One of the most effective Windows tools that allows you to detect malicious software and is devoid of any heuristic analysis tools is the Task Manager. And I must admit that it is actively used by many users to monitor the situation in the event of strange computer behavior. The ability at any time to track which process or application is inefficiently using PC resources is very important, because such processes are the main candidates for the role of a virus, Trojan or other software from the same category. Moreover, many have thoroughly studied the composition of the “Task Manager”, and any new name in it is immediately perceived as a potential threat. The lsass.exe process does not belong to such, since it is systemic and is present in all versions of Windows.
But … Not everything is so good in the Danish kingdom. Today we will talk about when this process should be treated with distrust.
Contents
Lsass.exe – what is this process
If you translate the decryption of the abbreviation LSASS from English, you get something like “local security subsystem authentication service”. Simply put, this is an operating system component responsible for authorizing users within a single PC. The process plays an important role in the functioning of Windows, and if it is removed, the login to the system will be closed for local users. Simply put, you will not get past the OS prompt window.
The lsass.exe application is an executable program located in the c: Windows System32 system directory and is approximately 13-22 KB in size. In view of the above, it can be argued that in the overwhelming majority of cases the process is not a virus, although its prevalence plays a bad joke with it: perhaps it is lsass.exe that is most actively used by virus writers as a target.
How the lsass.exe process works
The task of the system process is to identify the data entered during the authorization phase, and optionally during the login. If the data is entered correctly, the process sets a flag that is perceived by the system accordingly. If the authorization process is started by the user during the current OS session, the flag will be set, allowing to start the user environment (shell). If in the future there is an attempt to initialize the authorization procedure from the side of the application, it will receive user rights in accordance with the set flags.
It follows from this that the lsass.exe file should not be large and that it practically does not use computer resources, activating as needed, but in any case rarely.
And if you notice in the “Task Manager” that this is not so, that is, the numbers in the “CPU” column jump, deviating from zero by solid values, that is, lsass.exe loads the processor quite heavily – it means that you are not dealing with the original file.
Indeed, cybercriminals willingly use this process to infiltrate the system, infecting the executable itself or disguising itself as it. At the same time, they use a variety of tricks to bypass anti-virus protection and not get caught by the user. For example, by creating a file with a similar name, localized in the Windows system directory (System32 folder), or by placing an infected file with the same name in another directory.
Since the process appears in the Task Manager as lsass.exe (the first letter L is lowercase, not uppercase), virus writers use this by replacing l with I, in which case Isass.exe will look almost natural if not looked closely. In some fonts, these letters are almost indistinguishable. To identify the catch, you need to copy the file name, paste it into Word and convert it to uppercase. If the first letter is correct, the process will be displayed as LSASS, if the virus, then ISASS will remain.
There are other techniques that allow you to disguise a virus file as a real one – for example, insert a space (lsass .exe) into the name, add an extra letter (lsassa.exe, lsasss.exe), etc.

If you run the search procedure for a file named lsass.exe, and it appears in a folder other than system32, you can be sure that we are dealing with a virus. Such a file can be safely deleted without fear of consequences.
You can also check it directly from the “Task Manager” – just select it, right-click (in Windows 10 – go to the “Details” tab) and select “Properties”. A new window will display the full name of the file and the folder in which it is stored.
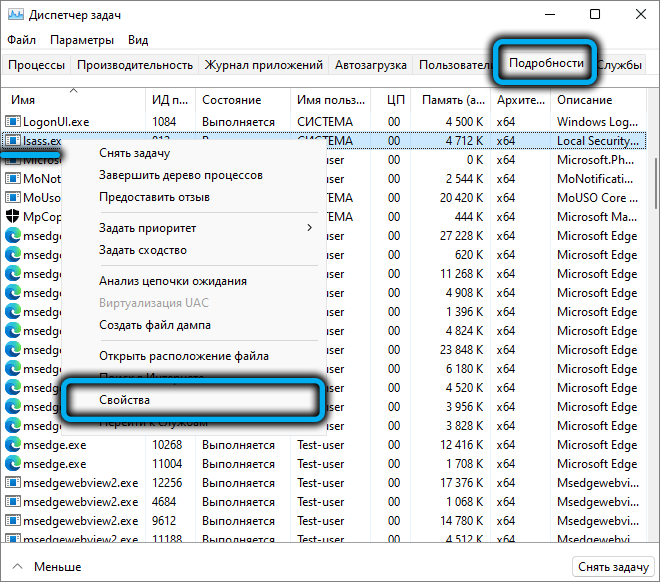
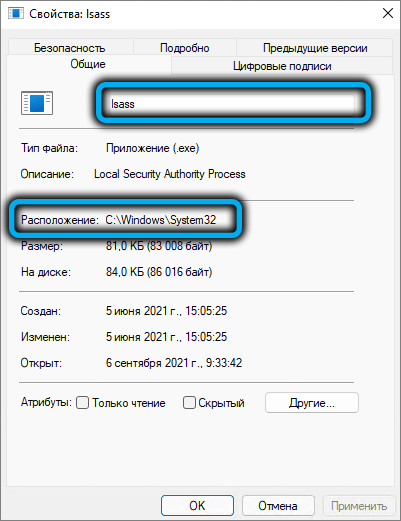
It will not hurt to check the authenticity of the file, for which you need to go to the “Digital Signatures” tab and make sure that the file is signed by the developer – Microsoft.
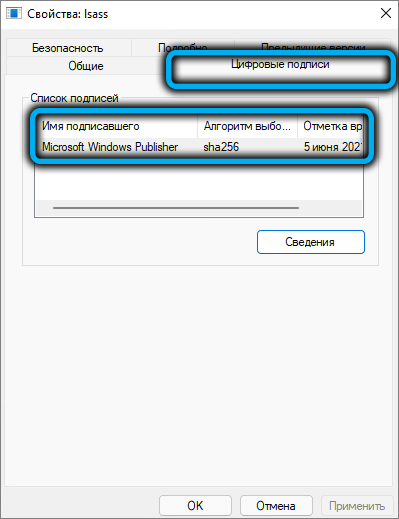
And since you have any suspicions about this, it is advisable to check lsass.exe with an antivirus: if it turns out to be infected, then with a high probability this fact will be revealed and the problem will be solved. And since the victim was a system file, it would be nice to check the rest of such files for their integrity using the built-in Windows tools, the sfc and dism utilities.
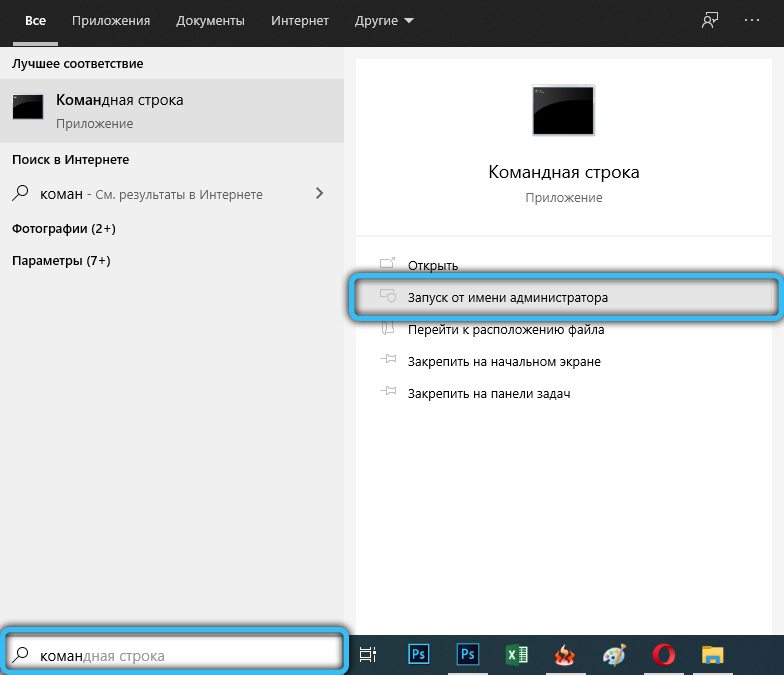
To do this, run the command line (always with administrator rights) and type the command:
sfc /scannow
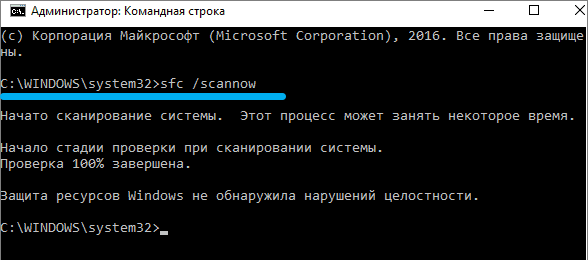
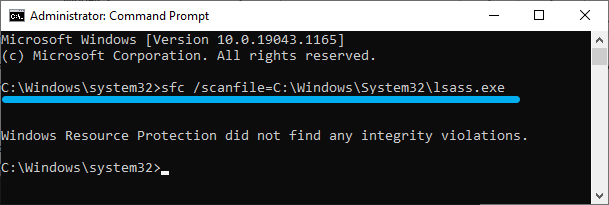
If you want to check only lsass, you need to specify this in the command parameters:
sfc /scanfile=c:windowssystem32lsass.exe
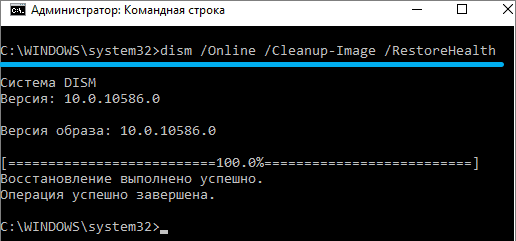
The dism utility also checks the repository of operating system system components for damage, which it can repair. Command syntax:
dism /online /cleanup-image /restorehealth
Once again, we note that you cannot delete the original lsass.exe file, even if it is infected, but you can unload it from memory, this will not lead to a system crash.
Disabling and removing the lsass.exe process
So, you found out that the CPU-loading lsass.exe process is not original. To eliminate the threat, you need to take a number of measures:
- download and install the AdwCleaner, CCleaner programs;
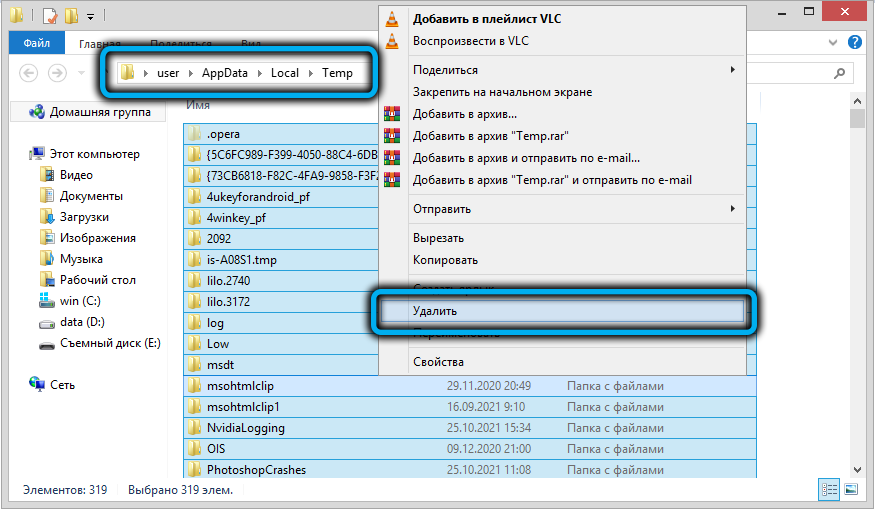
- delete all files in the c: users Administrator AppData Local Temp directory;
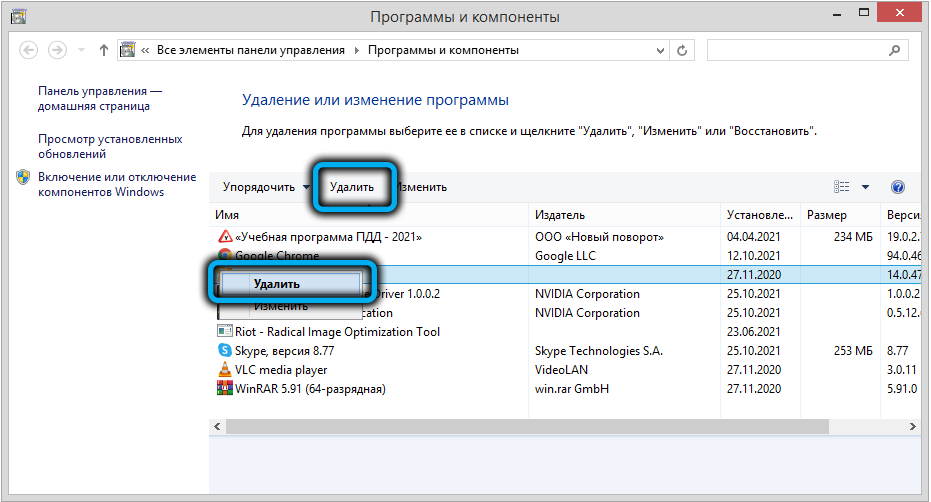
- run the “Programs and Features” tool, carefully study the list of programs installed on your computer, especially those that were installed relatively recently and which you do not know. If there are any, delete them;
- run the AdwCleaner utility, perform a full system scan, if a list of suspicious components is displayed, press the “Clean” button;
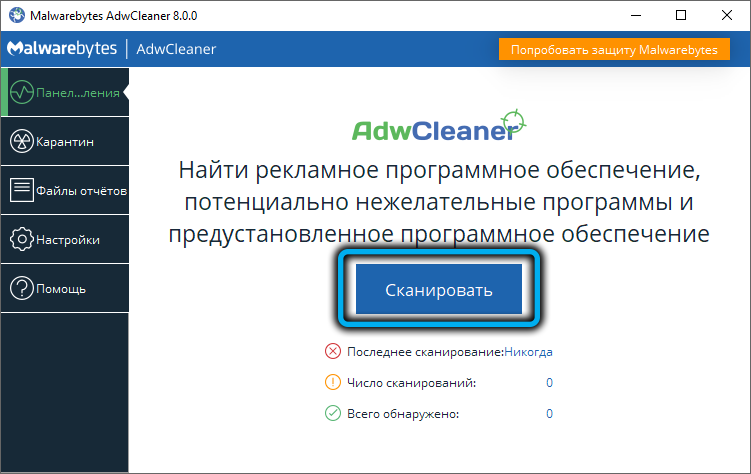
- we perform similar actions with the CCleaner utility, which will allow you to get rid of garbage in the system registry;
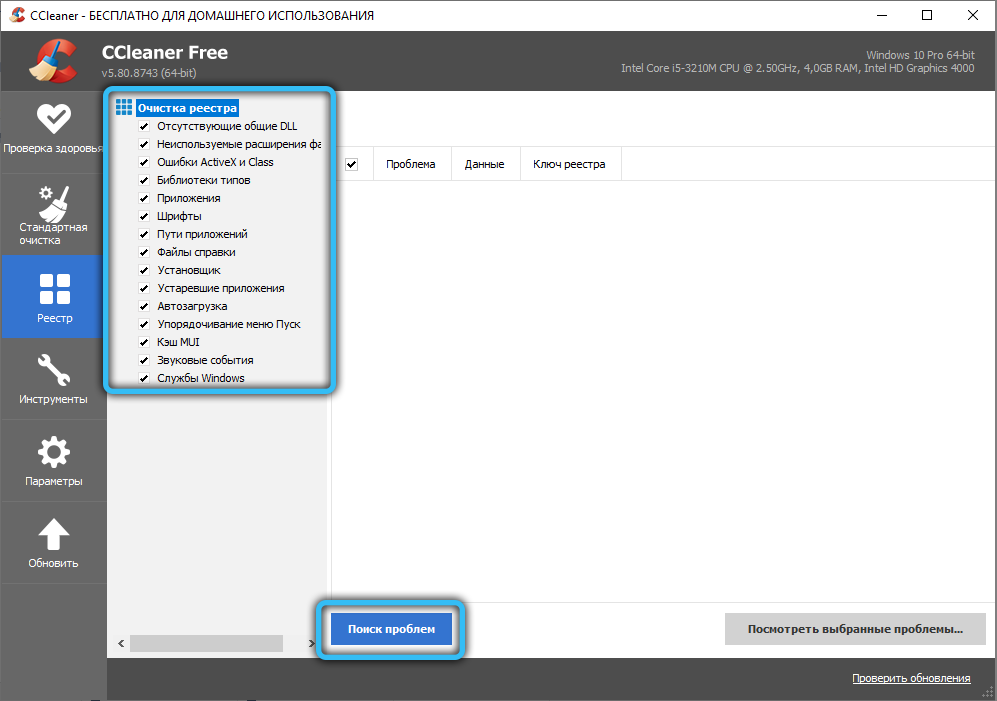
- launch the default browser and reset its settings to the initial ones.
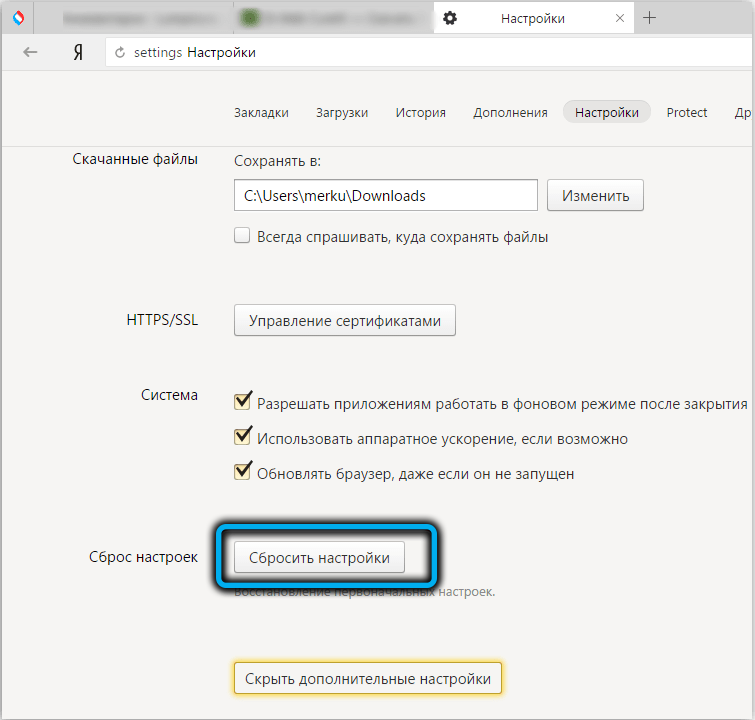
These steps are likely to be enough to fix your CPU usage and PC slowdown. We check this by restarting the computer. If the process is still loading the system, you can try to disable it.
How to disable lsass.exe
Sometimes an uninfected system process actually starts using computer resources, greatly slowing down its work. After a reboot, everything is usually normal, but if you want to unload the PC in the current session of the operating system, try simply disabling the process:
- click Win + R, enter “Run” services.msc into the console, confirm by clicking OK;
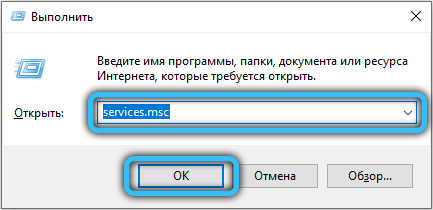
- in the window that appears for managing Windows services, we are looking for the line “Credential Manager” (for convenience, you can sort the list by name);
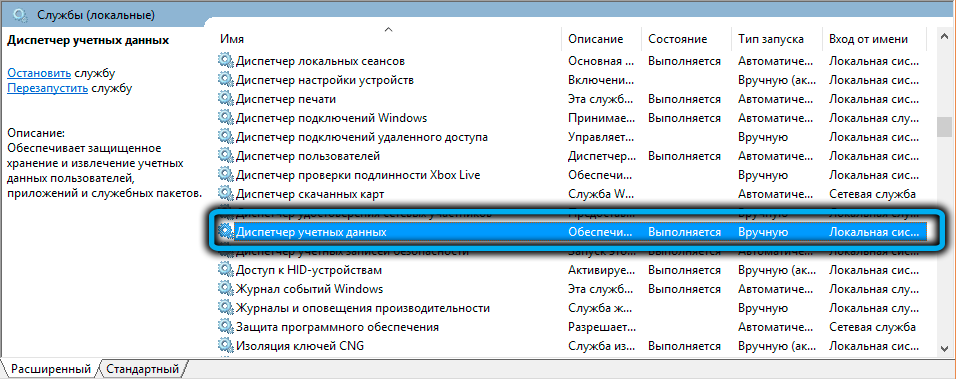
- click on the RMB line, select the “Properties” menu item;
- in the “General” tab, click on the “Stop” button, and opposite the “Startup type” parameter, select the “Disabled” option to exclude the process from starting at system startup;
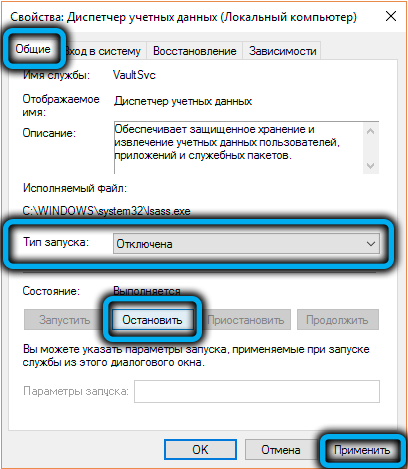
- restart your computer.
This will be enough to get rid of the CPU and memory load.
To delete the lsass.exe file, just go to the system32 system folder, select the file, right-click and select the “Delete” menu item. It is important to remember that this is an essential system process that is vital on multiuser computers, and deleting it can make it impossible to log in and use Windows recovery tools.