All programs launched on a computer run in processes launched by the system, by the user, or by applications on behalf of the user. Soft can use system processes or create your own, you can see information about the current state of affairs in the Task Manager, which displays the resource consumption when executing a task. So, in the operating system, certain processes are constantly running, and many of them are necessary for the correct operation of system services.

Sometimes users notice a serious decrease in device performance, which is caused by excessive resource consumption associated with the activity of any software, including malware. In some cases, the load can also be caused by system tools that perform useful functions and ensure the operability of the OS.
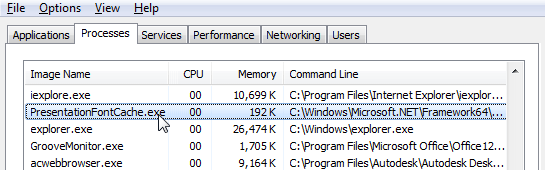
One of the processes from the side of which increased resource consumption can be observed is called PresentationFontCache.exe. Users who notice its gluttony ask themselves the question of the origin of the executable file, as well as deletion in order to increase the performance of the device.
What is PresentationFontCache Process
In search of the culprit in the excessive load on resources, users turn to the Task Manager, where, on the Processes tab, you can find presentationfontcache.exe. Few know what this process is and often suspect it of sabotage, although this is not at all the case. The presentationfontcache.exe executable file belongs to the Presentation Foundation Font Cache Service, a presentation font cache service, and was created by Microsoft for Windows. The executable is not malicious, it is a standard Windows process and the item is located at the path C: Windows Microsoft.NET Framework64 v3.0 WPF.
The object provides the startup and operation of the Windows Presentation Foundation service, so it is required for the correct operation of applications built with WPF, as it optimizes their operation by caching the font data used. In other words, presentationfontcache.exe is the Windows Presentation Foundation font cache. In turn, the WPF service is a presentation subsystem that is included in the .NET Framework 3.0 (the Framework is installed by default on Windows devices).
When the presentationfontcache.exe process heavily loads the processor, the phenomenon may be associated with a damaged font in the cache or the absence of some of the data required for the application to work correctly, as a result of which abnormal software behavior and slippage in the restart cycle are observed. Moreover, the process can load the device even in the absence of running applications that require technology support. If PresentationFontCache does not find WPF components in the usual place, it begins to actively search, thereby loading the processor up to 50% or even more.
Stopping Presentation Font Cache Service
The solution to the problem of increased resource consumption as a result of the activity of the service can be its stopping. Disabling WPF will result in poor application performance. To stop the service, do the following:
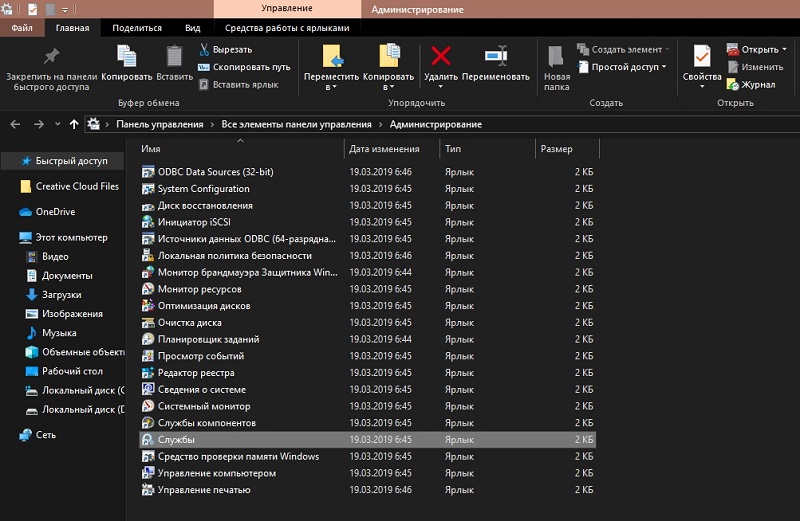
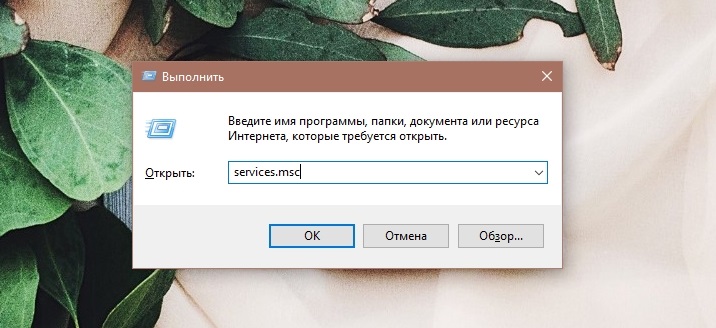
- Open the Run console (press Win + R or select an option from the Start context menu) and enter the services command in the field . msc (an alternative option for opening the same “Services” window involves accessing the “Control Panel”, section “Administration”).
- In the list we find the Windows font cache service, double-click on its name to go to the properties, or right-click to display the context menu, where we select “Properties”.
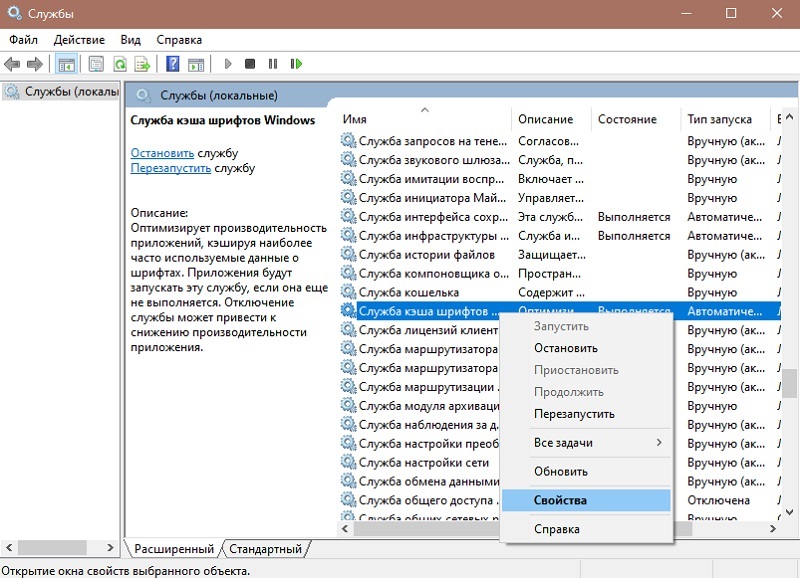
- Here, on the “General” tab, you can change the startup type by setting it to “Manual” or “Disabled”, and also click the “Stop” button if the service is currently running.
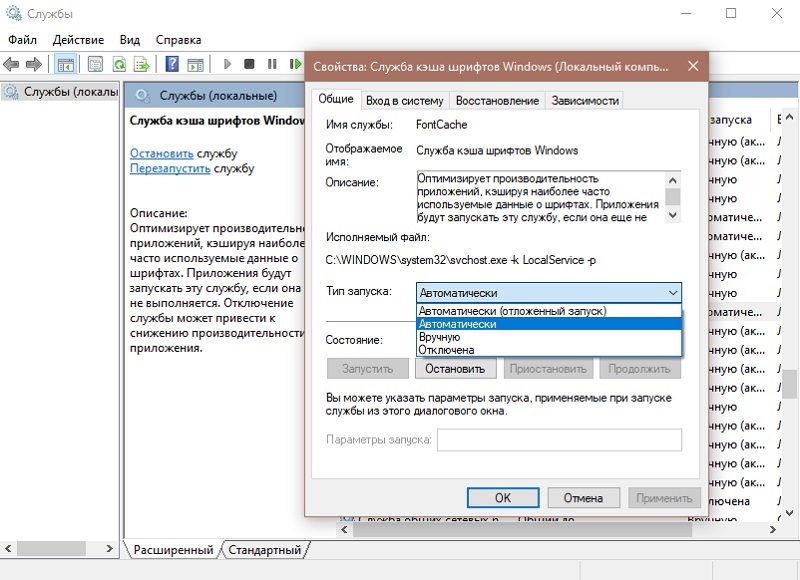
- Now all that remains is to apply the changes and restart the computer.
After these steps, the process will not take up resources, and the load on the processor should drop.
How to disable presentationfontcache.exe process
The second solution is to get rid of the process. To disable presentationfontcache.exe, do the following:
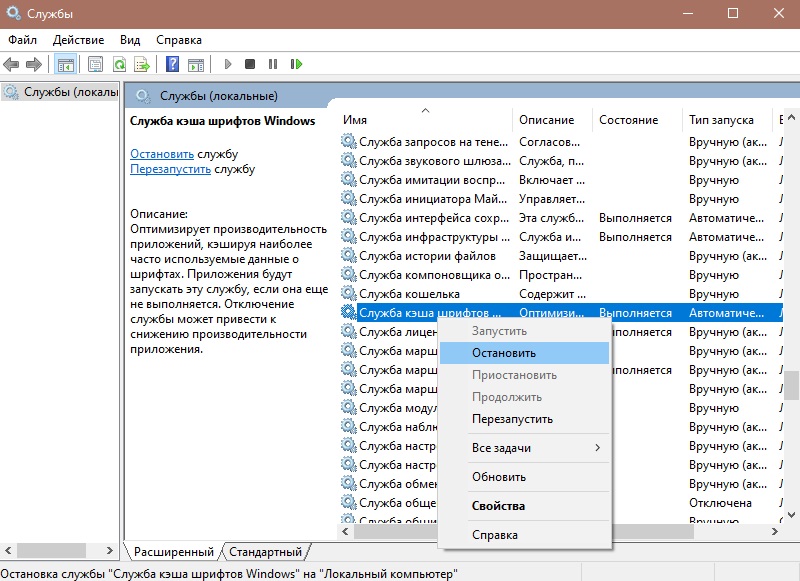
- We start the snap-in with Windows services (“Run”).
- Select the font cache service from the list and click the “Stop” button.
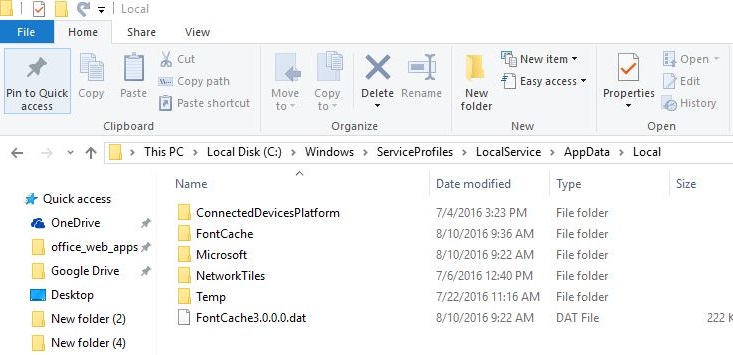
- After that, follow the path C: Windows ServiceProfiles LocalService AppData Local . If you do not see the AppData folder, you need to activate the display of hidden items (on the “View” tab of the Explorer panel, check the “Hidden items” checkbox). When a message says that you do not have sufficient rights to access the directory, we simply ignore it.
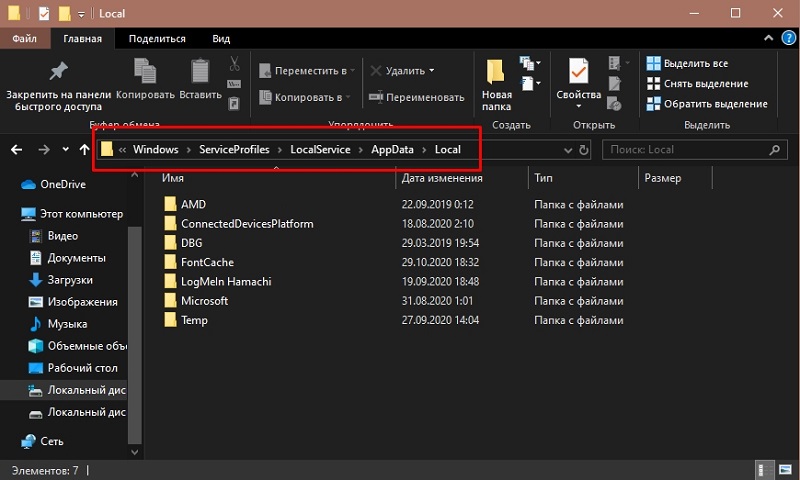
- Delete the Font * .dat files (FontCache0.0.0.dat or FontCache4.0.0.0.dat) in the folder.

- We reboot the computer.
You can also try updating the .NET Framework to a newer version to fix the CPU usage issue of presentationfontcache.exe.