Contents
The upcoming Android knows new screen variants and extends the connectivity API for 5G devices.Reading time:3 min.Save in pocketreadPrint viewread comments36posts
Google has released a developer preview of Android 11. The first Android with a simple version number instead of a letter or a candy appears regularly at the beginning of the year and relatively early: Google released the first versions for the previous versions up to Android Q in March. However, this time it is not a beta, but a preview variant that is explicitly only intended for developers.
As usual, it can be expected that the new functions of Android 11 will be distributed over the first three to four beta versions. The first innovations are aimed primarily at new device types and the 5G infrastructure. Google has also expanded the security and privacy functions. There is also an update for machine learning on the mobile device.
Removal for the sandpit
Android 10 already had some changes to the privacy functions on board, including scoped storage, which assigns each app an isolated sandbox on external storage such as SD cards. Android 11 introduces new methods in the MediaStoreAPI with which apps can request extended access to files such as photos, videos or music.
To simplify the changeover to the more restrictive access rights, apps can continue to request access to files beyond their own folder by setting the requestLegacyExternalStorageattribute, which, however, only applies up to API level 29, i.e. Android 10, not for full-fledged Android 11 apps.
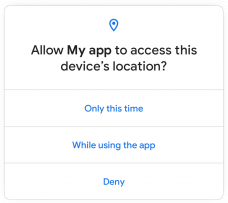
More control over the location
Users can also grant apps one-time approval for some critical data such as location, microphone or camera, which is only valid as long as they use the application. The next time the app is accessed, the app must obtain the user’s permission again.
Regardless of the Android version , Google has announced that it will limit the location to all apps. For example, developers whose application accesses the location data when the app is not active in the foreground must request special approval for Google Play. You need to explain what use background access has, what users expect from it, and whether it is necessary for the primary function of the app.
An app that sends emergency or security warnings based on the location and explicitly lists the function should therefore receive approval, but an app for finding suitable shops should not, because the location query in the foreground is sufficient for this. The new guideline officially applies from April, but brings transition periods: from May developers can request authorization, from August approval for new apps is required and from November developers must have approval for existing apps so that their app remains available on Google Play remains.
5G and screen formats
Android 11 extends the ConnectivityManagerfor network connections by two functions, which should benefit 5G devices in particular. For example, the day introduced in API 21 for unlimited access is available NET_CAPABILITY_NOT_METEREDfor 5G mobile networks. In the future, you can also query the methods for determining the bandwidth without test access to the network for measurement.
With regard to new screen formats, Android 11 is prepared for waterfall screens, where the picture goes over the edge, and pinhole screens with a recessed camera in the display, which is expected for the Samsung Galaxy S20. Google has DisplayCutoutextended the API for the latter , and for waterfall screens the interaction near the edge can now be better controlled.
Machine learning and security
Google updated the Neural Networks API (NNAPI) for machine learning applications (ML) to Android to version 1.3 and expanded it. New features include extended QoS functions (Quality of Service) to control the prioritization and timeouts when executing ML models. The memory domain APIs are intended to reduce the copying and transformation processes when using models repeatedly.
The authentication on the device can now be requested in three stages as BIOMETRIC_WEAKand BIOMETRIC_STRONGfor biometric or DEVICE_CREDENTIALnon-biometric methods such as PIN or password.
Google has also introduced methods to reduce memory access errors that lead to use-after-free or double-free vulnerabilities. The tool HWASan used for this has recently become available for app developers. Some measures to protect against errors such as the tagged pointers can lead to increased crashes in apps with memory errors.
Preview of R and tests
Developers can prepare their applications for the upcoming Android by setting targetSdkVersionthe value “R”. New is the option to activate or deactivate individual innovations via the developer options, logcat or an ADB command. In this way, developers can try out specific functions without changing the SDK version (Software Development Kit) and recompiling the app.
In order to give developers enough time to test their applications with regard to the stability in interaction with Android 11, Google has also announced a so-called Platform Stability Milestone, which not only brings the final APIs for the SDK and NDK (Native Development Kit), but also should behave as the final release with regard to the internal APIs and other framework conditions. The milestone is announced for June.
