Gamers are fastidious people: for them the convenience of the gameplay is so important that they are ready to sacrifice a lot in order to have decent equipment that will not let them down at the most crucial moments. But technologies are developing too quickly and what was top-notch yesterday is now moving into the mainstream category, be it a video card or a monitor.

As a result, you can observe interruptions in the game process, freezes, picture breaks. Often, buying a more powerful graphics adapter does not always lead to the expected results due to the mismatch between the characteristics of the video adapter and the monitor.
In such cases, vertical sync helps, but this technology must be implemented in both types of devices involved in the gameplay.
Contents
AMD FreeSync on the monitor: what is this technology
Work has been underway to synchronize the work of the graphics accelerator and the computer monitor since 2009. At first, a separate module was used for these purposes, which was engaged in scaling frames.
Later, the technology began to be implemented directly into video cards, and AMD was the first to do this, which made it possible to use the FreeSync function without the need to connect an additional device.

The image is displayed on the screen after this frame has been rendered (drawn) by the video card. She does this in a wide frequency range – from 10 to 250 Hz. Few monitors are capable of operating in such high-speed modes, hence the artifacts that I would like to avoid.
This problem is partially solved by FreeSync technology, which starts working at frequencies from 40 Hz. And one more condition for its activation is a mismatch between the refresh rates of the display and the rendering of frames by the graphics adapter. If the video card rendered a frame and sent it to the screen, which at this time is just finishing drawing the previous one, then it will be displayed with distortion, and if the desynchronization is serious, then there is a possibility that this frame will be missed altogether. In the first case, we will get a characteristic picture with breaks, displacements of a part of the frame. In the second, the actual decrease in the number of rendered frames per second, which will affect the quality of the picture, as well as the reaction to the player’s actions.

But do not expect miracles: problems cannot be completely avoided. The fact is that AMD FreeSync technology is actually only needed to synchronize the frequencies of the graphics card and monitor. If there are flaws in the game engine itself, it will not cope with them. Likewise, it is powerless if the CPU cannot handle its part of data processing. But if these two factors are in order, synchronization at the video adapter level will really save the game from artifacts.
You should not look for FreeSync technology on laptops and even more so on tablets, since there we are not talking about monitors with higher resolution and frequencies. Desktop PCs with monitors only! It is worth mentioning another limitation: to activate the mode, the monitor must be connected either via the Display Port interface, starting from version 1.2a of the 2013 sample, or via HDMI. In addition, the game must be running in full screen mode, otherwise nothing will work.

Following AMD, a similar technology was developed by the main competitor in the field of graphics equipment, nVidia. It is called G-Sync and is available to vendors on a paid basis, which is why monitors that support G-Sync have a higher price tag than those with FreeSync.
Synchronization from nVidia is still less common, and not only because of paid use for developers and ultimately for hardware buyers.

Video cards with G-Sync are not able to correct correctly if the frame rate produced by the adapter is higher than the threshold values for the display. This means that FreeSync is more versatile, moreover, it has the ability to change modes and color profiles of the monitor, which G-Sync also cannot boast of yet.
Until recently, it was not possible to use both technologies at the same time: if it is stated that your monitor supports FreeSync, then it will work only with video cards from AMD. Conversely, monitors with G-Sync were only suitable for working with Nvidia graphics adapters.
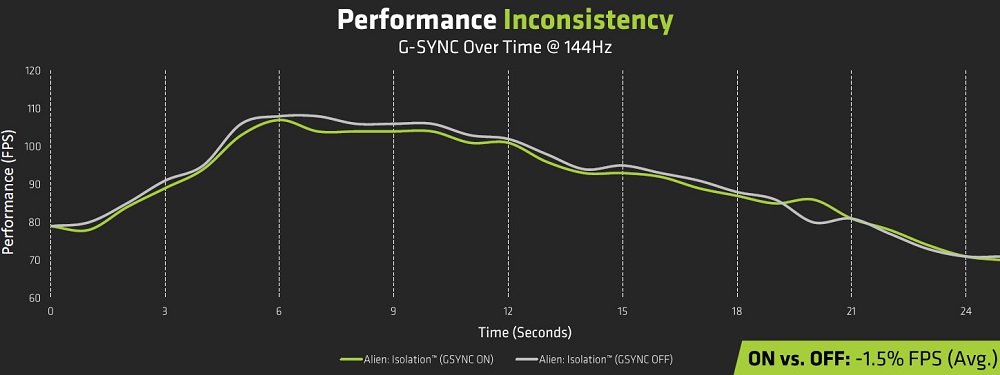
Since this fact hindered the distribution of the latter’s products, it was forced to somehow solve the problem. As a result, the latest models of video cards began to support synchronization technology from a competitor, and such products began to be labeled as G-Sync Compatible. True, the compatibility turned out to be far from complete, many monitors with FreeSync will not be able to synchronize with Nvidia video cards. For a complete list of officially supported G-Sync Compatible monitors, visit the official Nvidia website.
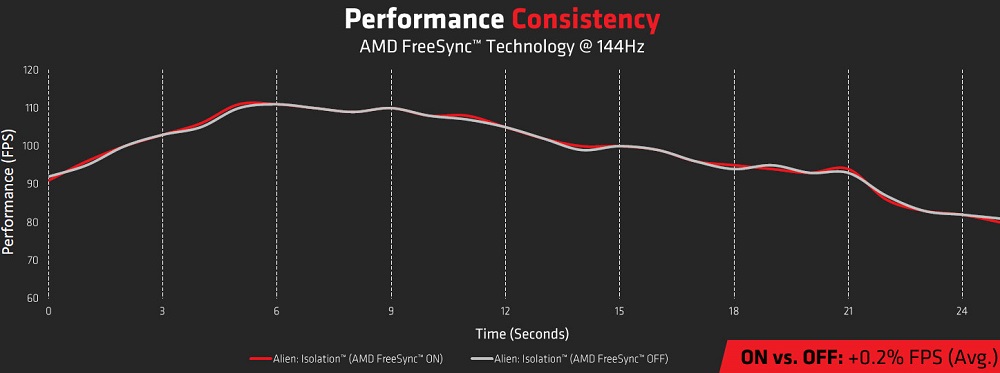
It should also be noted that although FreeSync allows you to get rid of freezes, tearing and skipping frames, as well as other artifacts caused by the desynchronization of the operating frequencies of the monitor and GPU, you will have to pay for this by purchasing a more expensive monitor that supports this technology.
However, AMD does not stop there. Dynamic refresh on the monitor has been enhanced with more advanced technologies, FreeSync Premium / FreeSync 2 HDR, which were already announced by the company at CES 2020. Using these modes allows you to cope with low frame rendering rates, as well as work with monitors capable of work at frequencies of 120 Hz and equipped with HDR technology. Nvidia does not stand aside either, its latest development in this area is called G-Sync Ultimate.

Consider the system requirements for devices that support FreeSync technology:
| Device | System requirements |
| Monitor | – laptop display, monitor or TV, the specification of which indicates support for FreeSync;
– the most recent driver; – Hybrid or pure GPU with FreeSync support. |
| Video card | – AMD: Radeon RX200 series and above (all Radeon consumer graphics cards built using GCN architecture from version 2.0);
– NVIDIA: GeForce 10 series or higher with DisplayPort Adaptive-Sync support or AMD FreeSync compatible. |
| Interface | – HDMI or DisplayPort;
– the corresponding connector on the motherboard; – compatible processor. |
How to enable FreeSync on the monitor
If the monitor supports this technology, it can be turned on through its menu (the sequence of actions is described in the user manual, usually the sequence Menu – Picture – Game settings – FreeSync, after which the function must be enabled).
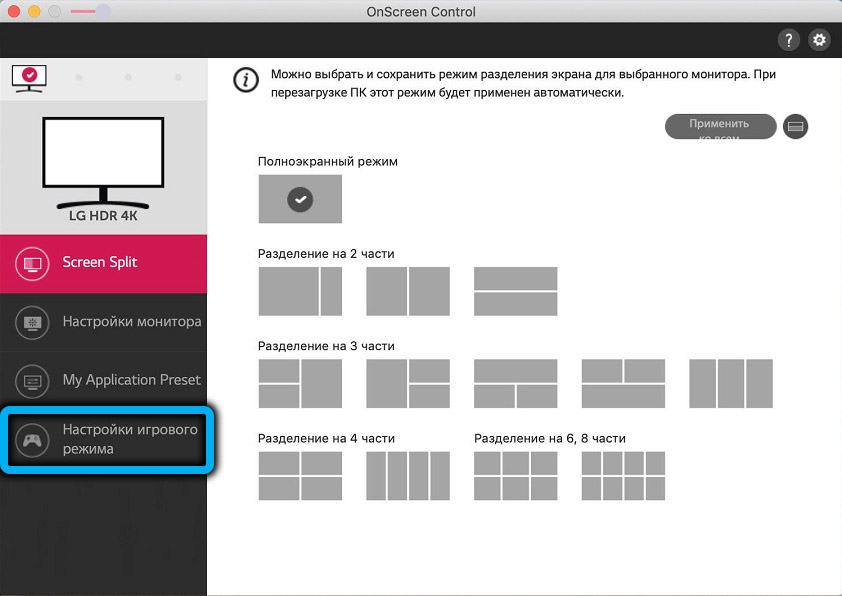
Some monitor manufacturers ship them with proprietary software to enable FreeSync. In particular, this is LG’s OnScreenControl utility, where you need to adhere to the following algorithm:
- go to the OnScreenControl tab;
- select the item “Game mode settings”;
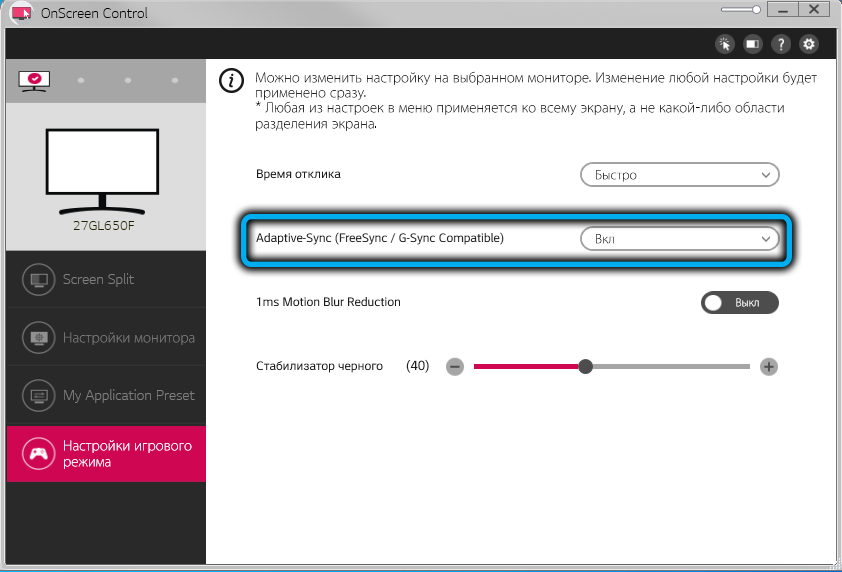
- set the switch opposite the Adaptive-Sync text to On;
- on an empty area of the desktop, right-click and select the “Screen Settings” option;
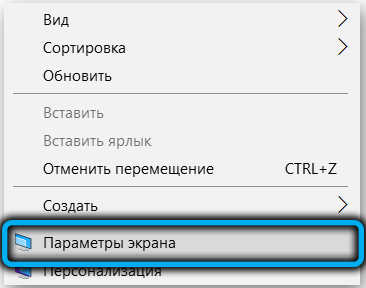
- click on the link “Additional screen parameters”;
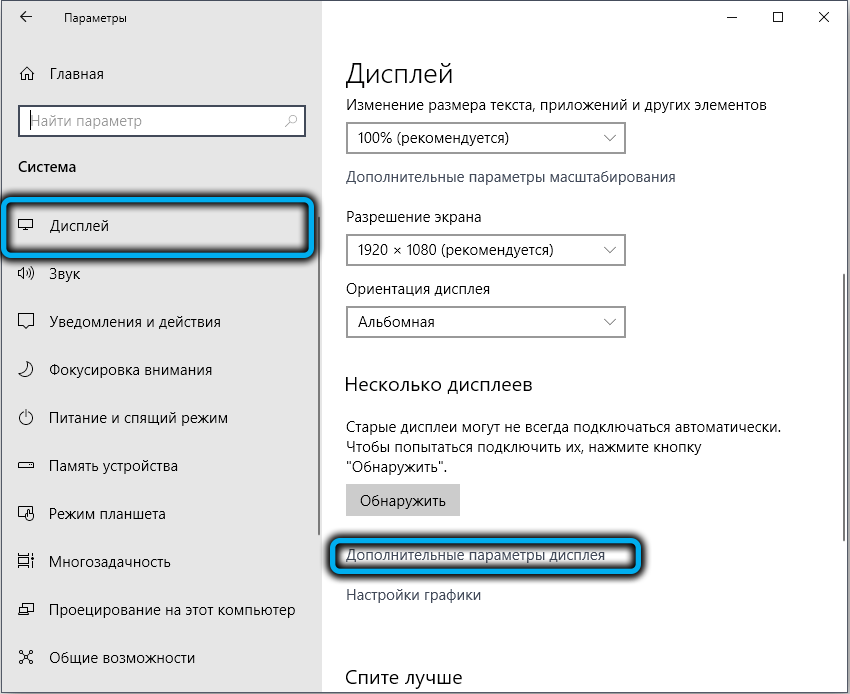
- select the menu item “Graphics adapter properties”;
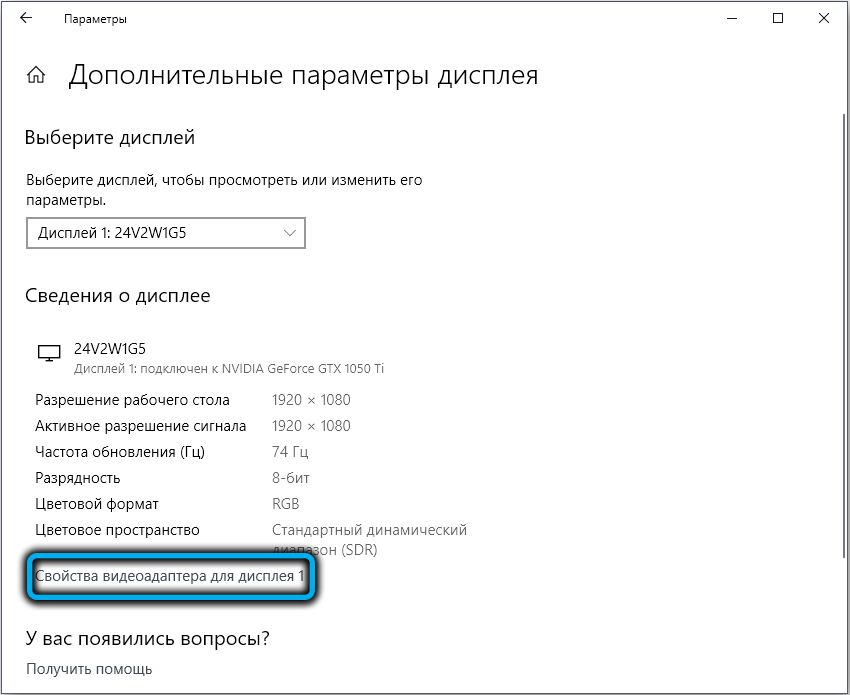
- go to the “Monitor” tab;
- put a tick in front of the text “Hide modes …”;

- select the maximum refresh rate for this monitor model.
If you have a latest generation Nvidia graphics card, you can enable G-Sync on FreeSync-enabled monitors. To do this, you need to install the driver in. 417.71 or newer and activate the variable refresh rate mode in the monitor menu.
How to enable AMD FreeSync on a Radeon video adapter
First you need to install the latest driver for your video card from the official website. Its name can be seen in the Device Manager.
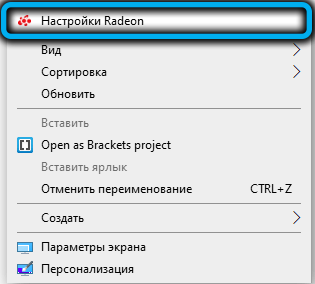
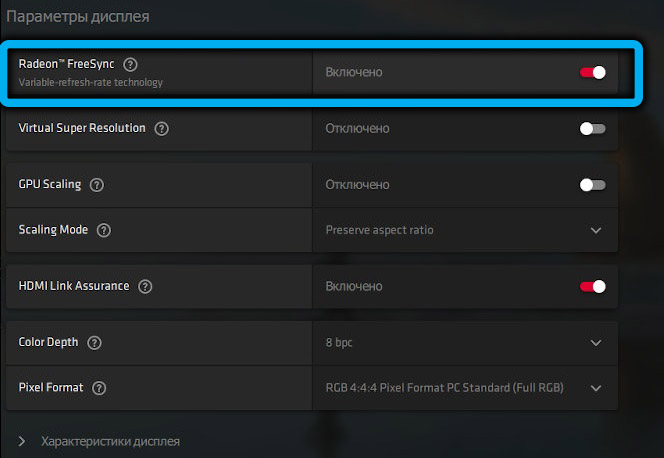
Then open the AMD Radeon Software utility, select the “Settings” tab, click on the “Display” menu item and set the switch next to the AMD Radeon FreeSync label to the “Enable” position.
You can disable FreeSync in the same way as activate it.
How to enable AMD FreeSync on Nvidia video adapters
We have already said that FreeSync technology works on modern Nvidia video cards, provided that a fresh driver is installed. Unfortunately, for most of the old cards, support from the company has been discontinued, so the drivers for them are automatically installed in Windows.
Attempting to install a fresh driver manually will be unsuccessful: the installer will determine that the hardware is outdated and shut down. So the owners of old Nvidia video adapters were out of luck in this regard. Which video cards do not support AMD FreeSync can be found on the manufacturer’s website.
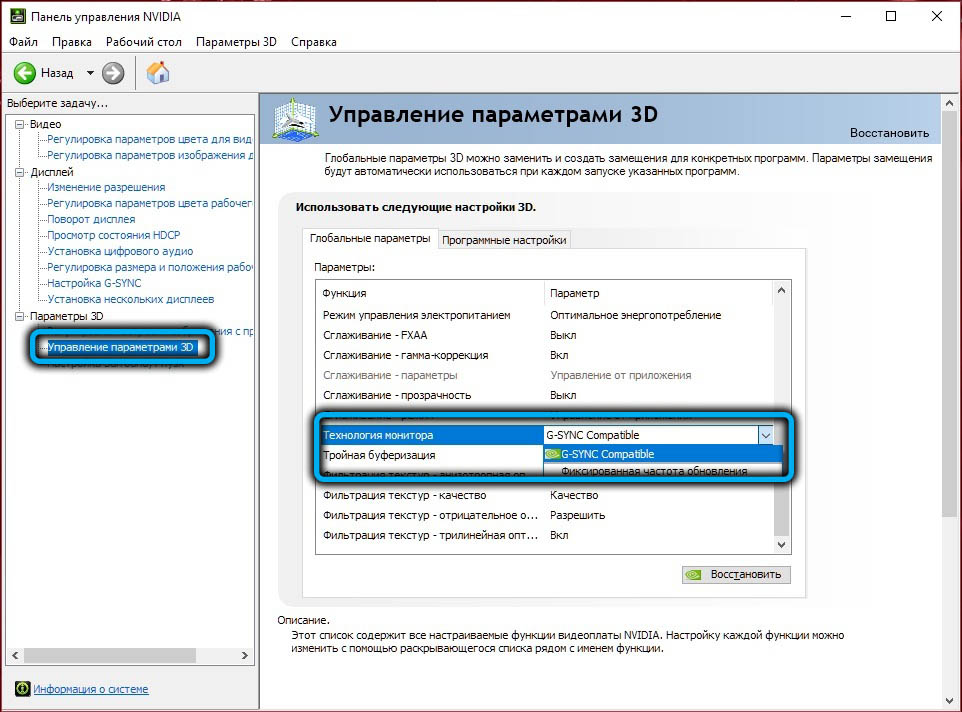
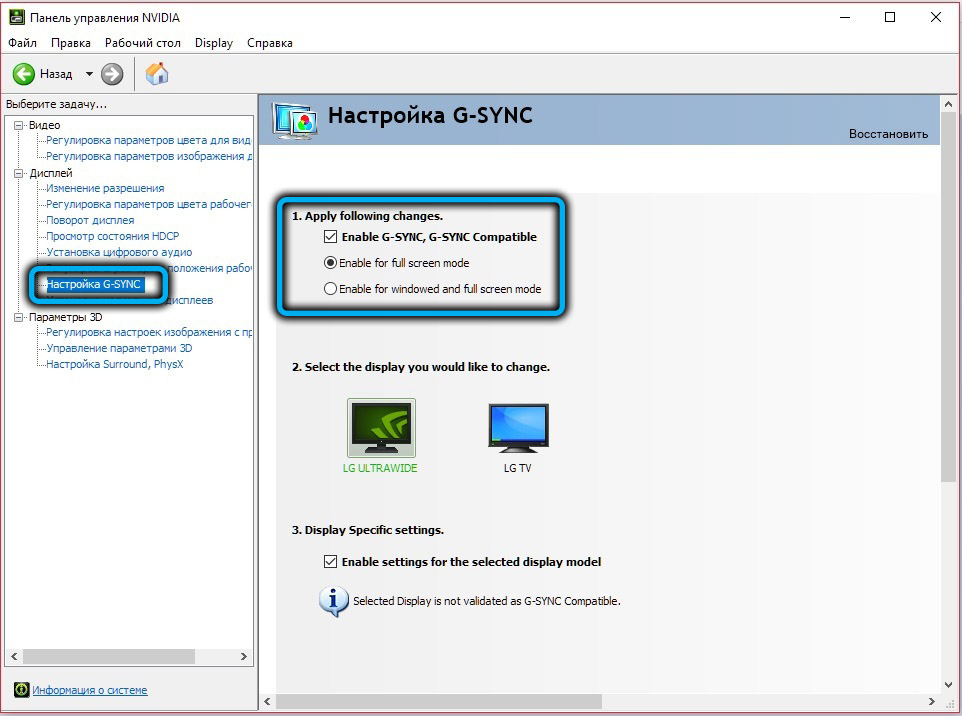
The mode is enabled through the proprietary Nvidia Control Panel software. You need to go to the Display tab, select the Set up G-SYNC item, and then set the Enable for full screen mode for the Enable G-SYNC and G-SYNC Compatible parameters.
Conclusion
Almost all modern gaming monitors specify AMD FreeSync support in the specification, and the newest ones also indicate FreeSync Premium. When this mode is activated, the screen refresh rate will be dynamic, which will allow the video card driver to synchronize the operation of both devices. And it really helps to remove various artifacts without using background utilities or additional hardware, practically without affecting the performance of the graphics subsystem.
Enabling the mode is usually provided in the monitor menu, but if this is not there, you can activate the technology programmatically, through the AMD and NVIDIA control utilities.