Contents
A repeater, what is it? What is the difference between WLAN n and ac? Change channel, please? What do I need to know about the frequencies? And what should a WLAN cable be ?! Do not despair, we will clarify – here you will find everything you need to know about WiFi.
- Control center WLAN: More and more devices form the smart home
- Do you take care of the power consumption of your smart home?
The different WLAN standards
There are different WLAN standards, which differ in several points. The most important thing for the users is the range and the maximum speed. In the table you will find all standards currently used in the private sector. They are identified with a letter after the name “IEEE 802.11”. Exception: The very first WLAN standard from 1997 has no letter and is no longer used today.
Overview of WLAN standards
| STANDARD IEEE 802.11 | WITHOUT ADDITION | WLAN B | WLAN G | WLAN N | WLAN AC | WLAN AX |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| New name | Wi-Fi 4 | Wi-Fi 5 | Wi-Fi 6 | |||
| speed | 2 Mbit / s | 11 Mbit / s | 54 Mbps | 600 Mbit / s | 6,939 Mbps | 4.8 Gbps |
| frequency | 2.4 GHz | 2.4 GHz | 2.4 GHz | 2.4 & 5 GHz | 5 GHz | 5 GHz |
| Backward compatibility | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | only for WLAN n | 802.11ac and 802.11n |
| Range | 20 metres | 38 meters | 38 meters | 70 meters | 50 meters | n / A |
WLAN ac is currently the end of most end devices, but there are already successors, namely WLAN ah, ay and ax. But at the moment they don’t play a role in practice.
The most important WLAN terms
WLAN router
The router brings the Internet and WLAN from the phone jack or the cable connection to the devices. A WLAN router therefore sends out the radio signal for the WLAN and connects all devices in the network to one another and to the Internet. Most providers now offer WLAN routers, but they can also be connected to a router without WLAN as a transmitting station.
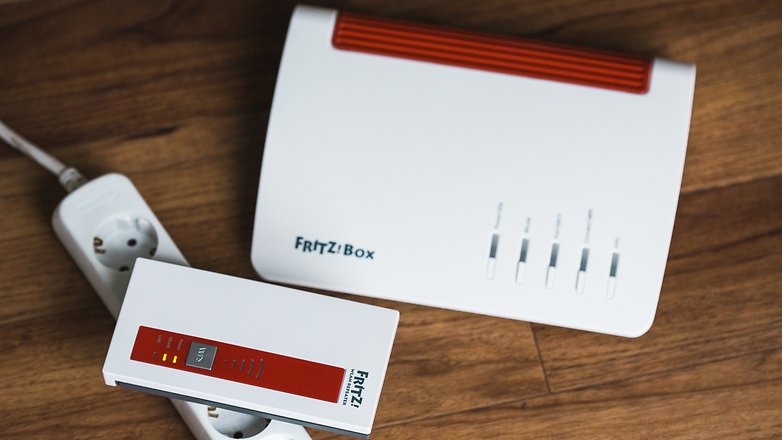

Repeater
A repeater is something like an extension cable, just without a cable and for WiFi. Installed at the edge of the reception area from the router , the repeater picks up the WLAN signal and sends it out again. This increases the network coverage, i.e. the range of the WLAN. The repeater usually uses the same SSID as the router, so that it appears to the end devices as an entire WLAN network.
Encryption
So that not everyone can access your WLAN with their device, you have to encrypt it, using a combination of network name and password. There are several standards, the most important of which are WEP, WPA and WPA2. WPA3 is the next step. WEP is considered quite insecure, with WPA and WPA2 your home network is adequately protected.
Mesh
A mesh WLAN is a network of different access points – usually a router and one or more repeaters – that communicate with each other. Roughly speaking, this ensures that the end devices are always connected to the access point that offers them the best reception and the highest speed.
SSID
The abbreviation SSID stands for Service Set Identifier and represents the name of your WLAN network. In order to log in, the name and password must be known. On the router, you can set whether the SSID should be visible or hidden to everyone.
channel
Since the usable frequency range is quite narrow, other WLAN routers in the vicinity often interfere. They often use the same radio channel and thus influence each other. So changing the channel can improve reception. You make the setting in the surface of the router, but many modern WLAN routers do it automatically.
Field strength
The field strength gives you information about how good your connection to the WiFi network is. The rule of thumb: the better you can see the router or the repeater, the stronger the WiFi connection .
WiFi cable
A popular joke to dupe amateurs. After all, WLAN is wireless, so it doesn’t need a cable.
WLAN basics clearly explained
Set up guest access
Anyone who is reluctant to open the door to guests in their WLAN can set up guest access. It offers guests the opportunity to use the Internet, but is separate from the actual network, so it does not offer access to your smart home devices, printers, computers or other networked devices.

Integrate WLAN printer
One of the most popular uses for WLAN is the printer. With WLAN, a printer in the house can be easily controlled from all devices. The setup can be done in two ways. On the one hand, the printer manufacturers provide their own software that can be used to make all settings. However, this does not have to be installed on every device. In Windows you simply go to Settings -> Devices -> Printers & Scanners and then Add Printer or Scanner . Then your computer searches in the network in which it is currently logged on for available printers that can be controlled with a click.
Network storage
Data backup is important so that all the documents, memories, music, photos and videos are not lost if the computer breaks down. So-called NAS (Network Attached Storage) systems have one or more hard drives that can be accessed by all computers in the network. Data can be automatically saved to the NAS via WLAN and conveniently called up, e.g. to play music or films or view photos. The faster the WLAN, the better the network storage works.
Do you have any further questions about WLAN? Then add it to the comments, we will expand this article step by step.