Anyone who went into the settings of the NVidia video card and carefully studied all the options present there, probably noticed such an item as shader caching. Many gamers try to play around with this setting, turning it on or off, but get different results. For some, enabling caching helps to get rid of freezes, for others, games slow down even more. Why is this happening, today we will try to find out.
What you need to know about shader caching in NVidia graphics cards
A little about terminology. A shader is usually understood as a kind of program code that is responsible for drawing the visual effects of the frame. When an image is required to be displayed on a monitor screen, such calculations may take longer than is allotted, and then the animation will occur with delays (jerks). On powerful computers with a powerful video card, this usually does not happen, but the problem is that the same Shaders are rendered many times if each subsequent frame contains the same effects as the previous one (for example, ripples in the water).
Caching is a procedure for writing to a disk or in a memory area of some frequently used data, and instead of everyone involved in calculating this data, the program reads ready-made parameters, which significantly speeds up its work. Even the CPU has a caching area to help predict which operation will be performed next, in order to prepare ahead of time.
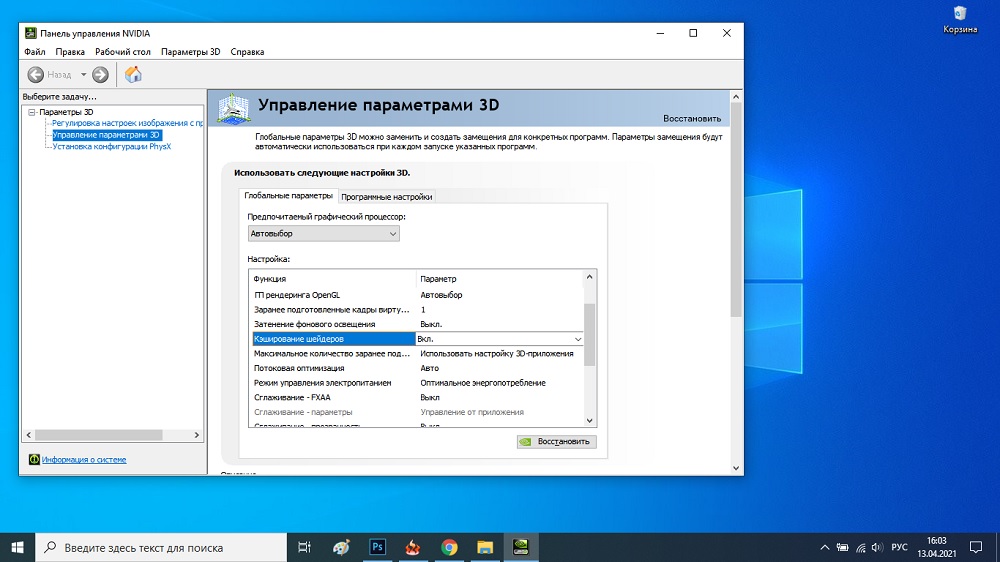
There is such a function for NVidia video cards, while shader caching involves writing the necessary data to disk. If it’s fast, then caching helps increase frame load times and improve animation smoothness. On the other hand, if the computer is weak or the disk is slow, ShaderCache will not give a tangible result. So should you enable or disable it? Let’s figure it out.
Enable / Disable NVidia Shader Caching
Note that the video card is involved in shader calculation, but old video accelerators may not have such a function. Secondly, the function may not be supported by a particular game, although the graphics chip does allow it. Thirdly, you need to understand that whether shader caching is enabled or disabled in the settings of the NVidia video card, the frame rate will not change.
This feature is enabled by default on most modern video chips.
Now let’s look at what the efficiency of using ShaderCache depends on.
The most important parameter is the speed of reading data from the cache, that is, how fast your disk is. If it is an SSD, then the effect will be noticeable here, because the read / write speed when working with solid state drives is much higher than that of classic hard drives. Therefore, if you have an HDD disk, the shader caching efficiency will not be as high or even zero. In other words, reading the cache from the hard disk will take about the same amount of time as it frees up as a result of unloading the video card from calculating the next Shader.

In any case, there is only one obvious drawback to shader caching – it uses disk space, and if there is a shortage of it, it is better to turn off the shader caching option on AMD NVidia video cards. But let us remind you once again that not all games implement this mechanism, and this already lies on the conscience of the developers who do not use the corresponding capabilities embedded in the chips at the hardware level.
And one more nuance regarding the use of SSD drives. As you know, for such media, such a parameter as the number of write cycles per memory unit is critical. Today it is significantly less than that of hard drives, and it is recommended to use them in a sparing mode – for example, as a system drive. In this regard, many users have concerns that ShaderCache will negatively affect the resource of the solid-state drive. In fact, the fears are unfounded: the cache is not written as often as it is read.
Note that those gamers who use the Steam client do not have to worry about whether ShaderCache is used in the video card settings or not, since support here is carried out at the level of the Vulkan / OpenGL libraries. And if the game uses these platforms, shader caching will not overload the processor, since you don’t need to compile shaders every time – they will be loaded from RAM.
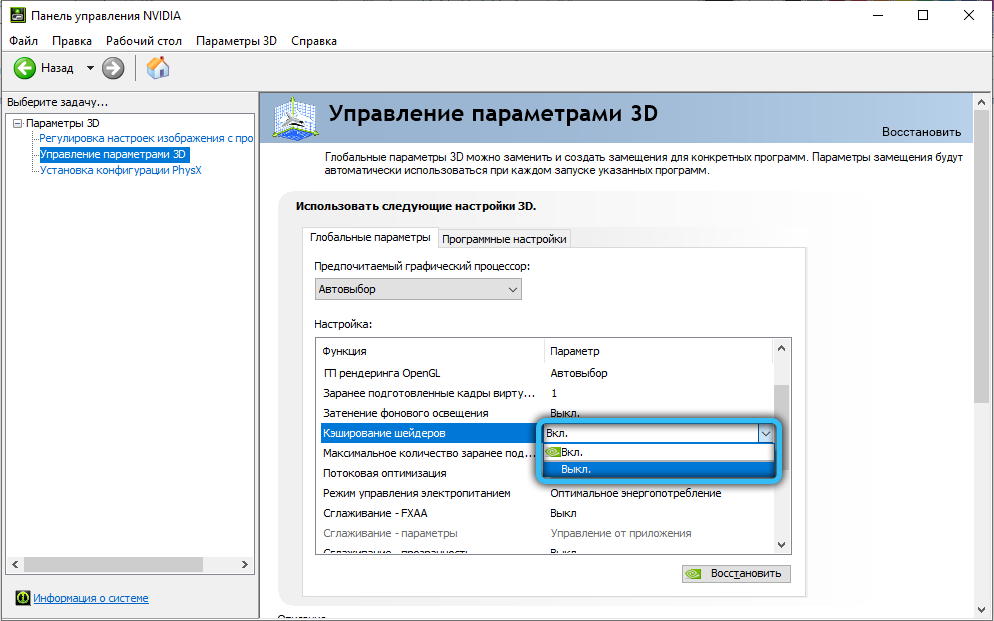
But if for some reason you want to refuse to use this function, you can do this in the settings of the video card. Here is a step-by-step algorithm on how to disable shader caching:
- open the NVidia Control Panel;
- go to the “Manage 3D parameters” tab;
- find the “Shader Caching” option and set the toggle slider to the “off” position.
As a result, you will free up disk space in the amount of several gigabytes.
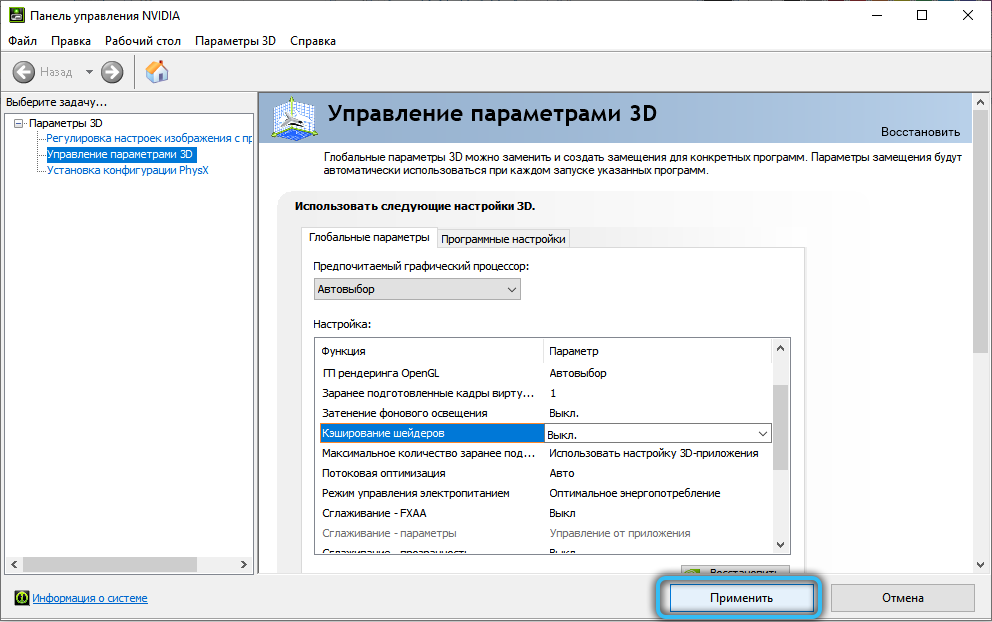
It is possible to disable the function for individual applications through the “Software settings”. If the “Global parameters” option is selected, then the cancellation will apply to all software products using shader technology.
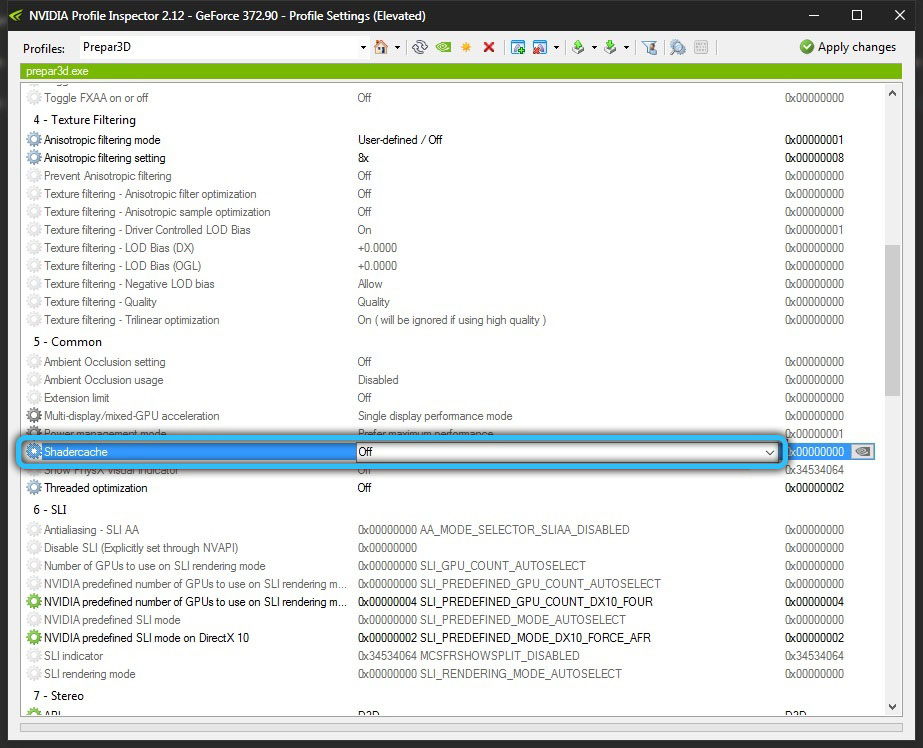
Another option to disable caching is hidden in the Steam settings: in the “Settings” section there is a “Shader Cache” tab with a switch that can be turned off or on. When this option is enabled, there may be a slight increase in network load. The function works only if the NVidia video card drivers are installed.
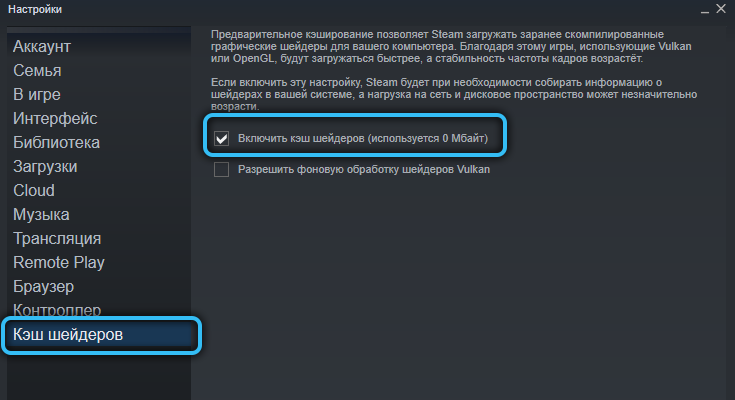
The quick recap is this: Using ShaderCache, while not affecting frame rates, improves frame quality and stability. But if the computer is weak, permanent loading of shaders from disk can negatively affect the performance of the PC, although without caching, an insufficiently powerful computer will slow down, constantly compiling Shaders.