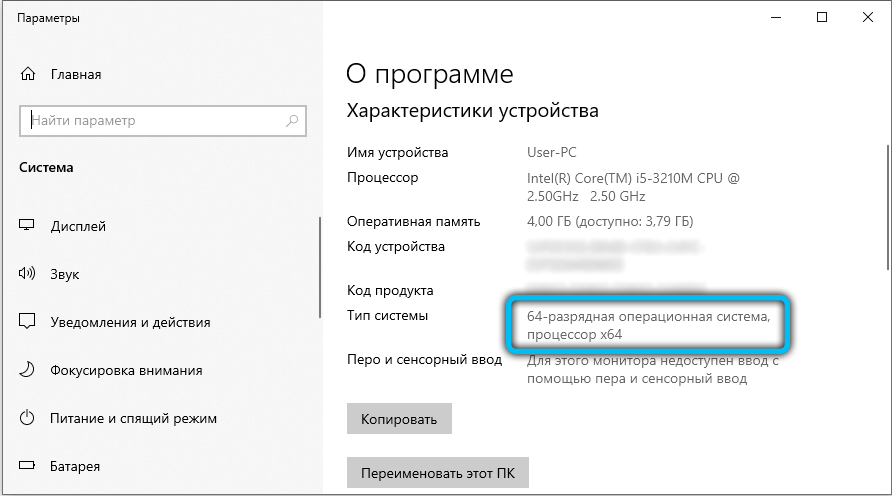
To find out the number of bits in your Windows OS, you need to right-click on the “My Computer” shortcut and select “Properties” from the list that appears. After that, you will see a window containing all the basic information about the installed OS, including its type. If you are using XP, this will be a little more difficult. In the properties window on the “General” tab, pay attention to the name – whether it contains the string “64-bit Edition”. If not, then the bit depth is x32.
Other popular ways of recognizing bit depth
If it was not possible to determine the desired parameter through properties and characteristics, we will try to go a more complicated way.
On the command line
The easiest option to immediately get to the command line is to press the key combination win + R. A window will open in front of us, where we must register the command “cmd” and press enter. Now the command line will appear directly, where we set the systeminfo command and again confirm it by entering.
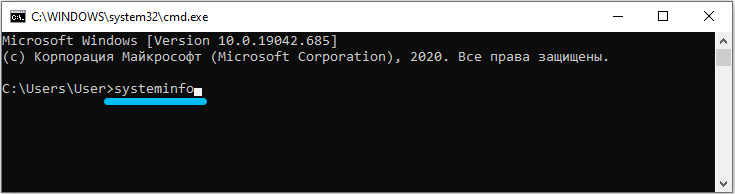
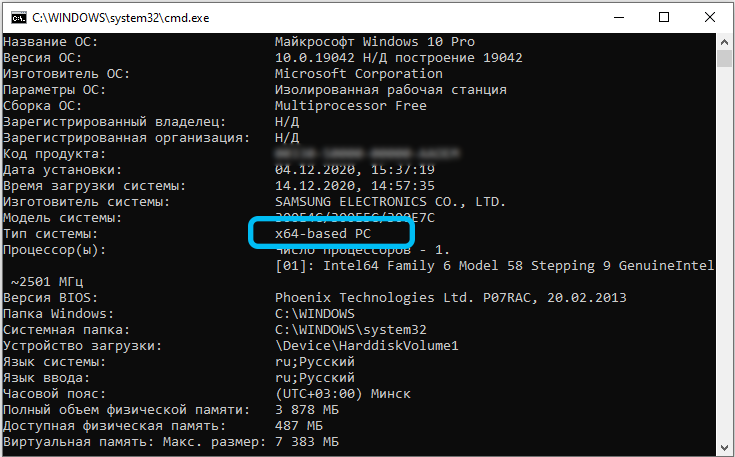
All information that concerns not only the computer, but also its filling, or rather the features of the operating system, will be displayed on the screen. Including we will be able to see its bit depth.
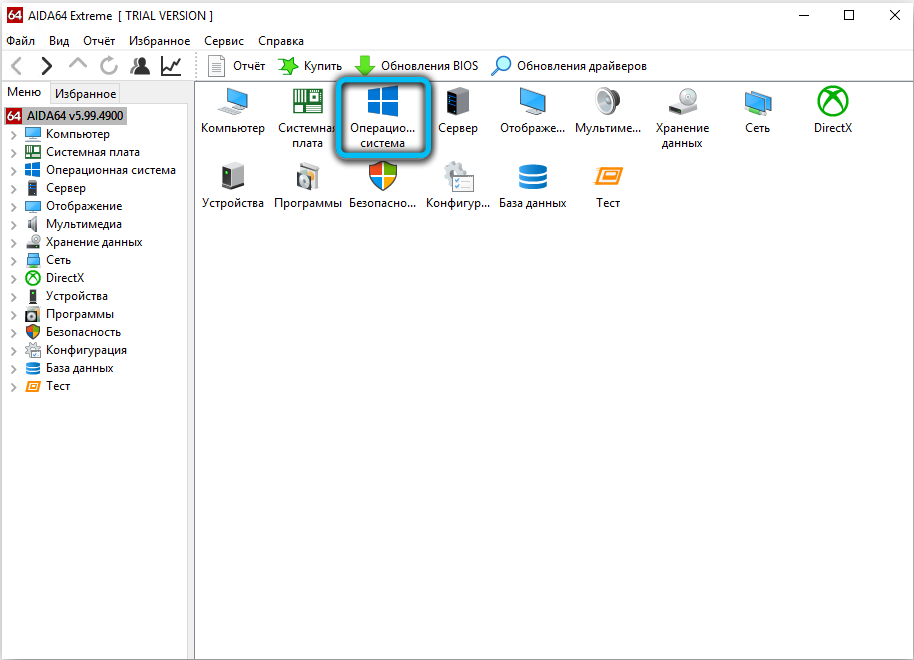
Through special utilities
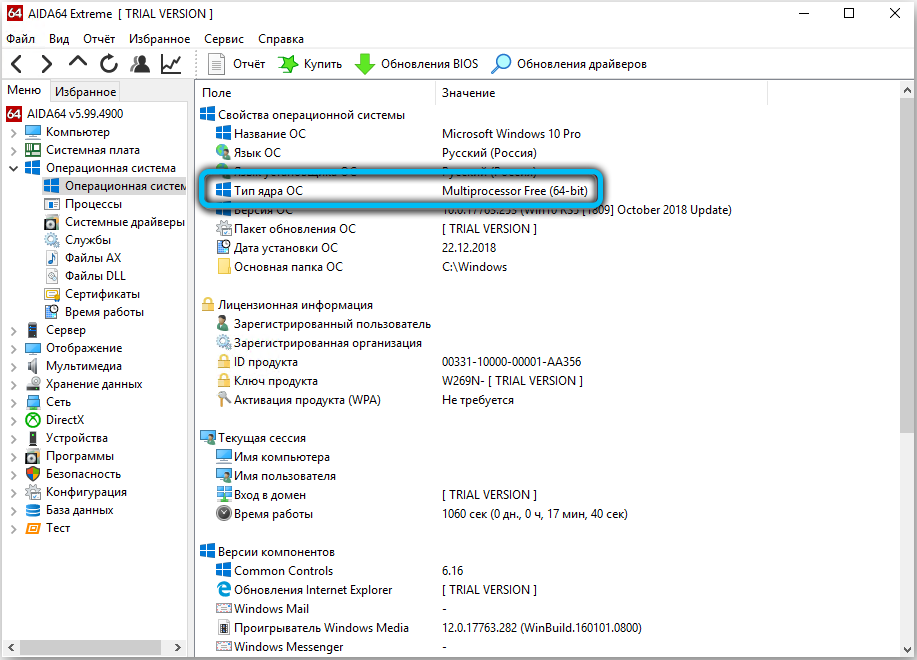
On the network, you can find many applications that will help monitor the state of the computer or its operating system, the need for cleaning or maintenance, etc. In the same way, users will find out information about whether they are 32 or 64 bits in their Windows.
Below is a list of such utilities that are downloaded completely free of charge, and some of them still do not need to be installed on your PC:
- HWMonitor;
- AIDA64;
- Speccy;
- HWInfo;
- CPU-Z;
- Astra33, etc.
Most of the applications described above are capable of performing complex diagnostics of both the state of the “hardware” and the “software filling”. They measure baud rate and temperature, which can be unsafe to function. They also provide information about the processor and motherboard, battery status, drivers, monitor, network, etc.
Despite the fact that the 64-bit version is designed for more RAM and faster performance, it does not make sense in all cases. Let’s see what differences and features between these OSs can be important for the user:
- it makes sense to upgrade to 64 uniquely in those devices that are equipped with 4 GB + of RAM. This will speed up the work of the entire system;
- rare software may also require a preliminary check before switching. The fact is that its manufacturers released their utilities for different operating systems;
- the transition to a more revolutionary OS will be justified when working with graphic editors – loading pictures and various illustrations will be faster;
- 64-bit accelerates the work with archivers, which is useful when you need to frequently compress and decompress files;
- impressive office suites with a large number of documents will also require switching to x64;
- It makes sense for accountants working in 1C to upgrade to a newer version, since processes will be faster and less memory is consumed.
Be sure to consider all the nuances when choosing a Windows version or processor. Write in the comments if the article helped you figure it out, and ask questions about the topic of the article that arose after reading.