Due to the fact that modern smartphones, even at a budget level, are equipped with an internal memory of 128 or even 256 GB, the problem of its shortage is becoming less and less urgent. Still, after only a dozen years ago, 250 GB hard drives were the most popular, and even today a considerable number of PCs and laptops have about the same volume. But no one is surprised that smartphones are equipped with powerful miniature multi-core processors that would be quite competitive with a PC CPU of the same 10-15 years ago. So the expression “there is never too much memory” is still true today, and the best way to increase it is to use memory cards. In other words, the question of why such a card is needed is not worth it for many, but how to choose it is of interest to a considerable number of users.

Contents
What is a memory card
Modern memory cards are a special type of non-volatile memory (the so-called flash memory) on microchips, enclosed in a plastic case. This type of memory has been known for a long time and is used in many electronic devices, but the massive use of flash memory for a long time was constrained by its small volumes and difficulties with rewriting.
The improvement of technologies, including the miniaturization of the technological process, has made it possible to solve many problems. Currently, in terms of volume, read / write speed, and resource, such solid-state drives are not much inferior to traditional media such as hard drives, which made it possible to use them in smartphones and other mobile gadgets as additional memory.

Such a memory card on a smartphone can theoretically exceed the volume of internal memory, and even more so – operational, allowing not only to store large amounts of data on it, mainly of the media type (video, audio, photos), but also to install and run applications from the memory card.
Now the main problem is considered to be the unification of such storage devices, since there are many standards, and they are often incompatible with respect to other factors. Note that in terms of the compatibility of physical interfaces, the problems are solved at the hardware level by manufacturers of mobile devices, including smartphones, the operating system is designed to solve software incompatibilities.
Therefore, there are smartphone models that support memory cards of a certain class and volume and on which newer types of media cannot be installed, but we will talk about this below.
Manufacturers
As in any other area, the competition is fierce, but the actual flash memory is produced by several brands that are well known – SanDisk, Transcend, Kingston. It is these manufacturers that produce memory cards of guaranteed high quality, but the cost of such solid-state drives is quite high. Recently, the products of Silicon Power have become more and more common, releasing inexpensive memory cards of excellent quality on the market.

Strictly speaking, the cost of drives from noname brands is not so low as to expose oneself to an increased risk of purchasing a low-quality or even defective product, so you need to focus on these four brands.
Criteria for selecting memory cards
And here the situation looks more confusing and complex, although there are so many criteria in fact. And if we dealt with one of them rather quickly (we are talking about which memory card is better), then we need to deal with others more thoroughly, which we will now do.
Common memory card formats
This parameter mainly affects the volume of the carrier and its form factor, so it can be considered one of the main ones.
Let’s consider what types and form factors memory cards are divided into according to the accepted classification:
- SD. A morally outdated format, the very first, with a relatively small volume (no more than 4 GB) and a write speed of 12.5 MB / sec. The only advantage of this form factor over more modern ones is its versatility – any newest and most sophisticated smartphone perfectly “understands” this format;
- second generation SDHC memory cards allow you to store up to 32 GB of data on a medium at the same read / write speed, and for a long time such drives were the most common;
- today they are being actively replaced by SDXC cards with twice the speed of data recording, while the volume of such media can be up to 2 TB. Of course, before choosing a memory card for your smartphone model, make sure that it is capable of supporting this format. Old models will not be able to read such a card.

Memory cards differ in types, and this factor mainly affects the size and form factor of the drive.
Let’s consider the main differences between the types of SD cards:
- SD – the largest type of solid-state media in terms of dimensions (24.0×32.0x2.1 mm), which allows them to be used in the maximum number of fairly large devices such as laptops, tablets, camcorders or digital cameras;
- miniSDs have smaller dimensions (20.0×21.5×1.4 mm) and can be used in devices of the corresponding size, such as mp3-players;
- microSD is the smallest form factor (11.0×5.0x1.0 mm), which is widely used in mobile phones.

As for the compatibility of form factors with each other, it is available from bottom to top: a microSD card can be used in large devices – there are special adapters for this. But there is no way to put a large card into a smartphone, so in the future we will assume that we are dealing with microSD cards.
Note that the supported file system format depends on the size and generation of the memory card – SD cards of the first generations (1.0 / 1.1) can work with FAT16 / 32, SDHC cards – only with FAT32, and SDXC drives also understand the exFAT (extended FAT) file system , since the usual one does not accept drives larger than 2 TB.
And one more important nuance that you need to consider when choosing a memory card for a smartphone. The fact is that the real available volume, which any conductor shows, will be slightly less than the declared one. This is due to several reasons (inconsistency of counting systems, the use of part of the card memory for operational needs).
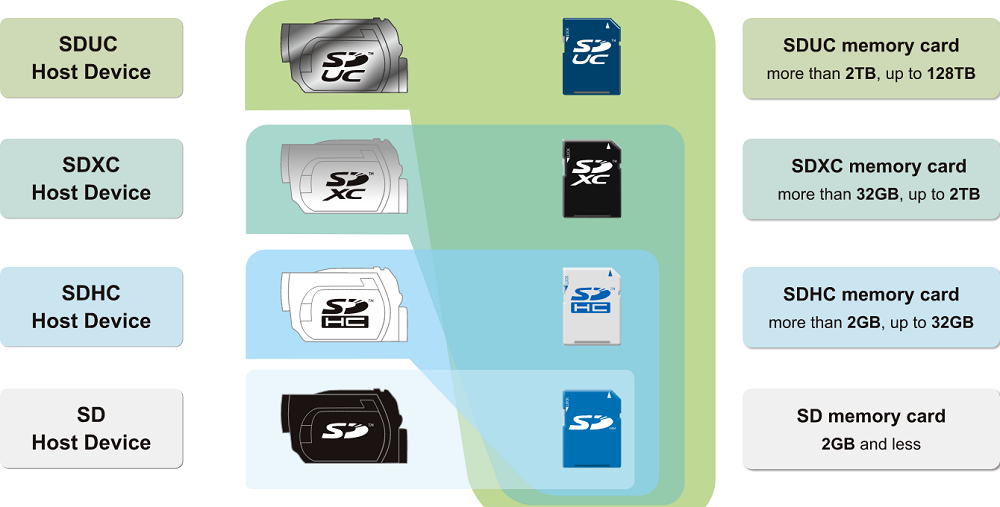
The promising new SDUC format allows the use of cards up to 128 TB, but currently the specification is not widely adopted.
Speed and class of memory cards
In addition to the volume of the medium, it is necessary to pay attention to such an indicator as the speed of data processing, first of all – the speed of the operation of writing information to the card. If you use an additional storage device relatively rarely, then the speed of information exchange is not so important, but if you operate with large files (for example, video), then this parameter becomes one of the defining ones.
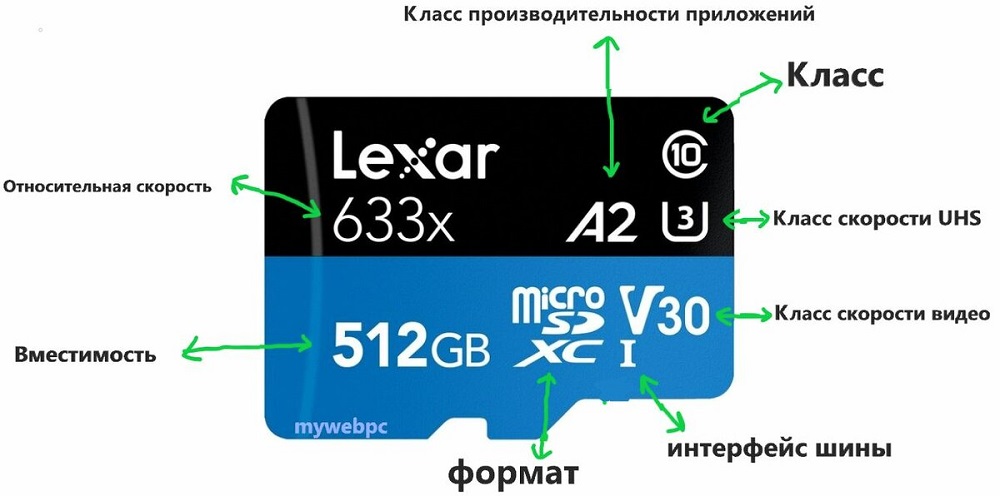
And it depends on the class of the card: the higher it is, the higher speeds the data will be processed (that is, at what speeds it is possible to write directly to the microSD):
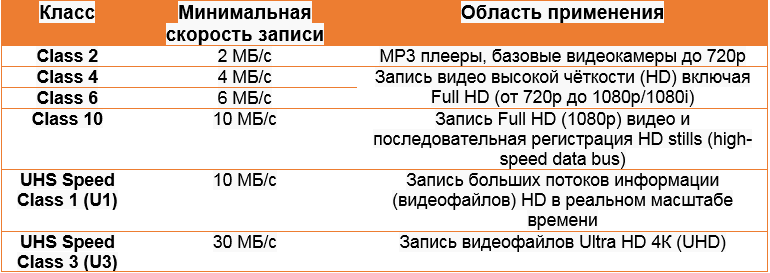
- SD Class 2 – Flash memory with a write speed of 2 MB / s, or 16 MB / s. This is enough for real-time video recording in standard definition;
- SD Class 4 is characterized by twice the write speed, that is, 4 MB / s;
- SD Class 6 (6 MB / s or 48 MB / s) allows you to record video with a resolution of 720 p (HD standard);
- SD Class 10 provides data recording at a speed of 10 MB / s;
- SD Class 16 (16 MB / s, or 108 MB / s) – speed sufficient to record video with a resolution of 1080 p (Full HD).
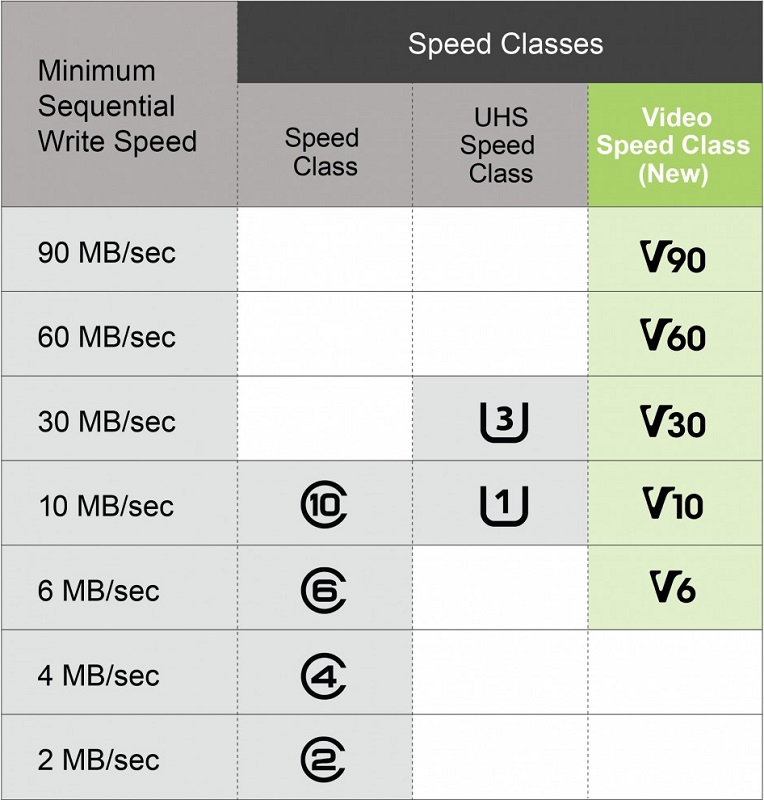
Modern microSD memory cards such as SDHC and SDXC support the UHS speed class, which is up to 312 MB / s, that is, the ability to record and play 4K video. For smartphones, this is a clear overkill, since this format is not supported on a small screen, but the general rule can still be formulated as follows: the higher the speed class, the better. But high-speed cards are much more expensive than usual ones.
Note that you can determine the speed of SD cards by packaging, but the actual performance will differ depending on the brand and other factors, and it is measured by special applications.
Summary
So is it worth overpaying for the brand? In principle, no one forbids you to buy cheaper memory cards, but if you intend to store critical data on such a medium, then it is better not to risk it. But photos, videos, and even more so music, if there are copies in cloud storage – you are always welcome. Remember that such drives serve less and at any time they can slip you what is called a pig.
If you have a budget smartphone, then it is worth considering whether you need a Class 10 memory card for it. For ordinary needs – definitely not, and if the characteristics of the phone do not allow you to shoot videos in FullHD format, then you can completely get by with the fourth class.
As for the volume, here, too, much depends on the capabilities of the smartphone. If its specifications indicate support for a maximum of 16 GB, then it makes no sense to shove a 32 or 64 GB card into the device. Unless you expect to change your phone model to a more modern and technically advanced one in the future.

But here, too, there are some nuances. 128 GB of internal memory will be enough for many years of use, and such smartphones are by no means uncommon today, and their cost is falling over time. But if you constantly shoot high-definition videos, then the additional storage space will definitely come in handy.
And finally, if you are in doubt about which brand memory card to buy for your smartphone, remember that they are suitable for any smartphones, regardless of manufacturer. It is impossible to meet a situation here when a Samsung drive will be recognized only by smartphones of the same brand.