Undoubtedly, a phone or tablet equipped with Android as an operating system is a tool that when we use it for the first time, it is very difficult to stop using, since it is capable of offering us multiple possibilities, both work, and entertainment, thanks to the applications that it includes, and that we can continue to expand from Google Play almost infinitely, obviously always depending on the available space. However, once we have some experience with the system, we want it to do certain things that by default it does not do, functions that could increase the performance or capacity of the system even more, but that, unfortunately, we cannot implement since they are out the scope of our permits.
Many of us have heard about a procedure called “rooting”, which allows us to perform these prohibited operations by extending the scope of our basic user permissions. Rooting a device is the best way to obtain greater functionalities and unique flexibility to achieve absolute control over everything that our team is capable of doing.

However, these advantages that the rooting procedure offers us come at a price: if we make a mistake during it, we can make the device completely unusable, and even if no problem arises during its application, we will have to have Be very careful with the normal operation of the smartphone or tablet, since we will have access to the very entrails of the device, with all that it means.
To avoid any complications arising from the rooting procedure, in this article we will find enough information to understand the advantages and disadvantages of this technique, and thus be able to really decide whether or not it is convenient for us to do it on our Android device.
Contents
Android and Linux: The Android Penguin
Android is a Linux-based operating system originally developed by a company called Android Inc, which was later bought by the giant Google in 2005. This mobile operating system, being based on Linux, inherits from this platform many virtues related to security , one of them are the so-called permissions. These permissions serve to limit access by the user or applications to data and system files that could result, through wrong manipulation, in a window to the theft of information or in permanent damage to its structure, with the consequent inoperability.

By default, Android users can use the system through a limited user account, which only allows them to access a certain part of its structure, ensuring that data or files vital to the operation of the system cannot be damaged. same. As in any Linux distribution, to access this part of the system we will need to obtain the so-called “superuser permissions”, basically the rooting procedure consists of this.
Why would we need root permissions on Android?
As we mentioned at the beginning of the article, once we are a little more experienced in using Android, we want our device to offer us a little more, and while for most users an account with the default privileges is sufficient, to Those of us who want to have the full potential of Android at our disposal, rooting the phone or tablet is the only viable way.
For many, rooting their device is not a whim and nothing more, since many of the applications that exist in the market, and that can be really useful to control Android as we really want, require that we have rooted the smartphone or tablet, Such is the case of some programs to make backup copies or follow-up of the device by means of GPS, very useful in case of theft or loss of the device.
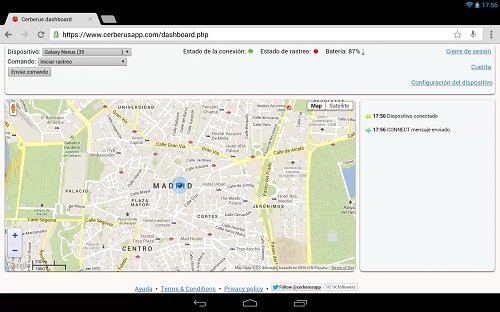
In this sense, one of the first things we think about when we buy a new cell phone or tablet is to add a security system that helps us to recover it in case of theft or loss. One of the most popular applications of this type is Cerberus Anti-theft, which will definitely require that we have the system rooted. Another instance in which it will be necessary for us to have the device rooted is in the case of backup applications. This type of software, in the case of an unrooted device, performs its task in a limited way, safeguarding only the data allowed by the permissions system.
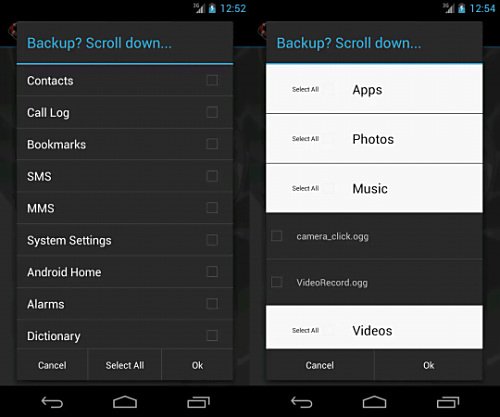
On the other hand, in a rooted system, we can make backup copies of all the elements that make up the system, including applications, account data, system files, and everything else. As we can see, rooting Android at this point is very necessary, especially if we are one of the users who permanently make changes to the computer.
Android root and customization
Another possibility that rooting an Android system offers us is that it offers us the opportunity to customize the equipment in the way we exactly want it. There are two basic ways to change the appearance and functionalities of an Android device, the first one is by making use of one of the so-called “custom Roms”, the best example of which is the one provided by Cyanogen, and the second, less deep but also very productive, and that consists of the possibility of removing all the software added by the manufacturer or the operator, leaving a stock Android, which will definitely have a positive impact on the overall performance of the equipment.
Although very dangerous and not at all advisable, rooting Android also allows us to apply the overclocking technique, which , as in PCs, can offer superior performance, but at the cost of the useful life of the device’s components. Although it may seem like an ideal solution for older devices, the truth is that we will jeopardize its operation and maybe even burn it.
The risks of rooting Android
The rooting technique may seem like an easy solution to many of the problems that Android users often suffer from, not because of Android’s design, but because of their own needs. Unfortunately, its implementation can bring with it many risks, especially if we do not take the necessary precautions, and include the not inconsiderable possibility of transforming the telephone into a “brick”, which in the terminology used in this field means causing such damage to the system that the device stops working.
Another consideration that we must take into account when thinking about the implementation of rooting is that if we have access to critical Android system files, certain applications will also have it, which can result in information theft or damage to the system. computer due to a malware infection.
We must also consider that by rooting an Android device, we would be losing the warranty offered by the manufacturer since they advise against and prohibit the use of this device due to the potential security and operational risks that its use implies.
conclusion
Although rooting a device with Android can involve certain risks, this procedure can offer us some new features and improve others, however, its implementation should always be considered based on having a deep knowledge about how Android works, especially if we want to avoid headaches or even the loss of the device. If not, or if we think that our smartphone or tablet is fine as it came from the factory, there is no argument that is significant enough to change your mind.