Owners of computers with powerful video cards do not always actively study its settings, but for gamers, especially those who prefer network or e-sports games, it is vital to understand the parameters of the Nvidia control panel. Among other items on the “Manage 3D Settings” tab, you can see an item entitled “Low Latency Mode”. Sometimes even experienced users are not able to clearly explain what he is responsible for, and even more so – how it works. Today we will try to deal with this parameter.
What is this mode
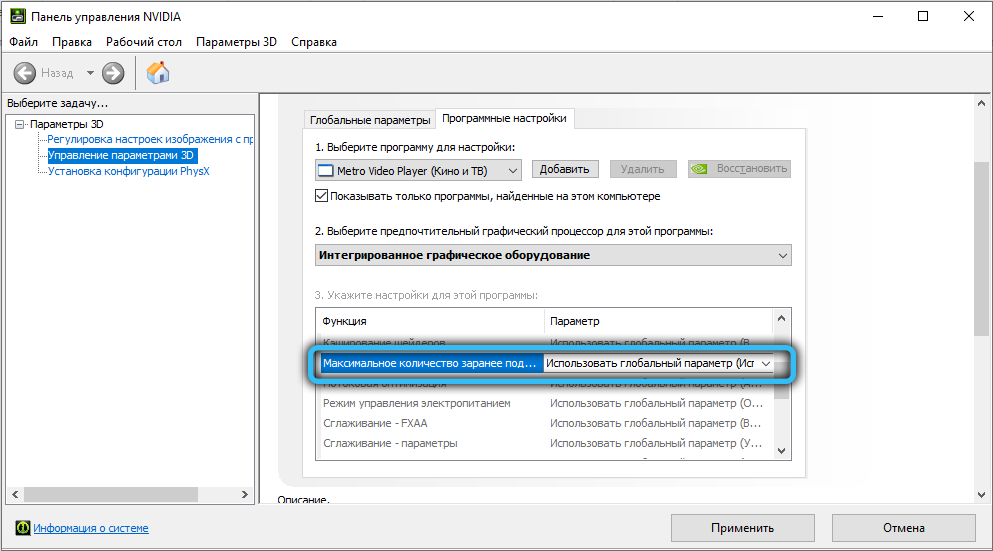
If you have an integrated graphics card, you hardly need to read this article. The fact is that the specified menu item appeared in the driver version starting from 436.02, and it is intended only for sufficiently powerful graphics accelerators. On older versions of the Control Panel, there is also a delay control mode, but it is called the “Maximum number of pre-rendered frames” and has values in the range of 1-4. In the low latency mode, numerical parameters gave way to symbolic ones, while it became possible to set the number of prepared frames to zero (“Ultra” mode).
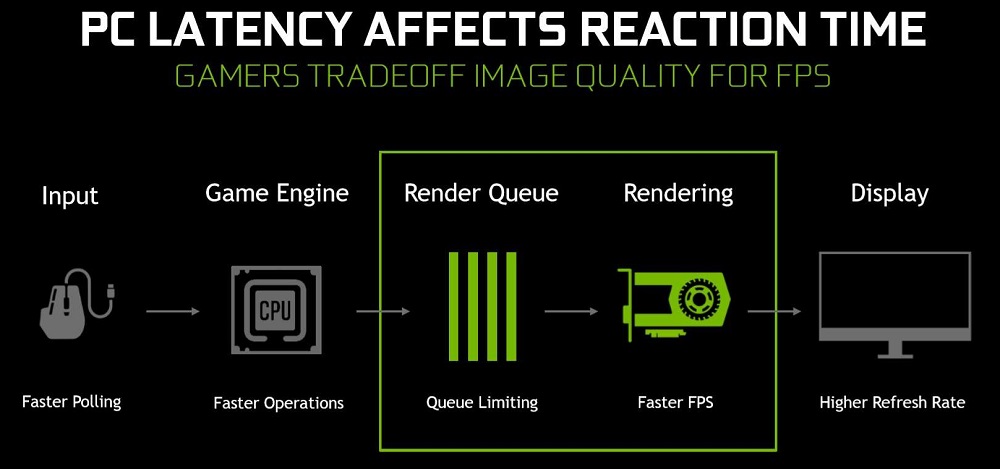
By default, the mode is disabled, which means that the parameter is controlled at the level of the game engine (graphics application). But what does the term “low latency” itself mean? The fact is that the video card, rendering (rendering) frames, takes on all the basic calculations necessary for the correct display of a picture described not by a simple set of pixels, but with the use of various effects and algorithms that require preliminary calculation. But the central processor also interacts with the graphics processor, preparing from one to several frames for it. If for some reason there is a delay during the transfer of information from the processor to the video card, we will observe a lag on the monitor, or a short-term freeze of the game process. There can be many reasons for the appearance of a lag,however, if you try to enable the ultra-low latency function to get rid of the queue of frames prepared by the central processor, you can get rid of such lags.
When you may need to turn on the mode
Zeroing the queue reduces rendering latency, but this will not affect the FPS parameter (the number of frames per second processed). In other words, activating the low latency mode does not lead to an increase in bit rate, rather the opposite. The main function of the parameter is to avoid the appearance of lags, which may appear at the stage of forming the CPU queue of frames waiting for processing by the GPU.
Micro-lags in a regular game only lead to certain inconveniences, but for network games, where every millisecond affects the final result, even minimal delays can be very expensive. Imagine that you are aiming, and you seem to have done it correctly and have already pulled the trigger, but at this moment there is a lag, and the next moment the enemy is no longer at gunpoint, but the shot is fired.
Of course, modern video cards are able to automatically adjust the queue latency depending on the situation with the load on the GPU / CPU (for this, the Reflex SDK is used), but sometimes they cannot cope with this, and then it is worth enabling the low latency mode manually. This happens especially often in online esports games like Dota / CS. As noted by the developers from NVidia, the real effect will be noticeable provided that you use an FPS of at least 60.
Setting this parameter to Ultra, that is, zeroing the queue, will allow you to transfer frames from the central processor to the video card chip just in time. In other words, the GPU will receive them exactly when it is needed for rendering.
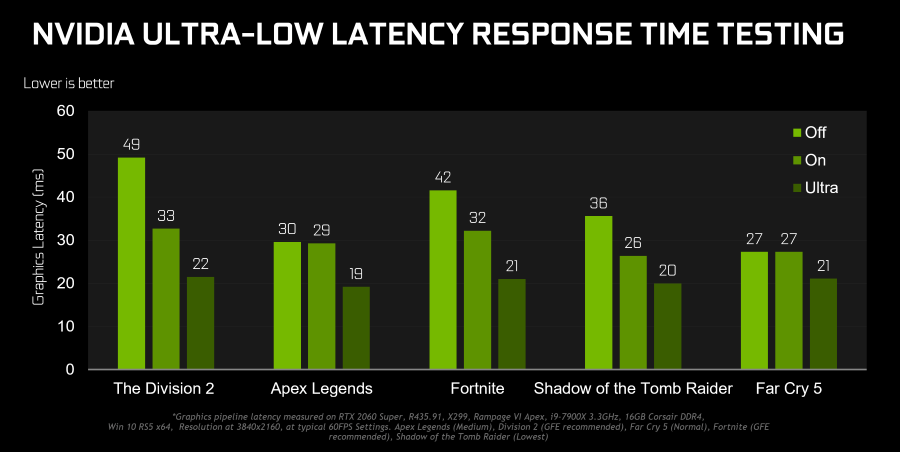
The above graph clearly illustrates the above. Here are the values of delays (lags) when displaying frames in milliseconds for some popular network games. Disabled mode (by default) is displayed in a lighter shade, Ultra mode – shaded. You can see that in some cases it is possible to achieve a decrease in game latency by 27%, and this is already a good result.
Whether you need to enable Low Latency Mode is up to you. If lags are present, it is worth trying, but one hundred percent result is not guaranteed. In any case, you can always set the default value, that is, Off.
Of course, the use of this function is associated with many nuances that you need to be aware of. We have already mentioned the limitations on the part of the video card – on those where the latest version of the driver has a number below 436, full zeroing of the queue will not be available, you can only adjust the number of prepared frames from 1 to 4.
The second limitation concerns applications – the game engine must support DirectX 9/11. If the Vulkan / DirectX 12 API is used, this feature is also available, but in the game settings, and not in the NVidia Control Panel.
Another limitation is related to the central processing unit. If it’s weak or heavily loaded with something else, buffering delays cannot be avoided, no matter what you put in low latency mode.

When we said that enabling the mode does not lead to an increase in FPS, we were not entirely right: in fact, there is a dependence, but it does not always manifest itself and it is unambiguous in the direction of decreasing the number of frames. According to the developers themselves, it is better to enable ultra-low latency in cases where the FPS value demonstrates stability in the range of 60-100 frames / second. If the FPS is “floating”, the driver or game engine is better at managing the controls.
In any case, one should not expect miracles from the mode, because we are talking about millisecond delays, which often the human senses are not even able to feel. And when we talk about a 30% decrease in latency, you need to understand that in absolute terms, at best, the gain was 20 milliseconds (two hundredths of a second). However, this is quite enough to prevent the appearance of microlags.
How to turn on / off low latency mode
Many games have an engine that allows you to manipulate the latency value in the parameters.For example, CS: GO also has a low latency mode, like in many other modern gameplay.
But we are considering the corresponding parameter of the “Control Panel” of NVidia, so we will describe how to enable the mode here.
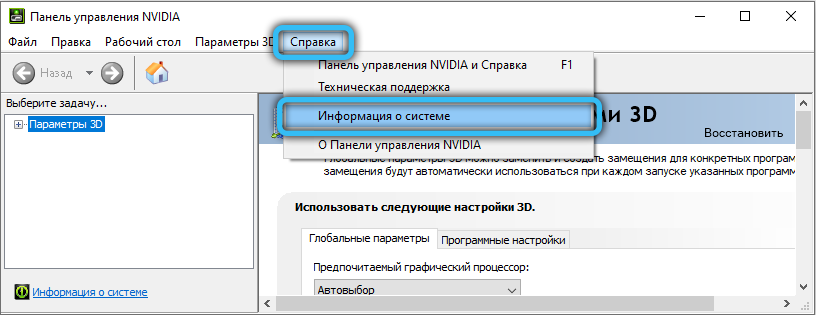
First, determine the current driver version, it must be at least 436.02 (menu item “Help”, sub-item “System Information”). If a driver update is required, use the GeForce Experience utility, an alternative way is to download the latest driver directly from the official NVidia website.
So, here is a step-by-step algorithm for activating the low latency mode using the NVidia Control Panel:
- right-click on an empty space on the desktop;
- in the context menu that appears, select the item “NVidia Control Panel”;
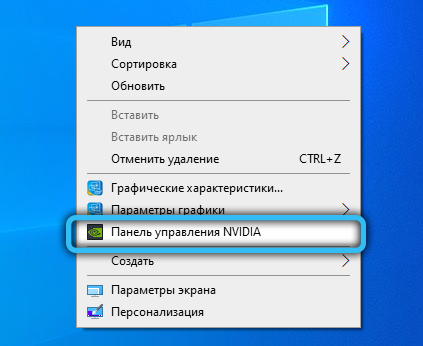
- in the right window in the section “3D parameters” select the sub-item “Manage 3D parameters”;
- a block will appear on the right, which will contain the parameters for controlling 3D graphics with two modes, “Global settings” and “Program settings”. The first mode allows you to set parameter values for all games and applications, the second – for specific games. In general, it is recommended to use low latency settings for specific games;
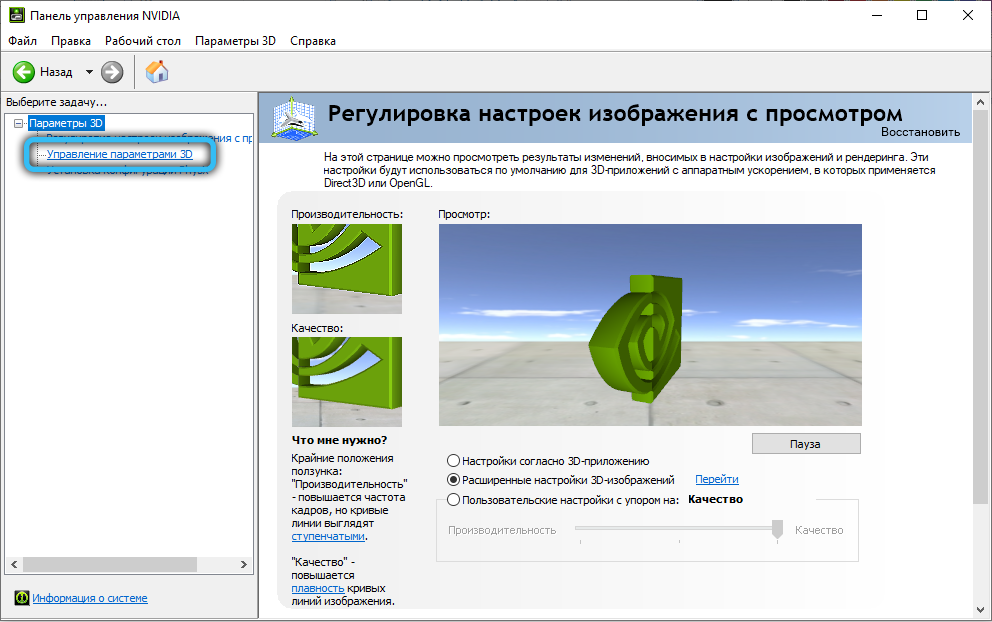
- so, click on the “Program settings” tab;
- step 1 will display a list of applications for which you can change the settings. Choosing the game you want;
- in point 2 we are looking for the item Low Latency Mode (or in Russian – “Low latency mode”);
- by default, the parameter value is set to “Off”, which means that the engine of the selected game will independently determine the optimal number of frames in the CPU buffer within values from 1 to 3;
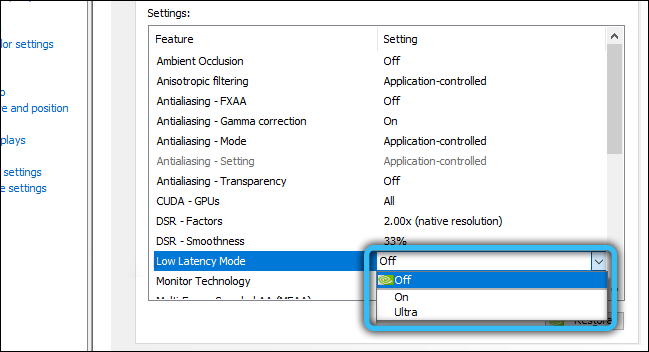
- if you select the “On” mode, the queue will consist of only one frame;
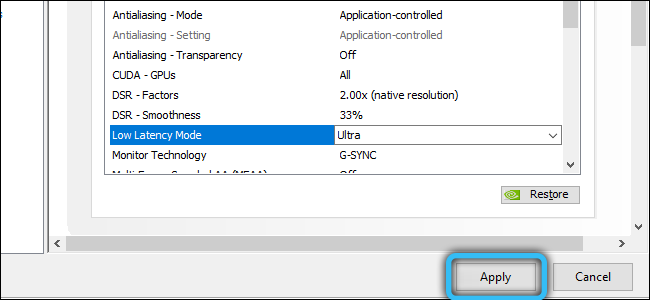
- enabling the “Ultra” mode will reset the queue, and the video chip will take a frame in real time;
- all that remains is to click on the “Apply” button and try to start the game to make sure that it is effective or not when the mode is on.
In older video cards, instead of the “Low latency mode” there will be a “Maximum number of pre-rendered frames” mode, which will not allow you to get rid of the queue, you can only manipulate the number of frames in the CPU buffer
In conclusion, we note that to measure the performance of the graphics adapter in games, you can use a variety of tools, for example, the already mentioned GeForce Experience utility.