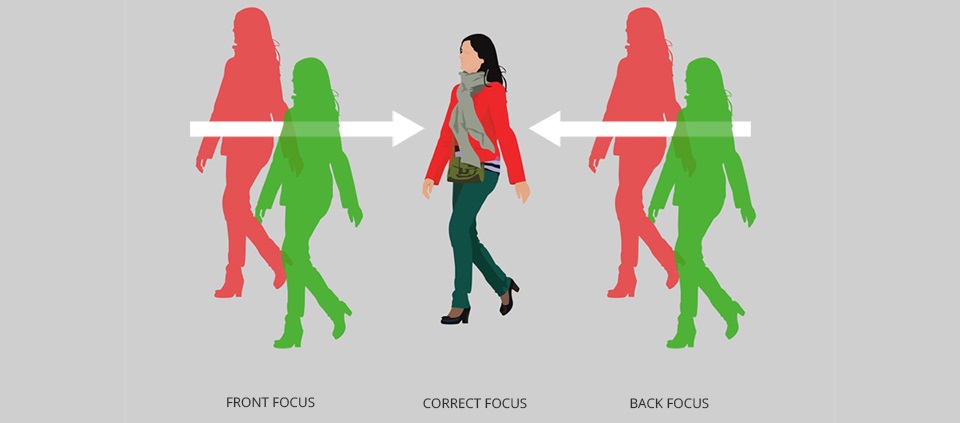
When taking photos with a smartphone, everyone wants to get high-quality images, where the photographed object will be clear and sharp, that is, in focus. Modern technology, including mobile devices, allows focusing in manual or automatic mode, and even professionals often resort to autofocusing. The device, without user intervention, places the lenses at the desired focal length, allowing you to capture the subject without blurring, and although when you point the camera, focusing is performed in an instant, at this time a lot of imperceptible processes and calculations take place.

Today, many smartphone manufacturers are improving autofocus technology, which allows you to take high-quality, clear pictures, even when the subject is in motion. And advanced users, when choosing a mobile device, pay more attention to the type of autofocus of the camera than the number of megapixels. Let’s talk about what types of autofocus are, what distinguishes them, and how they work.
Contents
What is autofocus and why is it needed
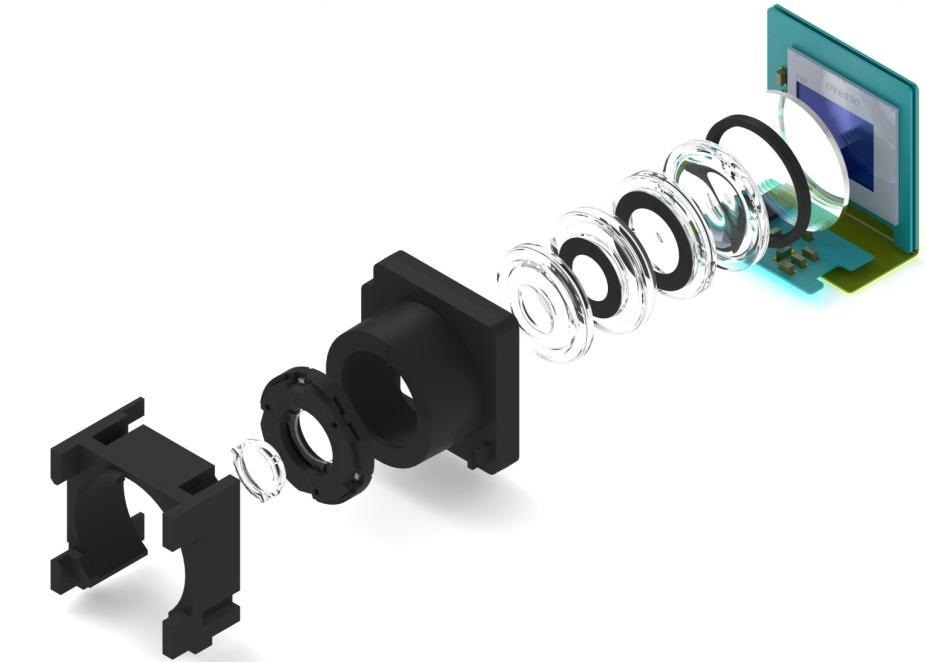
An autofocus system is present in any modern smartphone, including budget options. With its help, the camera lens is adjusted so as to almost instantly focus on one or several objects of shooting a photo or video, simplifying the process and removing the task of manual focusing from the user, as when shooting with a professional SLR camera.

Auto focus makes it easy to capture crisp, detailed shots by pointing the camera at an object and pressing the corresponding button. Autofocus includes a sensor, a control system and a drive that is responsible for moving the lens barrel or lenses.
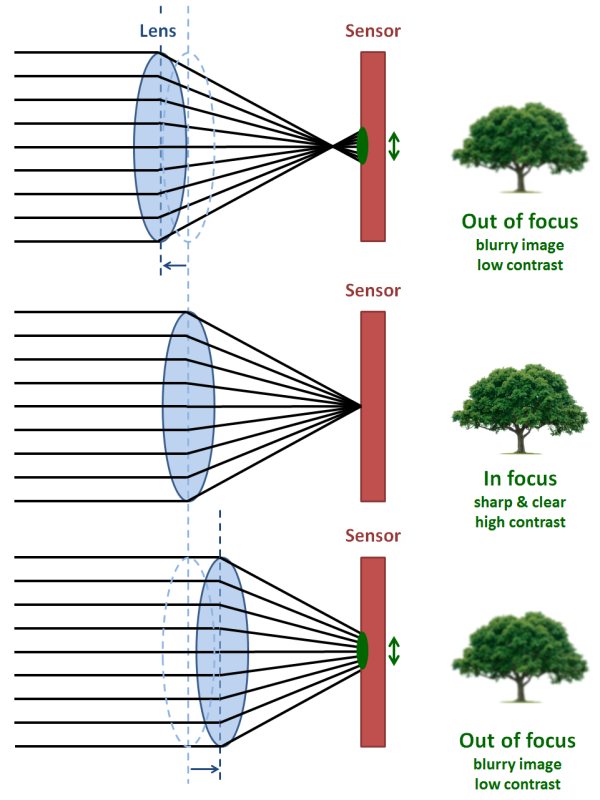
The camera is designed in such a way that the rays of light reflected from the objects of photography are captured by sensors that convert the flow of photons into a flow of electrons, then the current is converted into bits, this information is processed and sent to the device’s memory. How does autofocus work? It all depends on its type. The lenses focus the rays reflected from objects, while when the focus is set, the camera will be guided by the distance to the imaged object and the intensity of the illumination, while the sensor, in turn, will create a digital photograph. Unlike earlier models of smartphones, today devices provide the ability to adjust the distance between lenses and sensors, which allows you to get better pictures.
Modern camera phones are equipped with highly sensitive sensors and special algorithms that help the camera focus even in low light. In advanced devices, an artificial intelligence system is also being introduced, which adjusts the shooting and focusing parameters to obtain the highest quality frame, as well as the autofocus option in motion, which allows you to focus on a moving object, tracking its movements, so that it becomes possible to catch a good shot, provided the subjects are moving. …
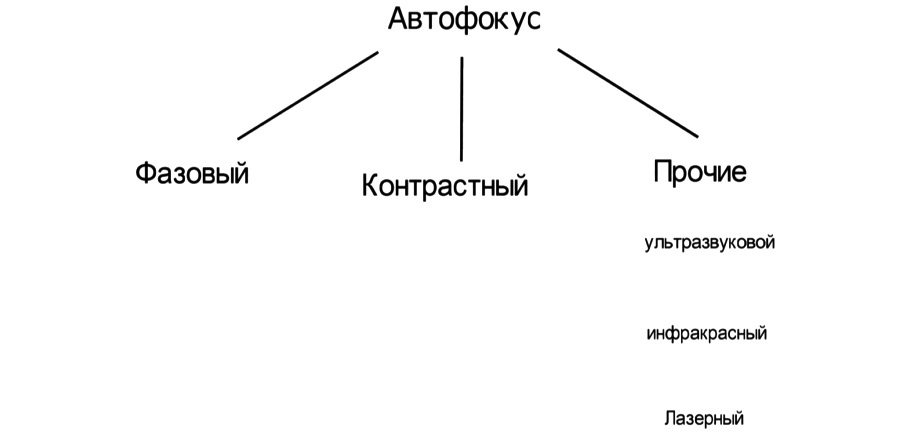
Autofocus is currently implemented in three relevant options: contrast, phase and laser. Let’s consider how each of them differs.
Contrast autofocus
The technology is based on the work of light-sensitive elements that analyze the contrast of the frame. Focusing is provided by shifting the objective lenses to achieve the desired image contrast. When the maximum contrast was achieved by evaluating this parameter and changing the position of the lenses, this means that the subject is in focus. In this case, the camera analyzes a small area of the matrix.
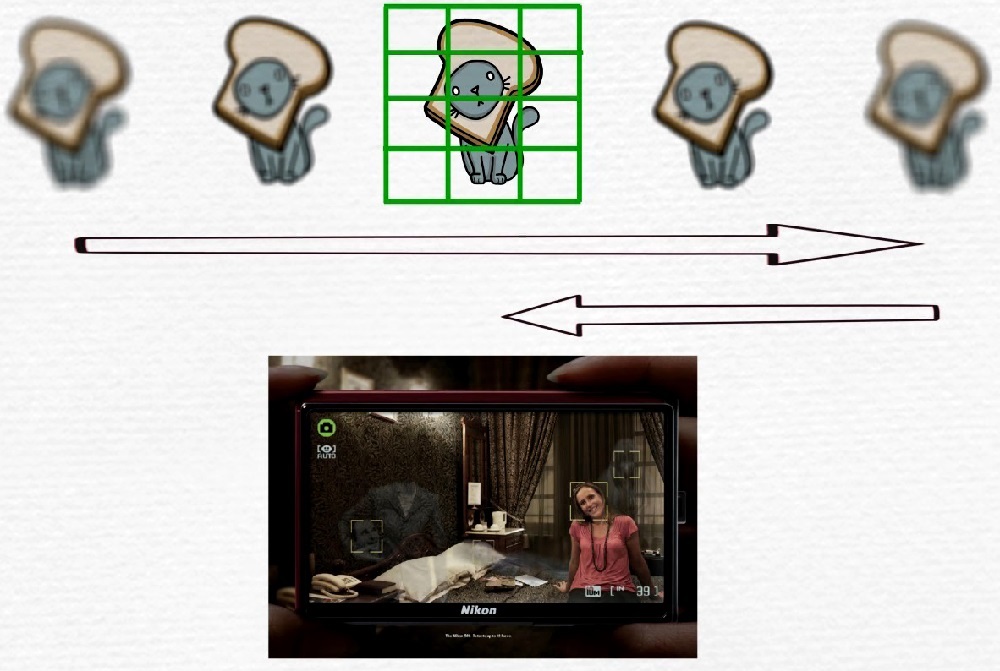
So, contrast autofocus refers to a passive type of autofocus, this solution is simple to implement and is used on budget smartphones. Autofocus is slower than other technologies due to the need to move the lenses several times to achieve a result. These movements and the assessment of contrast, carried out in several stages, take about a second and this is not much when it comes to shooting stationary or sedentary objects that can freeze for a photo, but in this situation it is easy to miss the moment, and it will not work to shoot in motion, since photography will be oiled. Contrast autofocus is also not endowed with a tracking focusing option, and the quality of photographs will suffer greatly in low light.
Phase detection autofocus: a fast and advanced alternative
Until recently, this type of autofocus was the privilege of flagship smartphones, but now autofocus based on scanning light phases is used in most devices.
Smartphone phase detection autofocus (PDAF) is an active type of autofocus that is most relevant today and provides high-speed operation, as well as the ability to focus on moving objects. The technology is borrowed from digital SLR cameras, initially it was intended specifically for photographic equipment, where it showed itself in the best way, and only later migrated to flagship mobile devices.
The principle of operation of this type of focusing is as follows:
- The light stream passing through the lens is divided in two, then the rays from different areas of the lens are directed to the sensors of the light-sensitive sensor, which evaluate the uniformity of the light.
- If the object is in focus, the light flux from it will converge to one point on the sensor. If not, the software, taking into account the measured distance, will give a command and the lens will move the lenses to the desired position. The camera decides how to move the lenses to get the best picture possible in an instant.
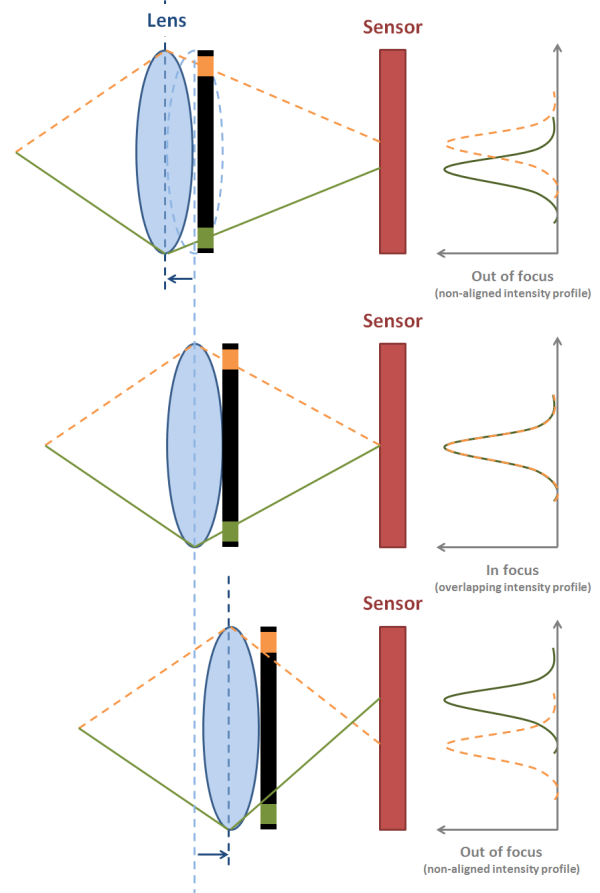
Since all these actions (the distance between the streams is measured and, according to the results of the assessment, the position of the lenses is corrected by the system, that is, the separated beams reach the distance specified by the sensors) are carried out in one step, this means that the phase autofocus will work several times faster than the contrast one. It takes a split second to focus on the subject. Object coverage with sharpness occurs at any point in the frame, and if there are several objects in the frame, equally distant from the lens, all of them fall into the high-definition zone. The camera evaluates the movement using the sensors of the matrix, resulting in the possibility of tracking autofocus.

For all its advantages, phase-detection autofocus is also not perfect. Its disadvantage is night photography, in which an insufficient amount of light enters the lens aperture, which causes a decrease in the focusing speed. In addition, the implementation of this type of autofocus is rather complicated, it requires precise installation of the prism and mirror system, as well as careful software adjustment. And yet, despite the disadvantages of the technology, as a rule, it provides the creation of high-quality images. Today, in addition to autofocus, manufacturers use special algorithms, an artificial intelligence system is built in, which can significantly improve the quality of shooting. The technology is improving as many manufacturers have taken the path of its development or the use of varieties of phase detection autofocus.

Laser autofocus: most active
The most advanced today is laser autofocus. It, like the phase one, belongs to the active type and uses the same principle of operation as optical rangefinders. So, the emitter illuminates the object, while the sensor measures the distance to it and the time of the reflected laser beam.
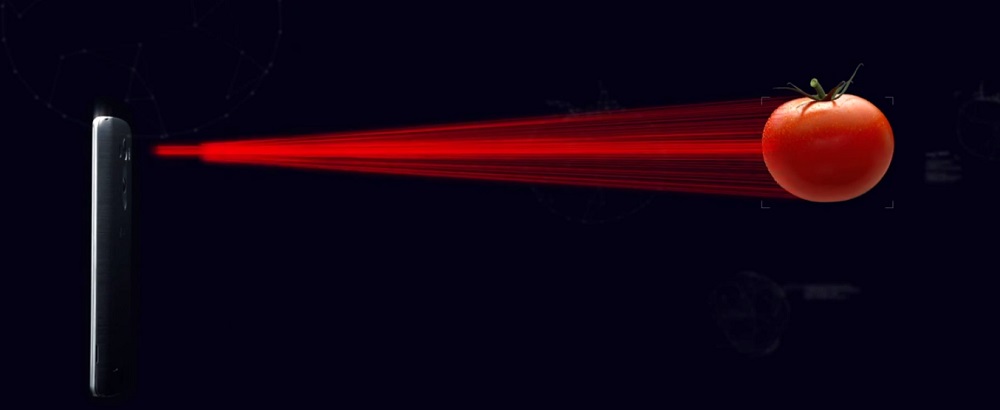

Laser type autofocus does not depend on illumination and works faster than phase autofocus, acting at a short distance. The best result is possible when the subject is removed by 0.6 meters. When shooting those that are already at a distance of 3-4 meters or more, the system will use a different type of focusing. The autofocus process takes even less time (the task is completed in just 0.276 seconds), allowing you to take high-quality images, and the speed is not lost even at night or in poor visibility due to weather conditions.
Summing up, we note that today the most relevant for smartphone cameras is phase-detection autofocus technology. Poor quality indicators with a lack of lighting are leveled by the presence of additional auxiliary software tweaks, such as intelligent algorithms that determine the best performance regardless of shooting conditions.