Extraneous noise, hiss and crackling in the headphones significantly reduce the sound quality, making listening to content uncomfortable. Such a phenomenon may be the result of various factors, and the user who encounters a problem will have to find out the cause by enumeration of solutions.
The noise in the headphones does not always indicate a malfunction of the devices, so you should not immediately write off even new equipment. Although the reasons are usually not obvious, you can solve the problem on your own without resorting to the help of specialists.

When starting to eliminate the phenomenon and figuring out why the sound is wheezing in the headphones, the primary task is to determine what exactly is causing the noise – the listening device or the sound source.
Often the problem is an incorrect connection, incorrect settings, or lack of contact when connecting, which can manifest itself for a number of reasons. If the sound wheezes and lags in headphones connected via Bluetooth, the most common cause of distortion is dead batteries, incompatibility of pairing devices via Bluetooth, or incorrect drivers.
Contents
Equipment check
Start looking for reasons if the sound in the headphones began to wheeze, you should start with the simplest thing: checking the health of the headset and connecting to a sound source. Connectors and plugs must be kept clean to ensure good contact and no interference. The need for visual inspection is also present in the case when the devices do not require wires.
Mechanical damage
We inspect the headset for damage or creases in the cord. Most often, wired devices are damaged at the points of connection with the plug and other elements (control buttons, microphone, ear pads).
If no external flaws are found, we connect to another device and see if the problem has disappeared, thereby finding out what creates it. Further actions to identify and eliminate the cause will be directed to work with headphones or a transmitting device.
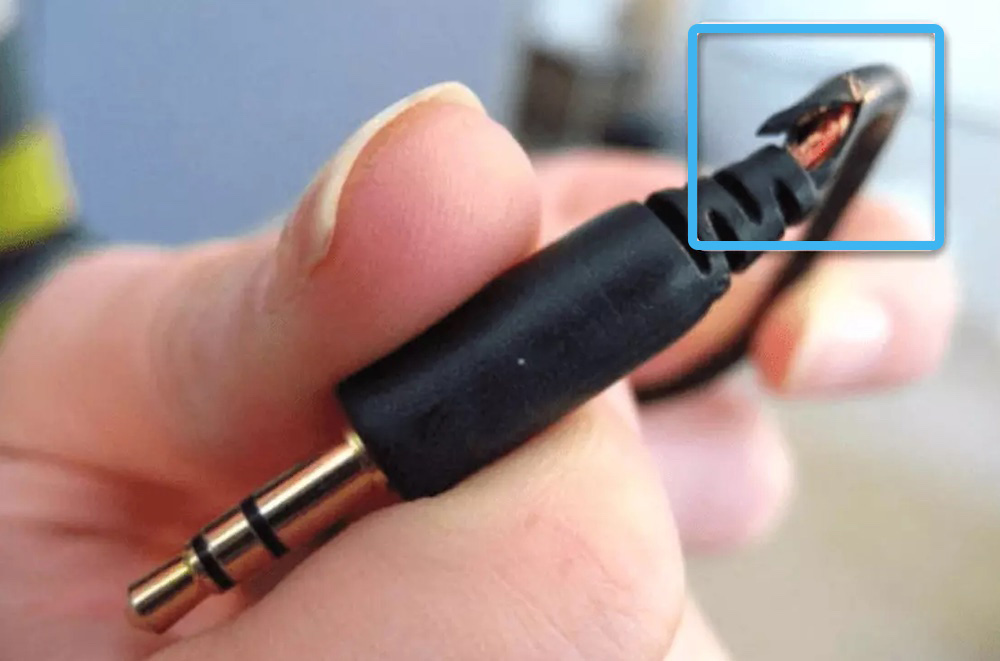

If there is a malfunction in the headset, the place of contact break in the cable can be found by bending the cord at the connection sites. When contact appears, when the parts of the core are connected, the sound will become clear. To return the device to working condition, it can be repaired at the place of damage or you can buy a new one, which is most often more advisable.
Audio jack failure
The computer most often has two inputs, one of which is located on the sound card and is located on the back of the case. You should check the serviceability of the connectors by connecting one by one to each of them. If the sound is worse when connected to the front audio input, you should connect to the connector on the back of the system unit.

Sound card malfunctions
Rarely, but it happens that the problem lies in the incorrect operation of the audio card. Sound card malfunctions prevent normal signal processing, causing the sound reproduced by the speakers to suffer.
If all the methods have been tried and had no effect (including installing fresh drivers), it is worth checking the equipment. The task is accomplished by disconnecting the board and connecting another one. If a breakdown is detected, it may be necessary to replace the defective element.
The audio card built into the motherboard cannot be removed for connection with another device, as an external one, therefore, in this case, the search for the source of interference is performed by disconnecting the internal components of the system unit from the card. All elements without which the computer cannot work will be turned off one by one.
Dead battery on headset
If you use Bluetooth headphones, the sound often wheezes and is due to low battery power. The sound in the speakers may be distorted, sound quieter or with noise in the background due to a lack of energy for normal reception and transmission of the signal.

To ensure battery life, you need to regularly charge your wireless headphones. To check the quality of sound reproduction, you will need to fully charge and reconnect to your computer.
Bluetooth incompatibility in devices
Poor sound quality, which is characterized by interruptions, interference and other extraneous noise, may be caused by Bluetooth incompatibility between the headphones and the transmitting device. Moreover, it is not the versions that matter, but the codecs through which the signal is encoded.
The standard SBC codec used for all Bluetooth audio devices does not provide good sound quality. If one of the paired devices does not support the AAC, aptX, LDAC audio codecs (the latter is superior in quality to the others, although it also compresses content), which are necessary for higher sound clarity, the signal is transmitted using a standard SBC, which means that the signal quality suffers.
Driver Issues
Incorrect operation of hardware drivers (their absence, damage, irrelevance) often leads to distorted, lagging, wheezing sound in headphones or speakers. If the sound remains unacceptable when connecting various audio devices, this is most likely the case. You can check the software and update it to the current version using the system snap-in or special utilities.
In Windows, you can perform the task using the system tools:
- We go to the “Device Manager” (for example, select the tool from the “Start” context menu).
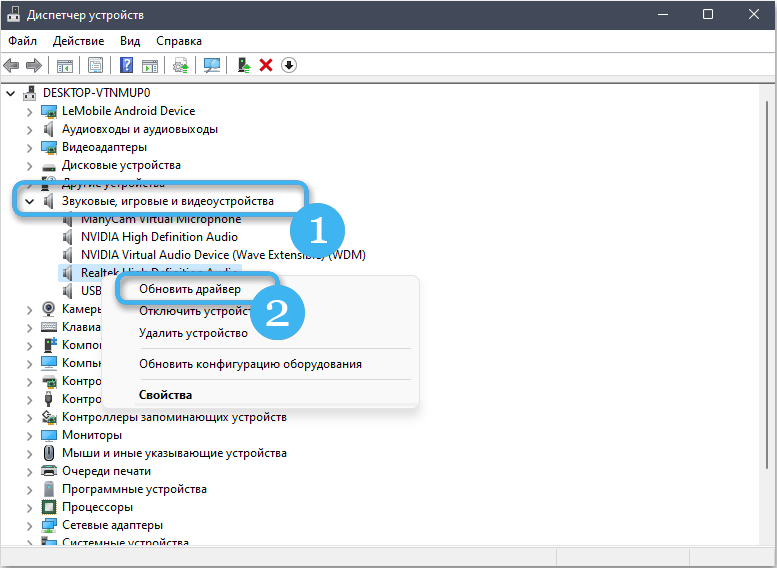
- Expand the “Sound, game and video devices” branch. If there is a yellow icon with an exclamation mark next to the sound card, the device needs to be updated. But even if there is no notification, it is better to reinstall the software.
- To update, right-click on the name of the sound card and select the appropriate item from the menu.
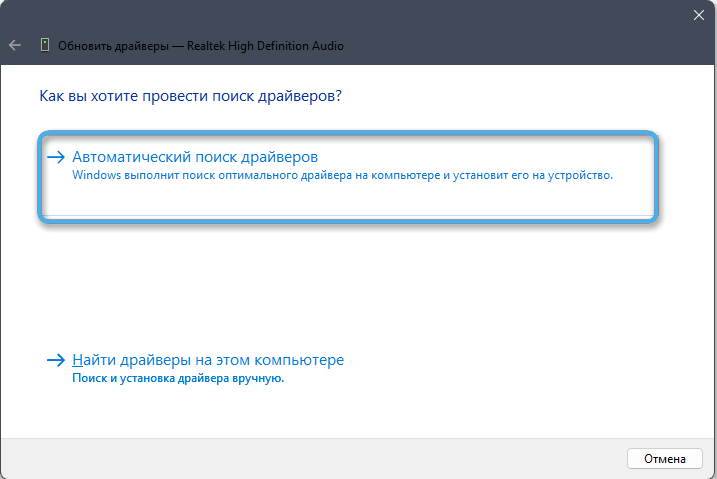
- There are two options for updating: automatic search by the system on the Internet and manual with the choice of the path to the file.
Wrong settings
In addition to Bluetooth connection problems, the relevance of drivers and hardware malfunctions, there are also software reasons on the side of the transmitting device that have a direct impact on sound reproduction.
Computer volume settings
An incorrectly adjusted volume can cause noise in the headphones. Increasing the volume threshold leads to a deterioration in sound, and when using low-quality inexpensive speaker models or a headset, the quality is lost already when it reaches the 50% mark, while high-quality headphones can wheeze at maximum volume. To fix the problem by reducing the load on the speakers, the volume on the transmitting device is increased, and the headphones themselves reproduce sound at a minimum of their volume.
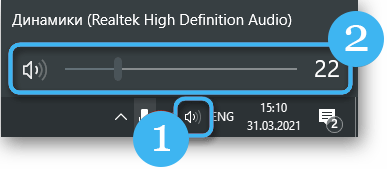
Sound management software also often provokes interference and noise. Volume controls in applications can be set to the minimum, causing the user to “squeeze” the maximum out of the hardware, which leads to a problem.
Additional sound effects and playback format
Enabled advanced sound options in Windows is another common cause of the problem. So, to get rid of distortion, sound effects need to be turned off. To deactivate, follow the steps:
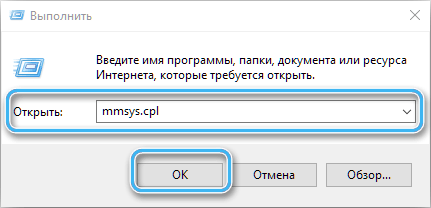
- open the Sound Device Manager (for example, by selecting the snap-in from the menu that pops up when you right-click on the sound icon in the tray, or through the Run console (Win + R) and the mmsys.cpl command);
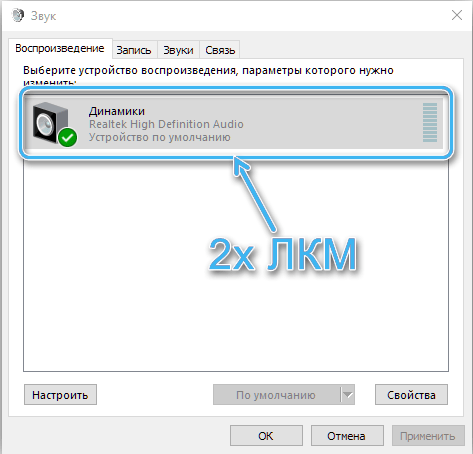
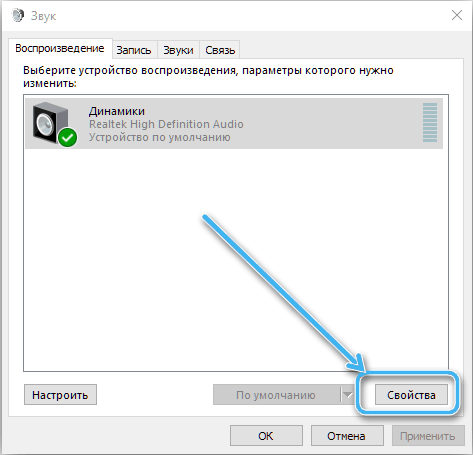
- on the “Playback” tab, select the sound device (speakers, headphones) and click the “Properties” button (or RMB – “Properties”);
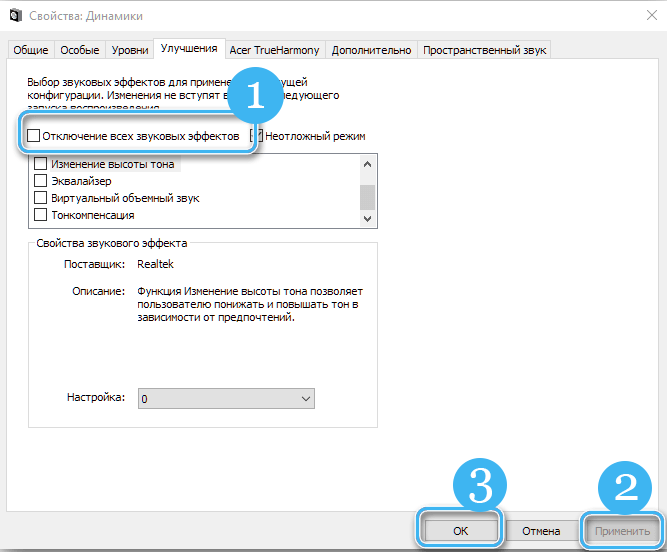
- on the “Improvements” tab, check “Disable all sound effects” and apply the settings;
- close the snap and reboot.
Sometimes noise appears due to incorrect output format settings. To make adjustments, you will need to go to the “Advanced” tab in the properties of the sound device and select “16-bit, 44100 Hz (CD)” in the “Default format” block to ensure compatibility with any audio card, confirming the changes.
Power saving mode
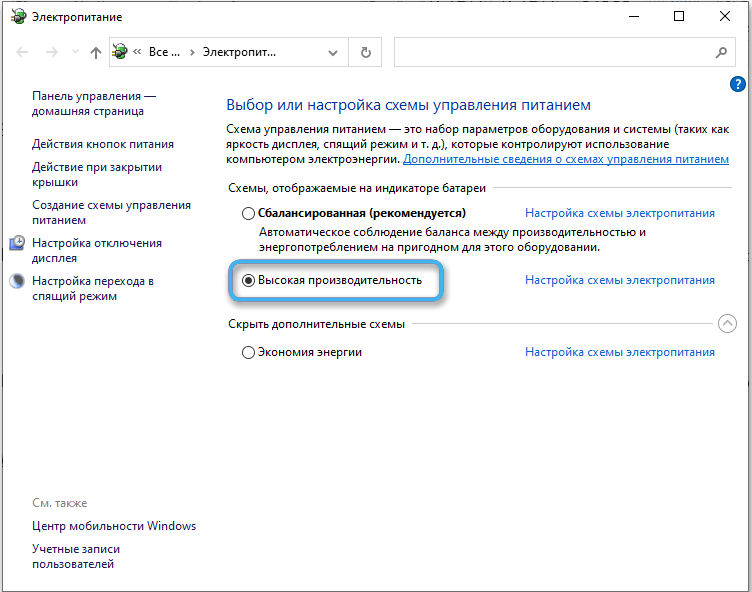
The problem caused by incorrect power saving mode settings is most common on a laptop, but can also occur on a smartphone or PC. When battery saver is enabled, the audio card is not prioritized and may run out of power. Then, in order to eliminate interference, you must select the “High performance” option in the device’s power settings (for smartphones, the battery saver mode is disabled). If the actions did not lead to the desired result, you can return the economy mode.
On a laptop, you can perform the task as follows:
- open the “Control Panel” and follow the path “System and Security” – “Power Options” (the window can also be opened by right-clicking on the battery icon in the tray and selecting the appropriate item from the menu);
- select high performance mode;
- save the settings and check if the problem has disappeared.
No grounding
Although infrequent, ungrounded sockets where the PC is connected can still cause interference. If the equipment has been checked and no problems have been identified, you should check for grounding, since power problems lead to more serious consequences than crackling in headphones.

Other devices causing interference
Noises, distortion of the sound transmitted to the speakers, may be the result of the operation of other equipment, including household appliances and even devices that are not in close proximity. Possible sources of the problem include:
- Turning on speakers near the headset may affect signal quality. The problem is solved by disconnecting them from the sound source.
- Any device that uses a Bluetooth connection. The solution is to disconnect them and reconnect the headphones.
- USB devices connected to the connectors of a computer or laptop (external drives, cameras, etc.). Extra devices should also be turned off.
- Computer accessories. You can find out which element caused the problem by turning off each one in turn.
- Appliances. Emission of electromagnetic waves can also reduce signal quality. The solution is the same: turn off the devices one by one.
- Cellular communication stations, TV towers nearby (relevant if the problem arose when using headphones on the street) often create interference, violating the purity of the sound.
Sound distortion when moving a computer mouse
If cods are created when moving the scroll wheel of the manipulator, you can fix the problem by connecting the mouse to a different port, by switching from USB to another type of PS / 2 connection or vice versa (you can buy an adapter), as well as changing the manipulator.

Active microphone
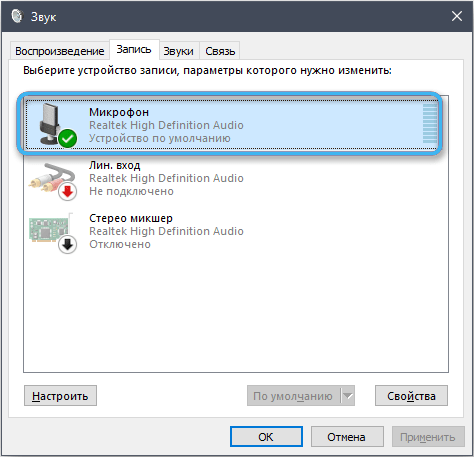
Even if the microphone itself is not connected, the microphone input can cause interference if it is activated in the system settings. To turn it off, do the following:
- go to the microphone volume settings (“Control Panel” – “Sound” or by selecting the context menu item that opens by clicking on the tray icon);
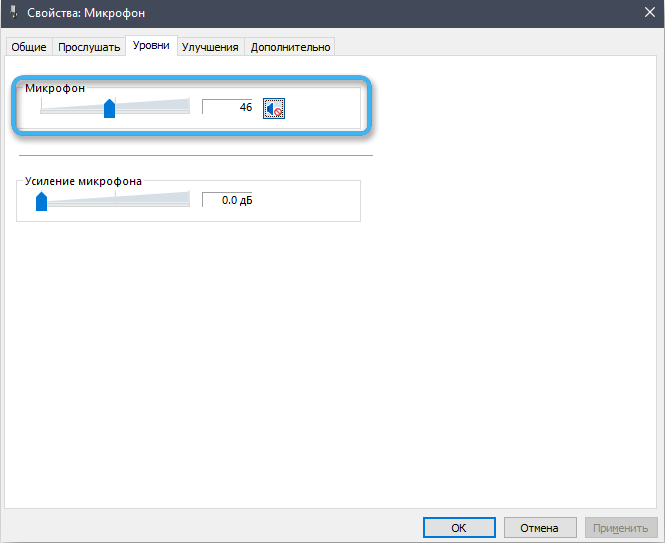
- on the “Record” tab we find the microphone and go to its properties;
- then open “Levels”, click on the speaker icon to deactivate it. It is important to turn off the device, and not just lower the volume level.
Having identified the source of the problem, you can most often fix it yourself, but in some cases you will need the help of a specialist or the purchase of serviceable devices.
What method helped you solve the problem? Share in the comments.