The Windows Remote Procedure Call service (aka RPC or Remote Procedure Call) manages a protocol that allows programs to perform their actions on other computers on a shared network just as they would on a given computer – without having to understand the intricacies of the connection.
The protocol turned out to be very convenient in practice: the latest versions of Windows use it for the internal interaction of programs located on the same device. Registry services, “Device Manager” and even the File Explorer application, which is responsible for the correct display of system windows and their properties, depend on its correct operation.
Contents
What does the error “Failed on remote procedure call” mean?
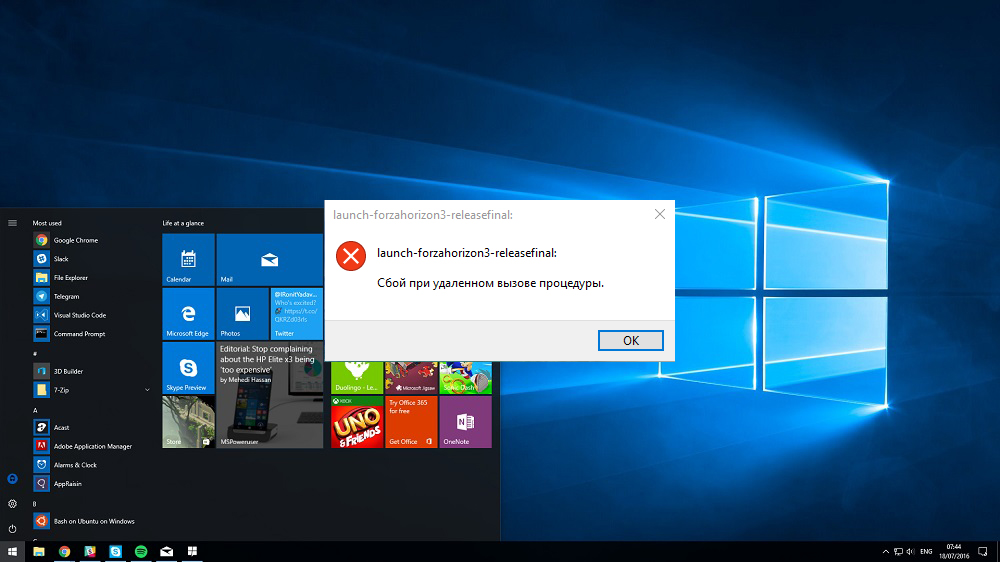
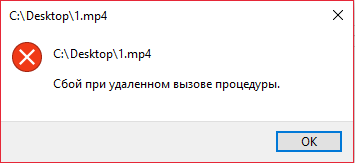
A remote procedure call fails when the RPC service or other services on which it depends is disabled or corrupted. The error was especially common in 2015 after the release of an incorrectly working Windows 10 update. Today, such an error almost certainly means a conflict between installed programs and standard Windows 10 programs or corrupted registry entries that we have to fix.
Ways to eliminate the error “Failure on remote procedure call”
First, make sure that the service and all the components it relies on are up and running as expected. Then we will try to remove some potential software incompatibilities.
Service check
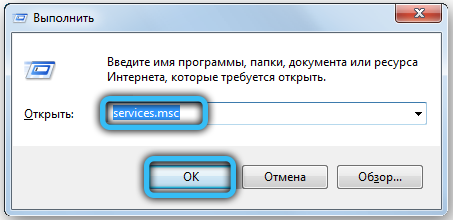
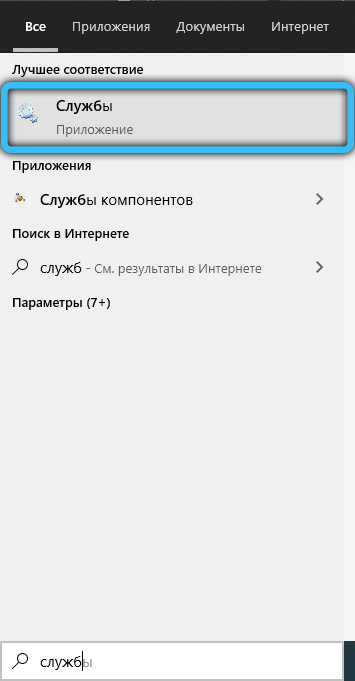
If a remote procedure call fails on Windows 7, open the list of services in this way: “Start” → Run → write services.msc , press Enter. In Windows 10, the service name can be entered into the search bar on the taskbar.
A fairly long window of services running on the computer will open. We are interested in four services:
- Remote Procedure Call (in English the service will be called “Remote Procedure Call (RPC)”) – the status of the service should be marked “Running”, and the startup type should be “Automatic”. If there is something else there, click on the line twice – in the window that appears, it will be possible to enable the procedure and select the automatic download type. If you cannot set the values, first check the next two processes below.
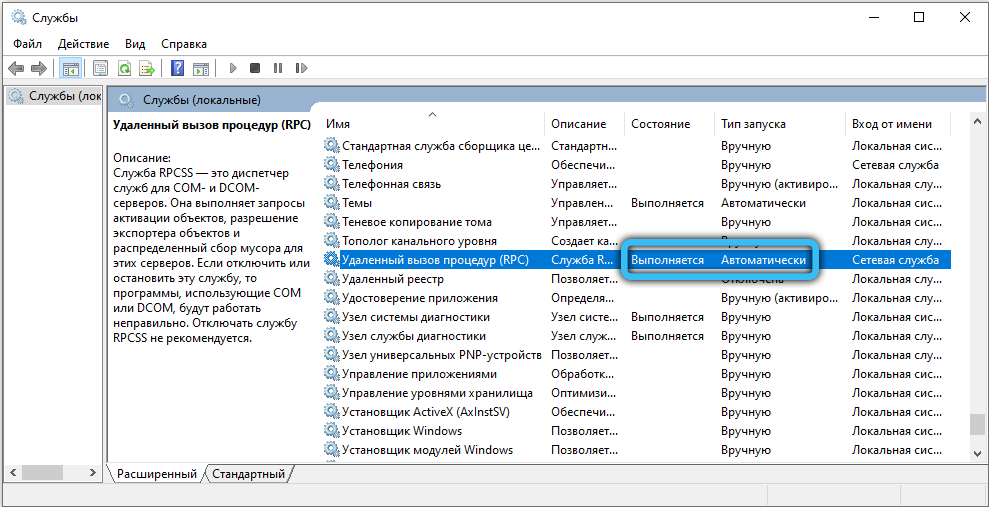
- DCOM Server Process Launcher – must be enabled, startup type “Automatic”.
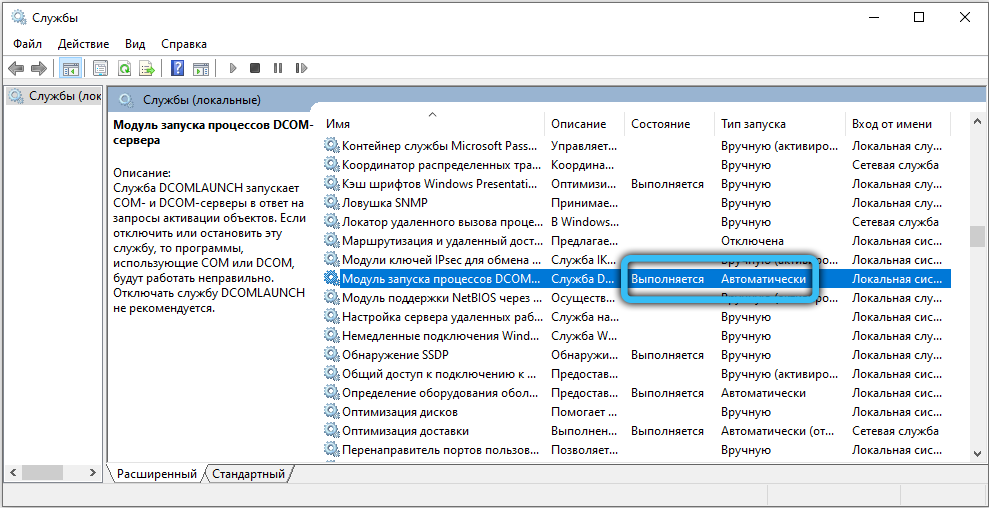
- RPC Endpoint Mapper – Likewise.
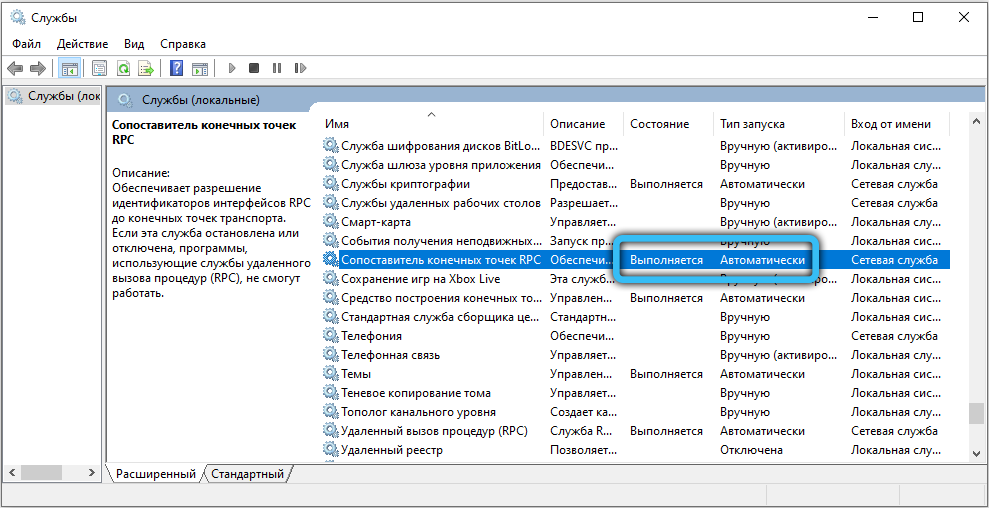
- Remote Procedure Call (RPC) Locator – The trigger type here must be Manual.
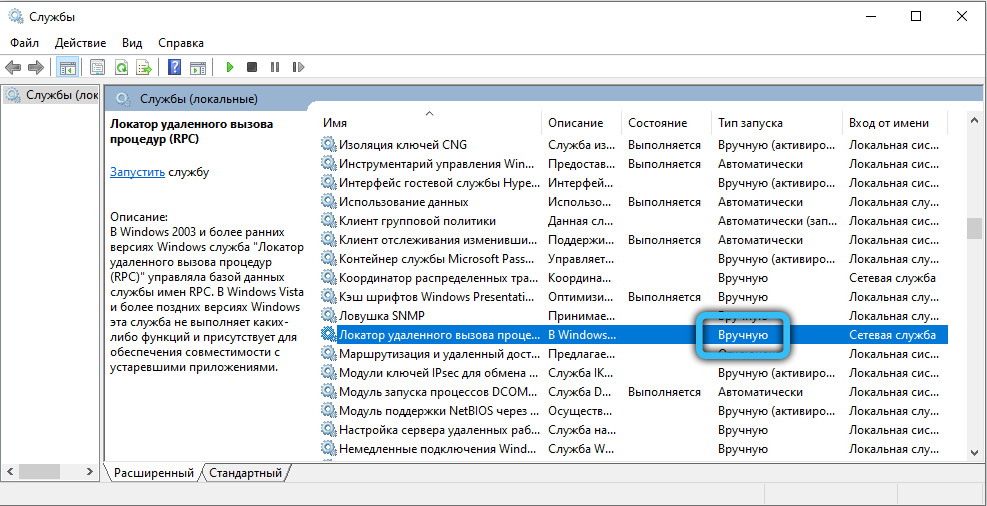
If we suddenly change something, restart the computer and check again for an error. Is the error still in place or are the services refusing to turn on? Let’s try to fix the situation through the system registry.
Editing the system registry
The Registry Editor opens in the same way as the list of services, but you will need to write the word regedit . We find there the branch HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE SYSTEM CurrentControlSet Services. Just in case, before starting editing, right-click on it and export – if something goes wrong, the current state of the registry can be restored by double-clicking on the exported file.
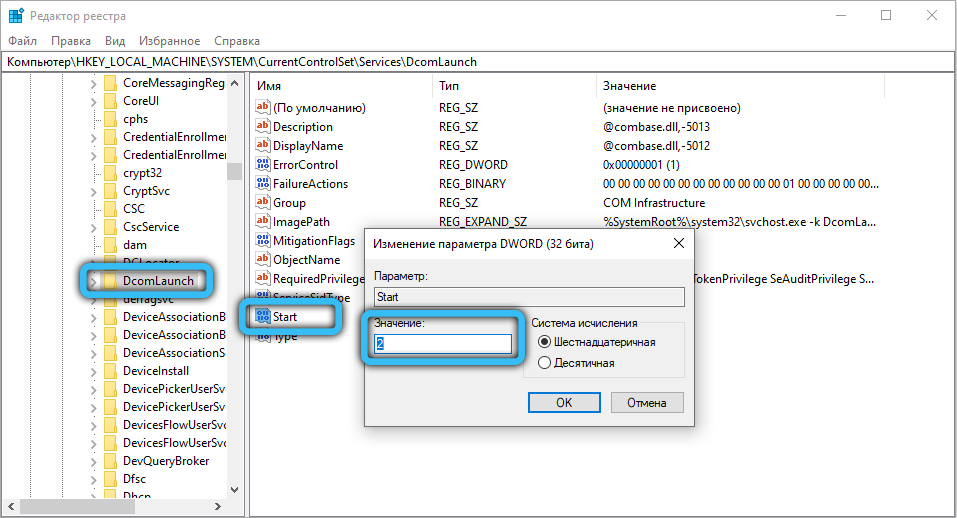
We make the following amendments to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE SYSTEM CurrentControlSet Services:
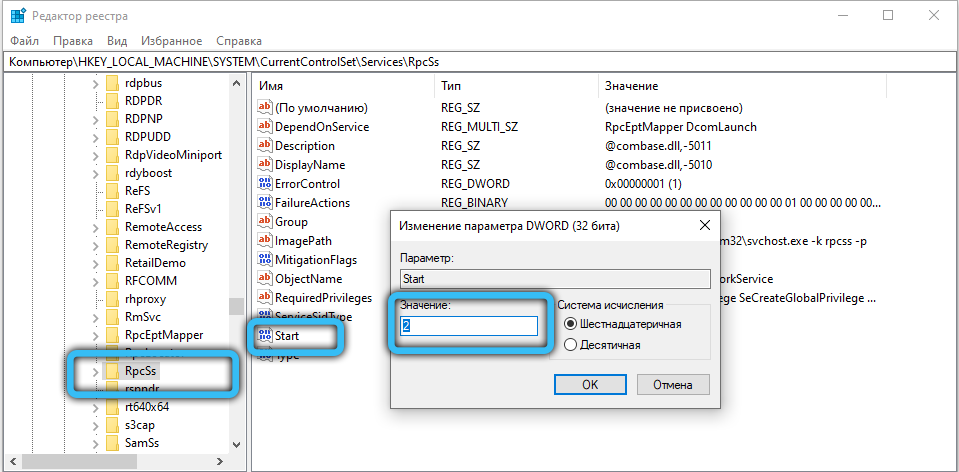
- in the DcomLaunch subsection, look for the Start key, double-click on it, set the value to 2;
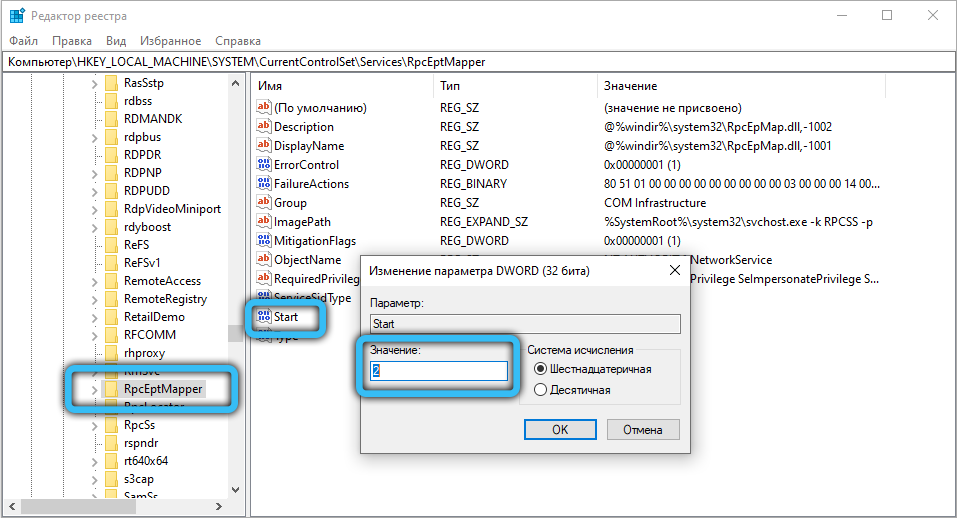
- in subsections RpcEptMapper and RpcSs – similarly;
- in the RpcLocator subsection, the Start key must have a value of 3.
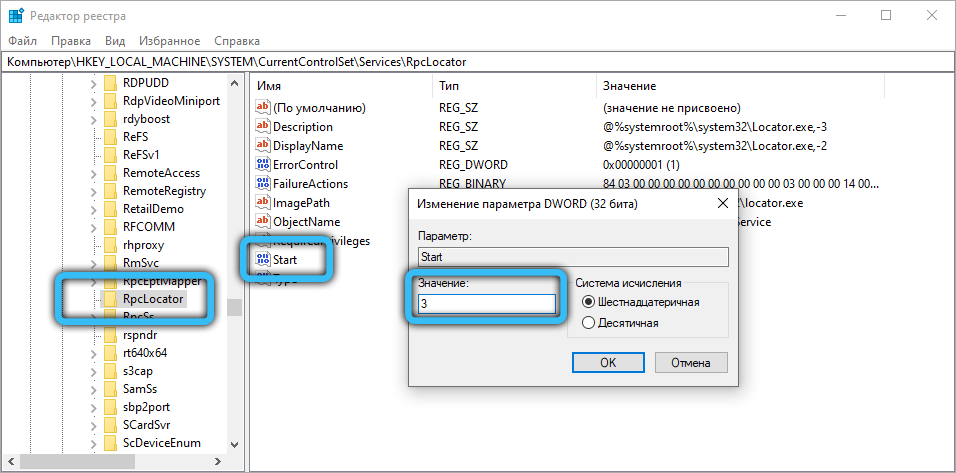
We do not touch anything else, save the changes and restart the computer. If the problem was related to incorrect start of services, it will disappear.
Check for software incompatibility
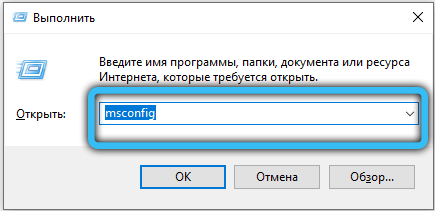
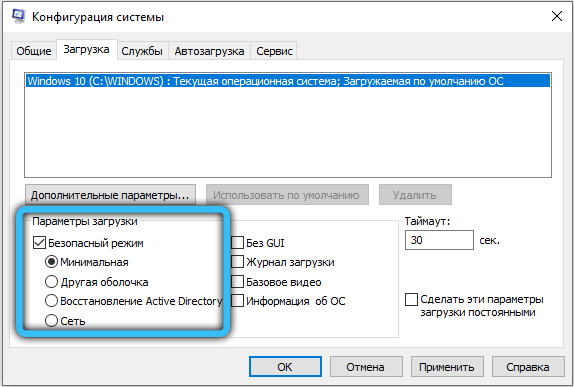
If all services work as usual (and did not turn off themselves after a reboot, check), it makes sense to look for and remove incompatible software. First of all – boot into safe mode: open the msconfig service (via “Run” or the search bar, depending on the system) and on the “Download” tab, check the corresponding option. After the next reboot, the system will turn on without the usual startup programs and with a minimum set of drivers – check if the error appears in this mode. If not, Startup will need to be cleaned up.
In Windows 7, this is done through the same msconfig service . In Windows 10, in principle, you can go there, but you will be redirected to the Task Manager, which manages this function on the new OS. The task manager can be invoked with the keyboard shortcut Ctrl + Alt + Del.
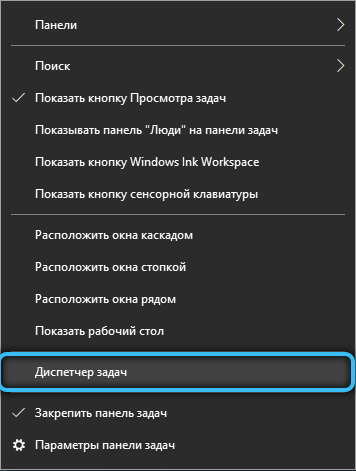
Go to the “Startup” tab and remove all programs from there. Then add back one at a time and reboot after each add until you find the program causing the conflict. Often these are antiviruses and file backup programs (Comodo BackUp, etc.). It is recommended to uninstall conflicting programs or at least use analogs that do not cause problems.
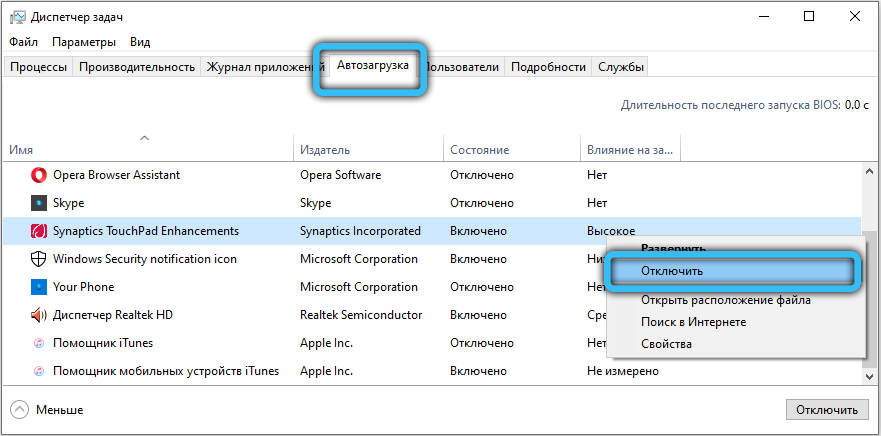
Checking and repairing system files
You can use the SFC and DISM utilities to troubleshoot system file problems.
Open Command Prompt as administrator: Start → Accessories → Command Prompt (Windows 7) or type cmd into the search bar on the Taskbar (Windows 10). To run as administrator, right-click on the program name and select the appropriate option from the context menu.
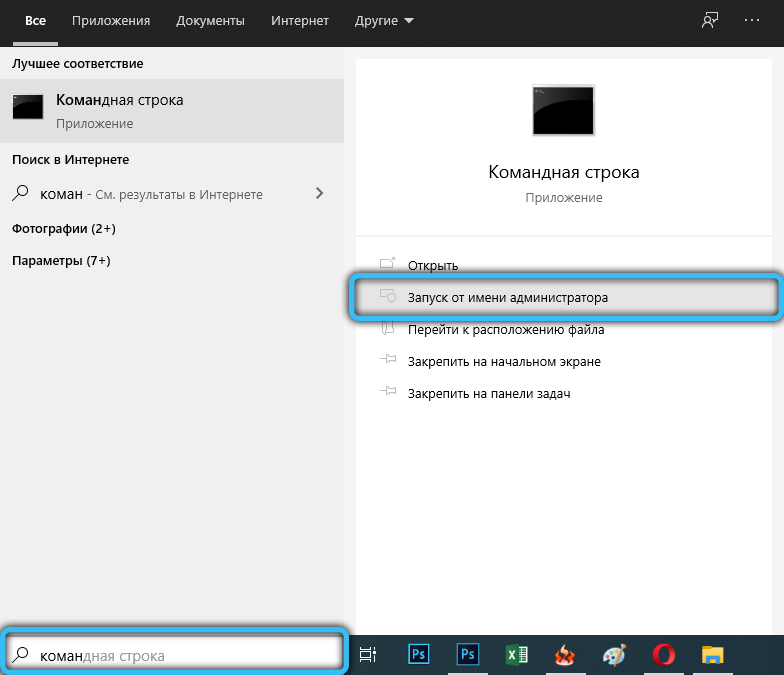
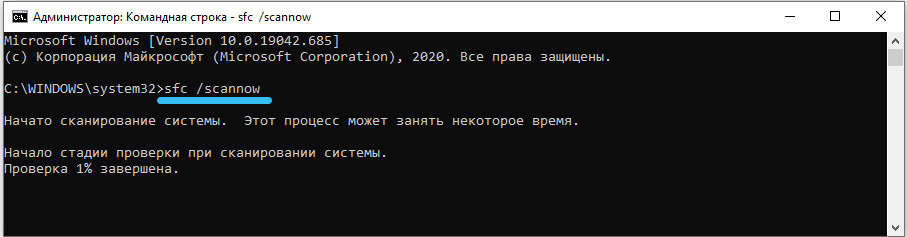
In the black window that appears, enter to start:
sfc / scannow
This command will check the main system files and try to restore them if it sees something wrong with them.
On Windows 10, there is a Deployment Image Servicing and Management (DISM) utility that allows you to repair files if sfc suddenly does not work.
There are two teams to choose from:
- DISM / Online / Cleanup-Image / ScanHealth – will scan system files and report possible errors.
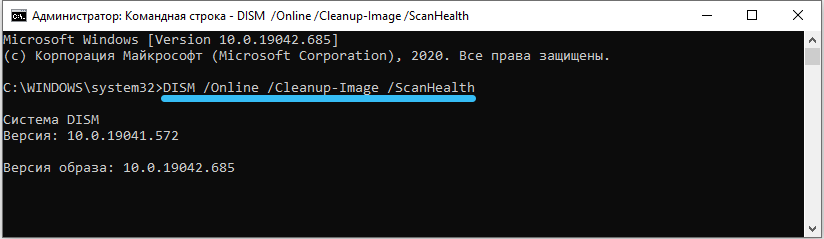
- DISM / Online / Cleanup-Image / RestoreHealth – will try to fix these errors.
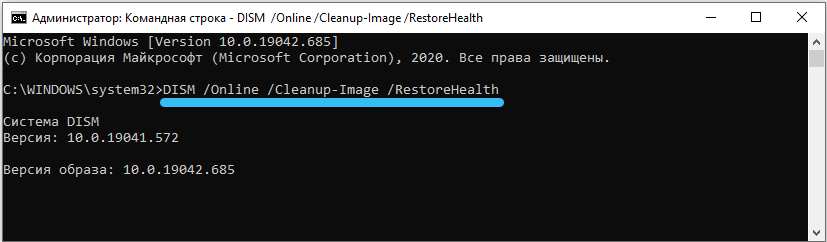
We enter commands in the same way as sfc, do not forget about the spaces before each “/”. After the completion of the repair, we reboot.
If “Remote Procedure Call Failed” occurs here (usually with error code 1726) – check if all RPC services are running as described above. Temporarily disabling Windows Search may also help.
If all else fails
The last resort before reinstalling the system is to try to create a new user. In Windows 10, the option is hidden far enough away: Start → Settings → Accounts → Family and other users. All system settings for the new user will be set by default, and the software conflict, if any, will disappear. In Windows 7, a user can be created here: “Start” → Control Panel → User Accounts.
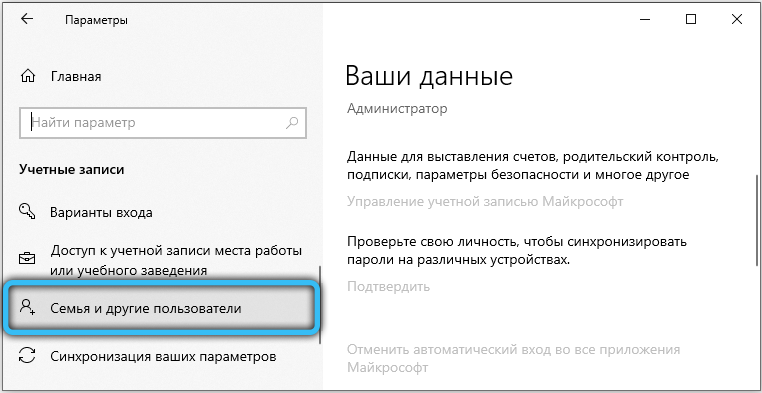
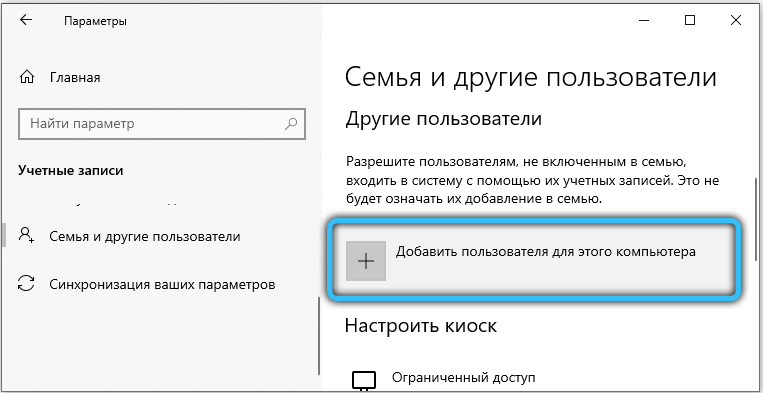
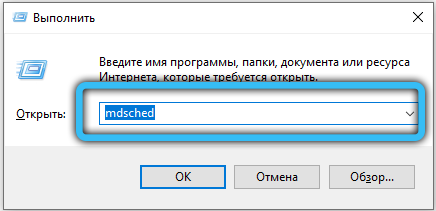
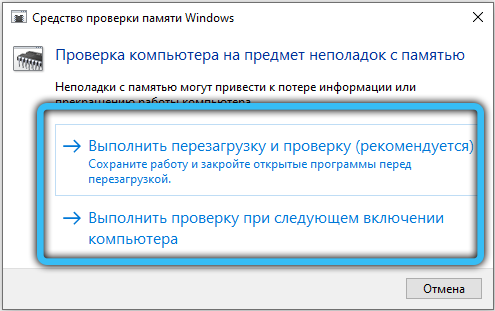
If the problem persists even on a new account, it is most likely a RAM defect. The memory can be checked by the standard Windows tool – the mdsched service . Verification can take several hours. Memory errors, if any, will not disappear after the check: you will have to reset the “overclocking” if you changed something, and in the worst case, change the RAM.
Did this article help you fix the annoying RPC service error? Maybe some of your own method, not described here, helped you? Share your thoughts in the comments – we will definitely answer you.