The Android 6 «Marshmallow» operating system literally and physically allows you to increase the internal memory of an Android, as long as the device has support for an external or micro SD card.
The trick is to configure that micro SD as internal memory, and for that Android 6 provides an “Adoptable storage” option in the system settings, “Storage” option. There you have to select the SD card installed in the device and choose the option that says ” Format SD card as internal storage “.
Although the total storage of the device will be shown as the sum of the internal factory memory plus the capacity of the micro SD card, the system allows you to separately view and track the capacity (used and free memory) of both.
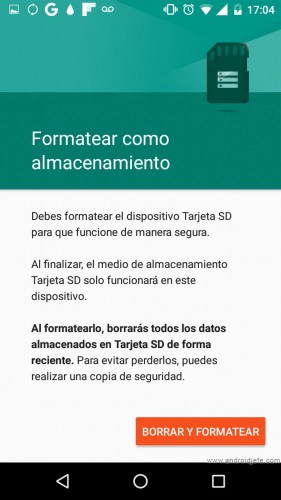
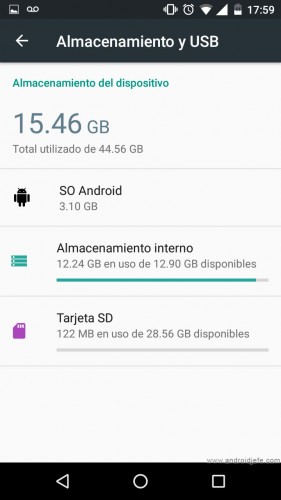

Above: Screen to format the SD as internal storage. Motorola Moto G device with 16 GB of internal memory originally (Device Storage), which increased to 44.56 GB after “adopting” a 32 GB SD card (28.56 GB of usable capacity).
The good thing about formatting SD as internal storage
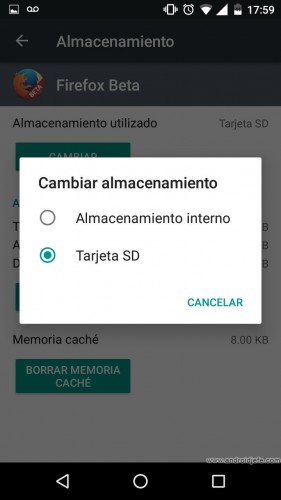
- By working as internal memory, applications can be installed on the SD card or moved entirely (Application, Data and Cache) from real internal memory. Normally this cannot be done when the micro SD card is configured as portable storage (in this case sometimes you have to resort to complex methods or root permissions to install or move the applications to the SD).
- Another good thing is that the system offers the option of freeing up considerable space in the real internal memory in case it is full, migrating data to the adopted SD card (files and applications can be included here) in a few taps. This option is available in the SD card settings (Settings, Storage, SD Card).
- The partition of the micro SD assigned as “internal” is formatted and encrypted with a unique key, so the data is protected and cannot be seen on any device other than the Android where it was configured. This partition cannot be managed independently from another device but only through the Android device (for example, when connected to the PC).
- Even if the SD card is adopted, there should be no problem removing it. The system will detect that the SD card is not available and if there are applications that were moved or installed there they simply will not work.
The bad
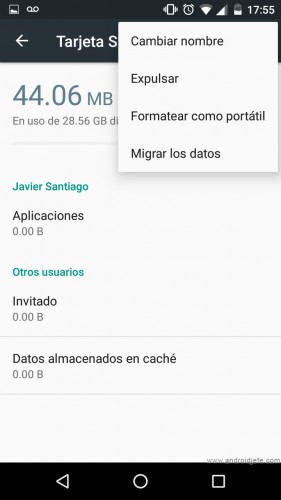
- The main problem is that the portability of the micro SD card is lost. That is, it will only work on the Android device where it was configured. If the SD card is connected to another device or PC to copy or transfer files, it will not even be recognized. You would have to format it to reuse it as classic portable storage or set it to mixed mode.
- Installed apps must be compatible with Android 6 and programmed to support adoptable storage, otherwise they cannot be installed on or moved to the adopted SD card. The applications that do have this support will automatically be installed where there is more space on the phone (be it the internal memory or the micro SD card). On the “Application information” screen (Settings, Applications, Application Name), “Storage” option, the “Change storage” button will appear.
- Since the external SD card is generally slower than the internal memory of the device, you can expect less performance or performance from the applications that are installed or moved to that SD.
- Unfortunately, some manufacturers such as Samsung or LG have removed this functionality from their versions of Android 6, only allowing to use the external SD card in normal or “portable” mode. However, applying the method of using the SD card in mixed mode, the functionality can be re-enabled.
More information : Android Developers
How to configure SD card as internal memory
How to expand the internal memory of a cell phone (LITERALLY)
How to fix FULL memory on Android
Receive updates: SUBSCRIBE by email and join 10,000+ readers. Follow this blog on Facebook and Twitter.