Modern computer games are inconceivable without the use of sophisticated technologies, on the basis of which effects are developed to improve the quality of the picture. This process can be called endless – the improvement of the technical base is accompanied by an adequate increase in the monitor resolution, so the struggle for pixels and PC resources does not see an end in sight. On the other hand, “in circulation” there is a significant amount of outdated technology, the owners of which have to solve very serious problems to find a compromise between the quality of the picture and the speed of drawing. Anisotropic filtering is an effect aimed at improving quality. But at what cost is this achieved?

What is anisotropic filtering for games
The term anisotropic filtering (AF) refers to a technique used in 3D graphics calculations that improves the rendering quality of textures on surfaces located at an angle relative to the player / viewer.
Let’s try to figure out what the use of anisotropic filtering means in terms of the technology used.

The principle of AF operation consists in a pixel-by-pixel analysis of the area of the rendered texture and the construction of a template based on the results of the calculations performed with its output to the monitor. At very large angles, each pixel can cover an area that is involved in a large number of adjacent areas of the texture, which is why anisotropic filtering is quite computationally intensive. And even the use of such advanced technologies as texture data caching is not able to significantly reduce the consumption of video memory when using AF.
Individual video card manufacturers develop their own filtering algorithms, optimized for drawing general geometric outlines typical for games (walls, corridor, sky, floor).
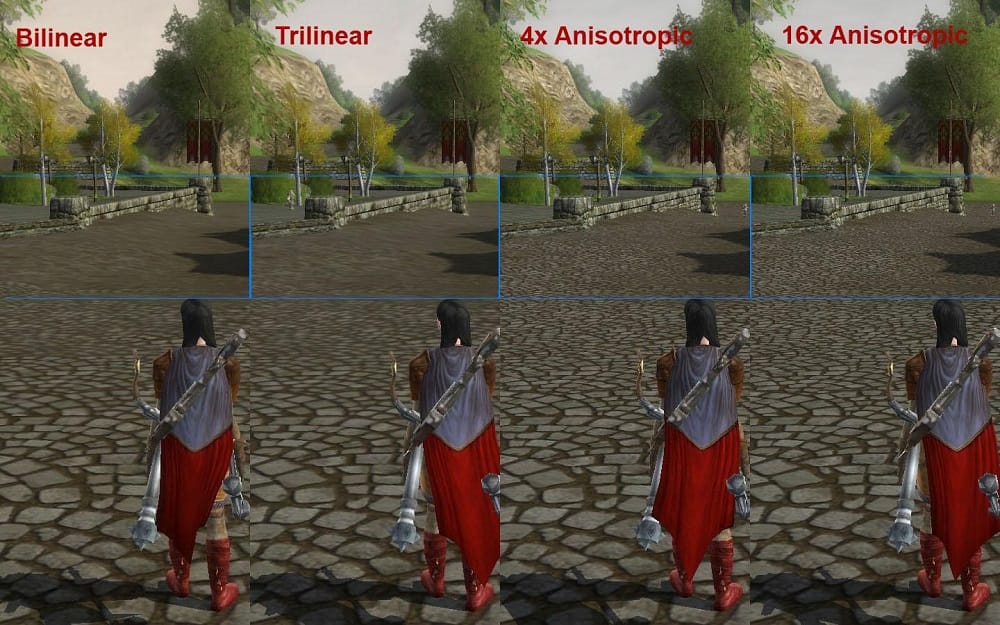

What does anisotropic filtering give in modern games? First of all, it removes the aliasing that is typical for oblique textures. This refers to the pixelation of the image in such areas. An additional AF effect is to smooth out the blurring of such textures, which is especially noticeable in comparison with other types of filtering, for example, trilinear and bilinear. Note one more important feature of anisotropic filtering: it concerns only texture rendering on the form, but the form itself remains unchanged.
From the above, you can understand why anisotropic filtering technology is needed in games: it allows you to achieve greater picture detail. Due to the need for large amounts of computing, AF has become available in the mainstream video card category since about 2004, although advanced graphics adapters have been able to use this technology since the mid-90s.
It can be activated either in the video accelerator settings, and we will tell you how to do it, or directly in the application you are using, most games have this option in the settings.
The only parameter that can be changed when using AF is the filtering coefficient, which takes one of four possible values (2x / 4x / 8x / 16x). What are meant by these ratios? This is the number of adjacent texels processed (the number of pixels per scene size), for which the color is averaged. It is clear that the lower the indicator, the worse the effect will manifest itself, but since anisotropic filtering creates a considerable load on the equipment, the choice of the optimal parameter value should be approached carefully, taking into account the power of the video card. The only point I would like to clarify is that there will be little difference in performance between 8x and 16x, so the latter can be recommended as preferred if you want to get the perfect picture.especially without risking the speed of drawing.

So, we found out what anisotropic filtering affects: the performance (fps) of frame rendering and its quality, and since NVidia and AMD use the same AF algorithm, it doesn’t matter which brand of video card is installed on your computer. The main thing is how powerful it is.
If you are playing a computationally demanding game on a weak computer, the color anti-aliasing mode will bring you more inconvenience and frustration than practical use.
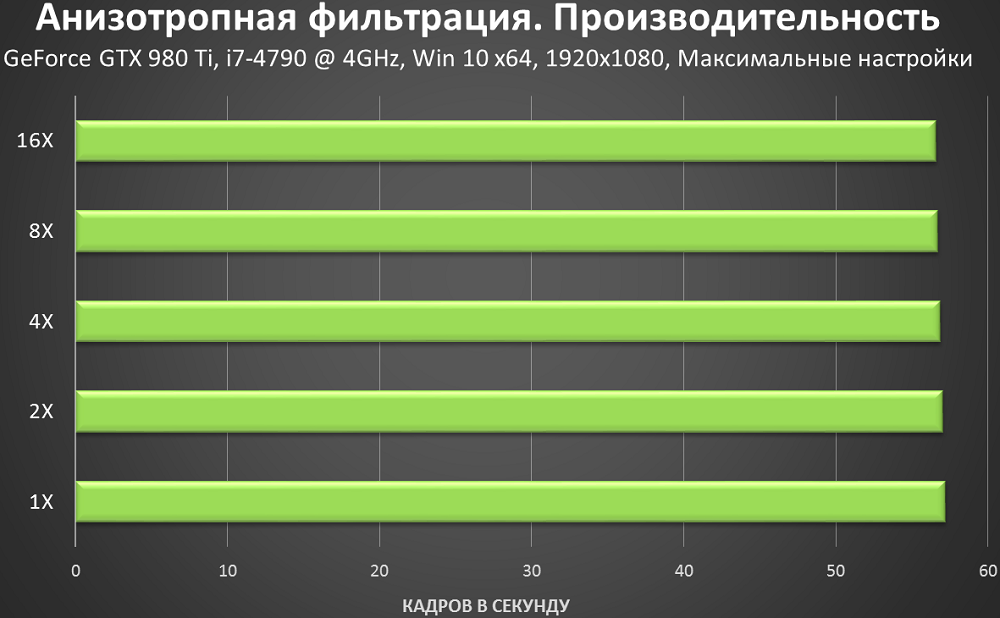
From a practical point of view, using 8x and 16x coefficients with anisotropic filtering will allow you to get less noticeable color transitions when approaching an object than with lower values of the parameter. On the other hand, with a sharp acceleration of the object or the rotation of the camera, pixelation at the joints of textures cannot be avoided.
How to enable anisotropic filtering mode
If you have a Radeon video adapter installed, right-click on an empty area of the desktop and select “Radeon Settings” in the context menu that appears.
If you have the proprietary AMD Radeon Software utility installed, just run it. Then go to the “Settings” tab and select “Video Card”.
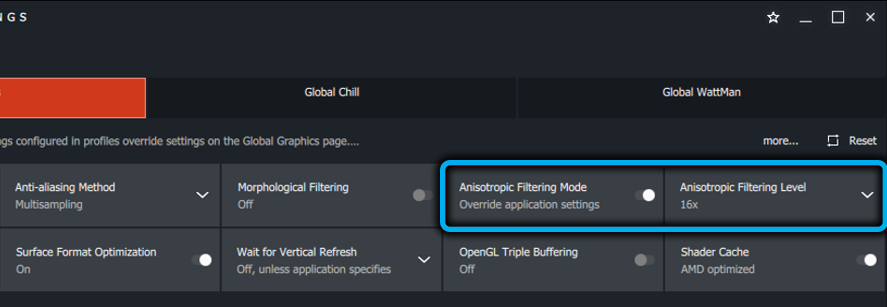
The list of available effects will include “Anisotropic Filtering”. To enable it, you need to move the slider to the appropriate position, and then the AF parameter selection will become available, from 2x to 16x.
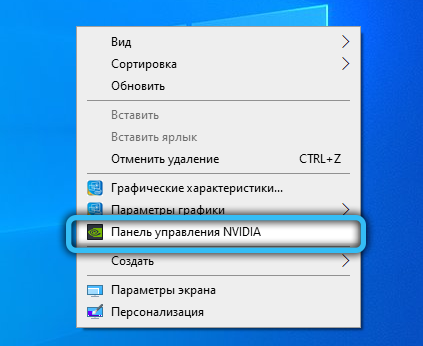
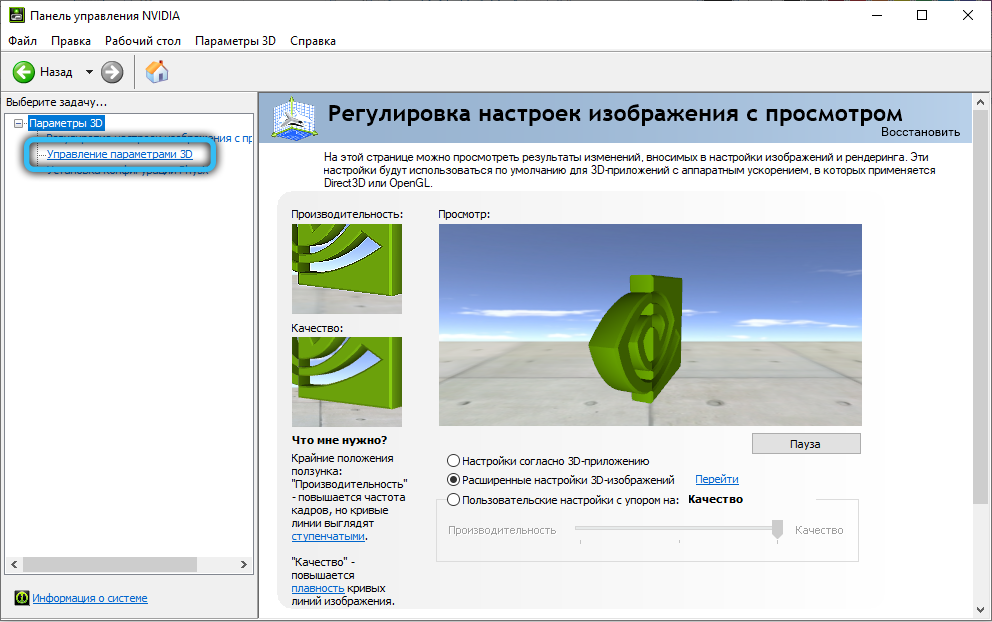
For those who have an NVIDIA video adapter, open the NVIDIA Control Panel, select the 3D Settings tab and select the 3D Settings Management menu item.
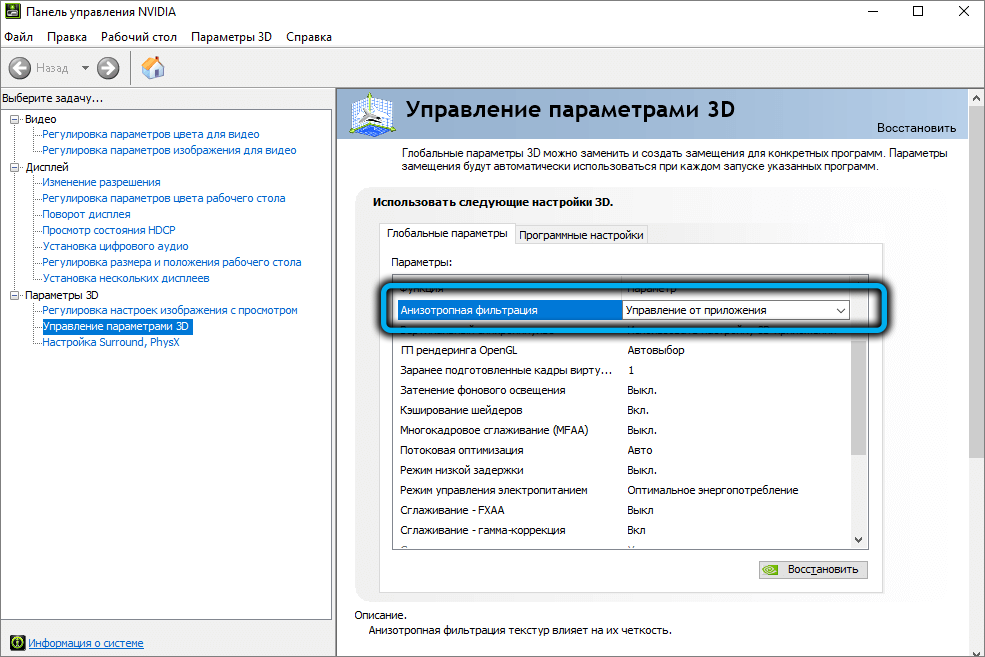
A window with a list of global parameters will open, in which you need to find Anisotropic filtering and enable it. It is also possible to activate AF for individual applications, also present in the list, and this is the mode that is used by default.
You can turn off anisotropic texture optimization in a similar way.
Conclusion
With a sufficiently powerful hardware, the use of AF is clearly shown, especially in games with a large number of oblique textures and objects. In this case, an elongated pixel image without anisotropic filtering will appear with a noticeable ladder, especially when approaching an object. If AF is selected instead of bilinear, the color smoothing will result in a better picture.
What’s the best level of anisotropic filtering? Depends on several factors, first of all – the performance of the hardware and the complexity of the application, how high its system requirements are. You can experimentally establish in which game it is better to use AF, in which – bi- or trilinear. As you gain experience, you will be able to “automatically” determine the optimal mode for a particular game.
And finally, here are some practical tips for the types of games in which the use of anisotropic filtering will be useful. These are shooters, especially first-person shooters, races, or various simulations. They are characterized by dynamic landscapes with an elongated perspective on a stretched terrain.
You can not turn on AF in sports simulators or strategies, where all the action takes place against a static background that occupies most of the monitor.